IADR Abstract Archives
BMP-2 mRNA increased rat bone formation: Micro-CT and histological study
Objectives: Bone morphogenetic proteins (BMPs) are signaling molecules that stimulate bone formation, and the most commonly used BMP is recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-2 (rhBMP-2). However, rhBMP-2 has a short half-life, requiring high doses to be effective and can cause adverse effects, such as ectopic bone formation. A promising alternative, mRNA encoding BMP-2, is simple to manufacture, more cost effective, and can rapidly translate BMP-2 protein without integrating into the host genome. Therefore, this study was designed to investigate bone formation in rat femurs after delivering rhBMP-2 and mRNA encoding BMP-2 compared with natural bone formation using micro-computed tomography and histological analysis.
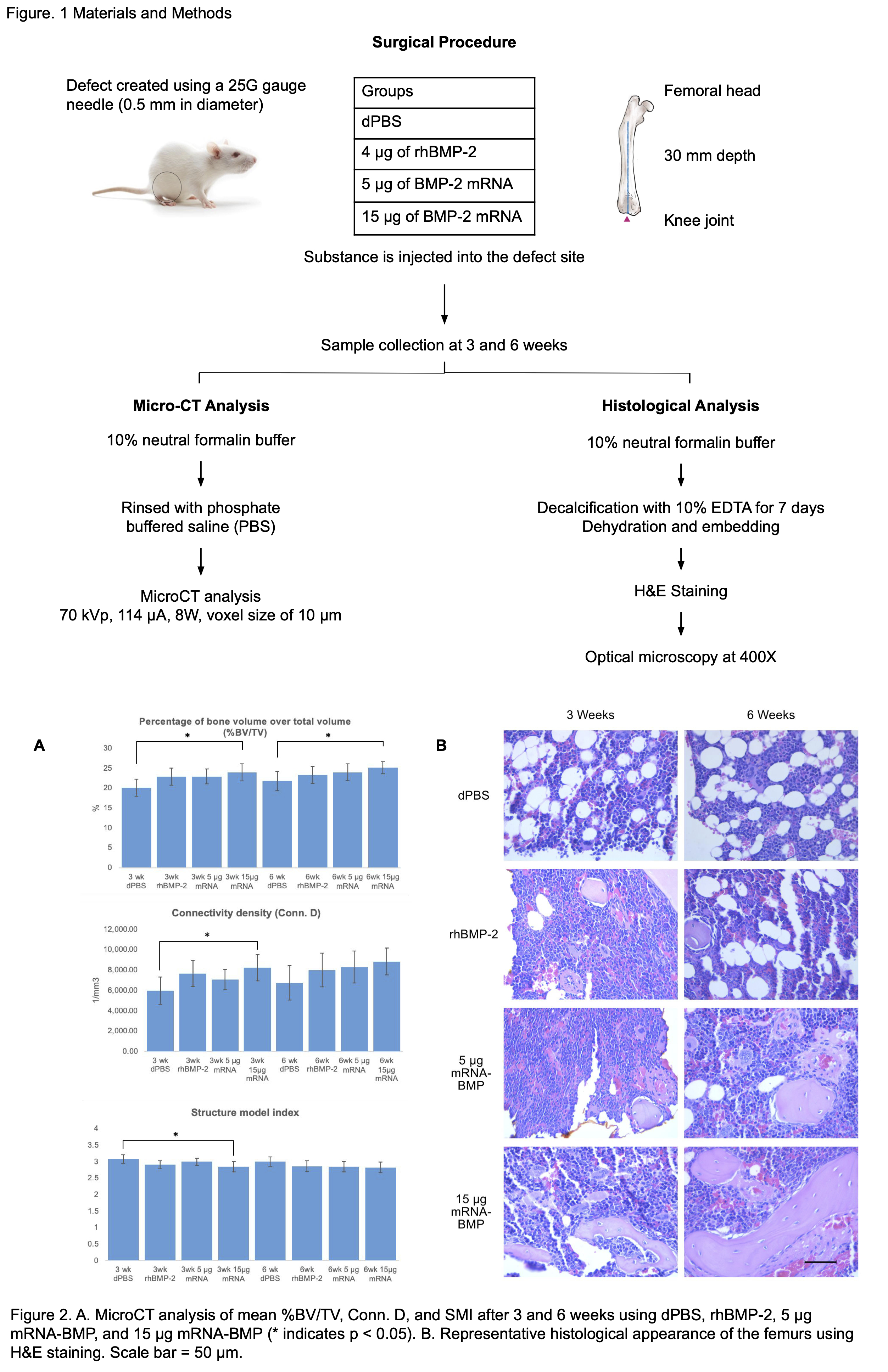
Methods: Defects (0.5 mm diameter) were created using a 25 gauge needle in the left and right femurs of 11-week-old male Sprague-Dawley rats (N=60). Each femur was allocated into one of four groups: phosphate-buffered saline (dPBS), rhBMP-2, 5 μg mRNA encoding BMP-2, and 15 μg mRNA encoding BMP-2. After 3 or 6 weeks, the rats were euthanized and the femurs were collected. Micro-CT analysis was performed to measure the percentage of bone volume over total volume (%BV/TV), connectivity density (Conn. D), and structure model index (SMI) to assess bone formation. Hematoxylin-Eosin staining was performed to evaluate the histology of the bone.
Results: The mean %BV/TV from lowest to highest in both the 3-week and 6-week groups were dPBS, rhBMP-2, 5 μg mRNA-BMP, and 15 μg mRNA-BMP. At both 3 and 6 weeks, the 15 μg mRNA-BMP group had a significantly higher bone volume than the dPBS group. The Conn. D of the 3-week 15 μg mRNA-BMP group was significantly higher than the dPBS group. The SMI was significantly lower in the 3-week 15 μg mRNA-BMP group compared with the dPBS group. The histological evaluation also revealed that the 6-week 15 μg mRNA-BMP group had the greatest size and quantity of lamellar bone.
