IADR Abstract Archives
Physical/mechanical properties of glass ionomer cement containing elastomeric micelles
Objectives: This study assessed setting kinetic, biaxial flexural strength, and surface microhardness of the self-healing glass-ionomer cement containing elastomeric micelles (Deltafil; DF) and compared with the other commercial conventional glass-ionomer cements (EQUIA Forte HT Fil; EQ, Fuji IX GP extra; F9, and Ketac molar; KT).
Methods: Setting kinetic after mixing for 10 min was examined using ATR-FTIR (n=5). The biaxial flexural strength/modulus after immersion in water for 24 h was determined by a universal testing machine (n=8). The surface microhardness of the material after immersion in water for 24 h was performed using a Vickers microhardness tester (n=8). Data were analyzed using the one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey post hoc comparison.
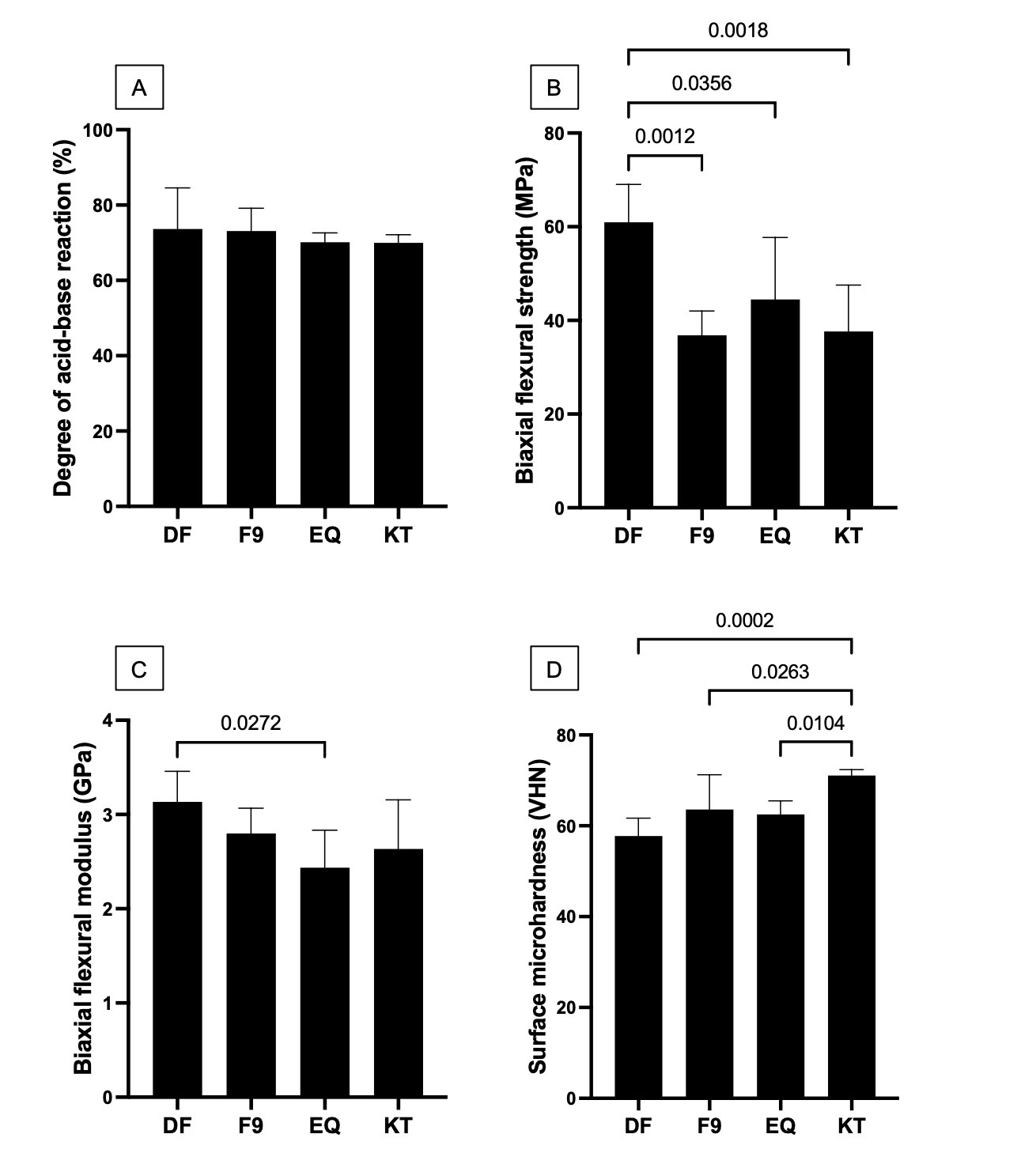
Results: The calculated degree of acid-base reaction observed with DF (73.6 ± 4.4 %) was comparable to that of KT (71.0 ± 1%), F9 (73.1 ± 2.4 %), and EQ (70.1 ± 1.0 %) (Figure 1A). Additionally, DF exhibited a significantly higher BFS (61.8 ± 8.8 MPa) and BFM (3.3 ± 0.5 GPa) compared with other materials (p<0.05) (Figure 1B). The lowest BFS and BFM values were observed from F9 (34.8 ± 7.1 MPa) and EQ (2.4 ± 0.4 GPa), respectively (Figure 1C). DF showed the lowest surface microhardness (58 ± 3 VHN) compared to F9 (64 ± 6 VHN), EQ (63 ± 2 VHN), and KT (71 ± 1 VHN), respectively (Figure 1D).
Conclusions: Deltafil demonstrated a rapid acid-base neutralization but showed a similar final degree of acid-base reaction. The flexural strength of Deltafil was higher than other tested materials, but the surface microhardness was lower than other materials.
Methods: Setting kinetic after mixing for 10 min was examined using ATR-FTIR (n=5). The biaxial flexural strength/modulus after immersion in water for 24 h was determined by a universal testing machine (n=8). The surface microhardness of the material after immersion in water for 24 h was performed using a Vickers microhardness tester (n=8). Data were analyzed using the one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey post hoc comparison.
Results: The calculated degree of acid-base reaction observed with DF (73.6 ± 4.4 %) was comparable to that of KT (71.0 ± 1%), F9 (73.1 ± 2.4 %), and EQ (70.1 ± 1.0 %) (Figure 1A). Additionally, DF exhibited a significantly higher BFS (61.8 ± 8.8 MPa) and BFM (3.3 ± 0.5 GPa) compared with other materials (p<0.05) (Figure 1B). The lowest BFS and BFM values were observed from F9 (34.8 ± 7.1 MPa) and EQ (2.4 ± 0.4 GPa), respectively (Figure 1C). DF showed the lowest surface microhardness (58 ± 3 VHN) compared to F9 (64 ± 6 VHN), EQ (63 ± 2 VHN), and KT (71 ± 1 VHN), respectively (Figure 1D).
Conclusions: Deltafil demonstrated a rapid acid-base neutralization but showed a similar final degree of acid-base reaction. The flexural strength of Deltafil was higher than other tested materials, but the surface microhardness was lower than other materials.