IADR Abstract Archives
Properties of 3D-printed zirconia for dental prosthesis
Objectives: This study aims to investigate the accuracy, aging resistance, and ceramic-ceramic compatibility and surface roughness after chairside polishing procedure of 3D-printed zirconia.
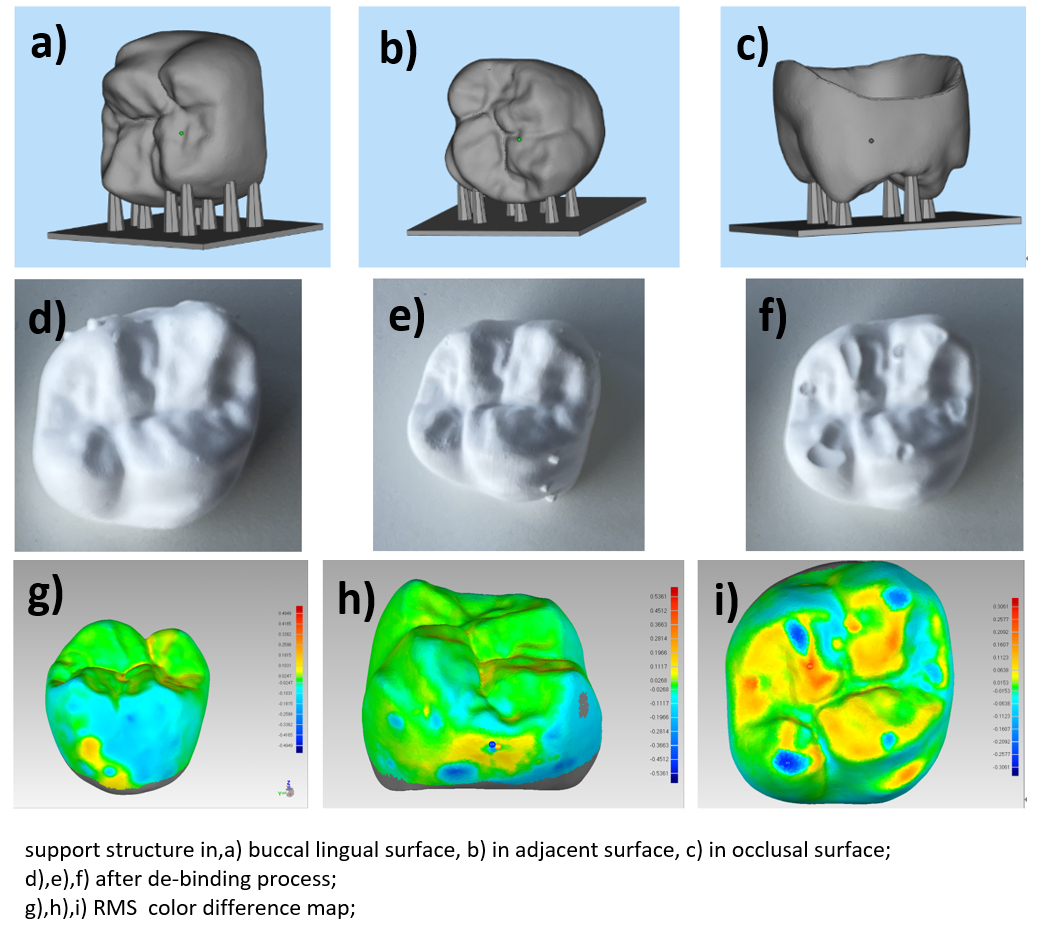
Methods: A photosensitive slurry containing 42vol% of 3mol% yttria-stablized zirconia solid phase content was prepared. Samples were then fabricated using a homemade DLP 3D-printer equipped with a 405 nm UV light source and a resolution of 70 μm pixels in the X/Y plane with 50 μm layer thickness. After printing, the green bodies underwent de-binding and sintering processes at a maximum temperature of 1480 °C. In terms of accuracy, 3 groups of crowns (n=3 for each group) were manufactured with different printing directions and supporting positions (buccal lingual, adjacent , occlusal surface). The external surfaces were scanned using a desktop scanner, and 3D deviation analysis was performed. For ageing resistance, 3D-printed zirconia ceramic samples (4.0x3.0x45mm3) underwent an accelerated ageing test according to ISO standard 13356:2015. Then, the 4-point bending strength was tested (n=7 for each group). In terms of ceramic-ceramic compatibility, test following ISO 9693-2:2016 standard was conducted (n=8). For surface roughness (Ra), both 3D-printed zirconia and conventional milling zirconia samples were used (n=3 for each group) and underwent a two-step grinding process using coarse and fine diamond grinders.
Results: For accuracy, the buccal lingual (0.053 ± 0.004 mm), adjacent (0.051 ± 0.007 mm) and occlusal surface (0.047 ± 0.104 mm) groups show no three no statistical significant difference (p < 0.05) in the RMS values. The 4-point bending strength of the 3D printed zirconia before (832 ± 65 MPa) and after (812 ± 64 MPa) the ageing process showed no significant difference (p < 0.05). The debonding/crack-initiation strength of the 3D-printed zirconia ceramic samples was measured to be 34.2 ± 3.1 MPa, exceeded 20 MPa in ceramic-ceramic compatibility test. The mean Ra for 3D-printed zirconia (0.669±0.140mm) and conventional zirconia (0.575±0.144mm) exhibited no significant difference (p < 0.05)
Conclusions: According to ISO standard requirements and comparison results, the 3D-printed zirconia has the potential for dental application.
Methods: A photosensitive slurry containing 42vol% of 3mol% yttria-stablized zirconia solid phase content was prepared. Samples were then fabricated using a homemade DLP 3D-printer equipped with a 405 nm UV light source and a resolution of 70 μm pixels in the X/Y plane with 50 μm layer thickness. After printing, the green bodies underwent de-binding and sintering processes at a maximum temperature of 1480 °C. In terms of accuracy, 3 groups of crowns (n=3 for each group) were manufactured with different printing directions and supporting positions (buccal lingual, adjacent , occlusal surface). The external surfaces were scanned using a desktop scanner, and 3D deviation analysis was performed. For ageing resistance, 3D-printed zirconia ceramic samples (4.0x3.0x45mm3) underwent an accelerated ageing test according to ISO standard 13356:2015. Then, the 4-point bending strength was tested (n=7 for each group). In terms of ceramic-ceramic compatibility, test following ISO 9693-2:2016 standard was conducted (n=8). For surface roughness (Ra), both 3D-printed zirconia and conventional milling zirconia samples were used (n=3 for each group) and underwent a two-step grinding process using coarse and fine diamond grinders.
Results: For accuracy, the buccal lingual (0.053 ± 0.004 mm), adjacent (0.051 ± 0.007 mm) and occlusal surface (0.047 ± 0.104 mm) groups show no three no statistical significant difference (p < 0.05) in the RMS values. The 4-point bending strength of the 3D printed zirconia before (832 ± 65 MPa) and after (812 ± 64 MPa) the ageing process showed no significant difference (p < 0.05). The debonding/crack-initiation strength of the 3D-printed zirconia ceramic samples was measured to be 34.2 ± 3.1 MPa, exceeded 20 MPa in ceramic-ceramic compatibility test. The mean Ra for 3D-printed zirconia (0.669±0.140mm) and conventional zirconia (0.575±0.144mm) exhibited no significant difference (p < 0.05)
Conclusions: According to ISO standard requirements and comparison results, the 3D-printed zirconia has the potential for dental application.