The histological images revealed that the 3-week 15 μg mRNA-BMP group had slimmer plate-like pieces of bone compared with the spherical bone in the 3-week dPBS group. The microCT results corresponded to the histological images.
Conclusions: The results suggest that mRNA encoding BMP-2 can induce bone formation. Further gene expression studies will help elucidate the mechanism of this particular mRNA.
Methods: Defects (0.5 mm diameter) were created using a 25 gauge needle in the left and right femurs of 11-week-old male Sprague-Dawley rats (N=60). Each femur was allocated into one of four groups: phosphate-buffered saline (dPBS), rhBMP-2, 5 μg mRNA encoding BMP-2, and 15 μg mRNA encoding BMP-2. After 3 or 6 weeks, the rats were euthanized and the femurs were collected. Micro-CT analysis was performed to measure the percentage of bone volume over total volume (%BV/TV), connectivity density (Conn. D), and structure model index (SMI) to assess bone formation. Hematoxylin-Eosin staining was performed to evaluate the histology of the bone.
Results: The mean %BV/TV from lowest to highest in both the 3-week and 6-week groups were dPBS, rhBMP-2, 5 μg mRNA-BMP, and 15 μg mRNA-BMP. At both 3 and 6 weeks, the 15 μg mRNA-BMP group had a significantly higher bone volume than the dPBS group. The Conn. D of the 3-week 15 μg mRNA-BMP group was significantly higher than the dPBS group. The SMI was significantly lower in the 3-week 15 μg mRNA-BMP group compared with the dPBS group. The histological evaluation also revealed that the 6-week 15 μg mRNA-BMP group had the greatest size and quantity of lamellar bone.
The histological images revealed that the 3-week 15 μg mRNA-BMP group had slimmer plate-like pieces of bone compared with the spherical bone in the 3-week dPBS group. The microCT results corresponded to the histological images.
Conclusions: The results suggest that mRNA encoding BMP-2 can induce bone formation. Further gene expression studies will help elucidate the mechanism of this particular mRNA.