IADR Abstract Archives
Biodegradable Magnesium Implant Enhances Angiogenesis and Alleviates Medication-Related Osteonecrosis of the Jaw in Rats
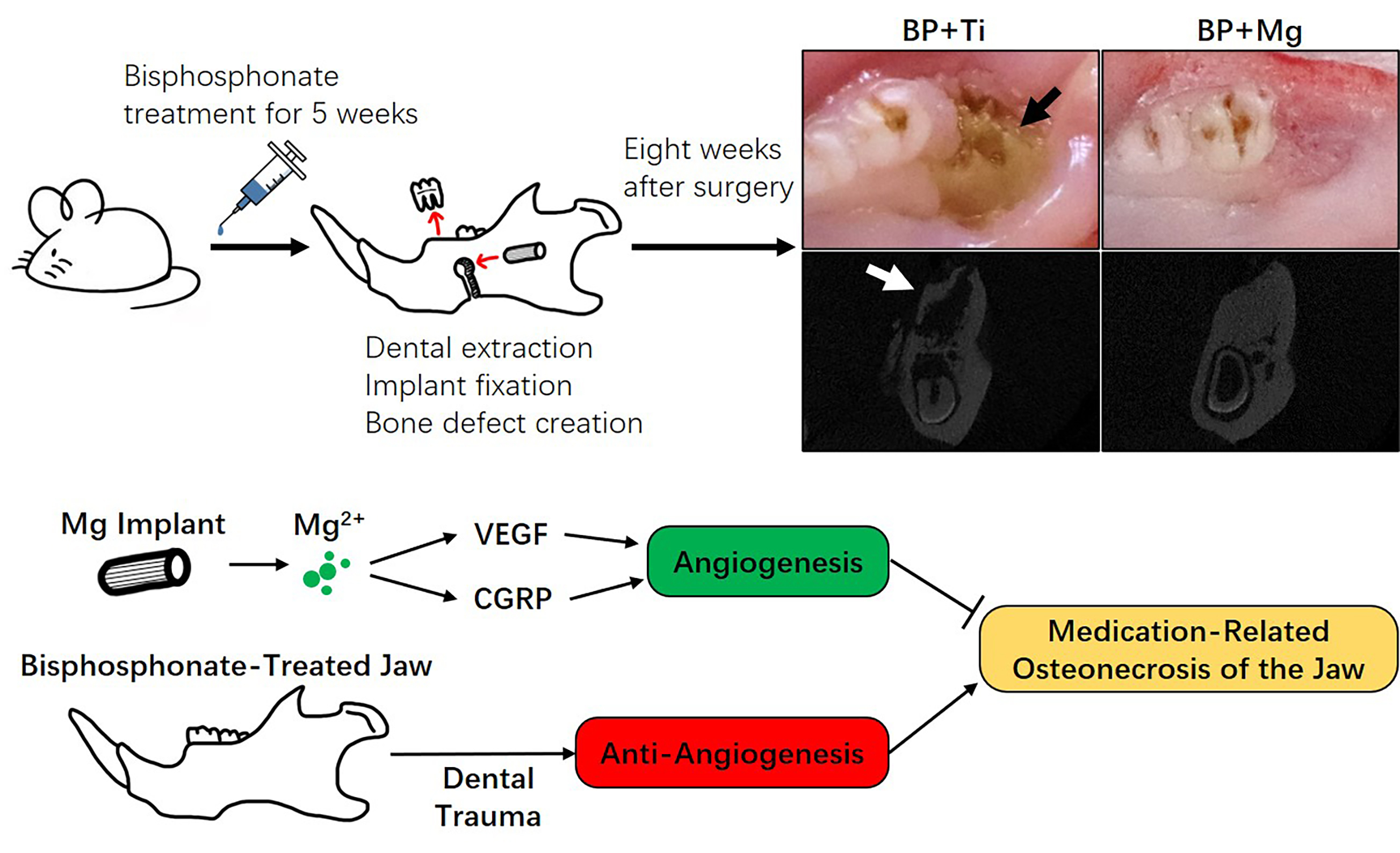
Objectives: Medication-related osteonecrosis of the jaw (MRONJ) is a serious complication associated with antiresorptive and antiangiogenic medications, of which impaired angiogenesis is a key pathological alternation. Since Magnesium (Mg)-based implants possess proangiogenic effects, we hypothesized that the biodegradable Mg implant could alleviate the development of MRONJ via enhancing angiogenesis.
Methods: MRONJ model was established in 50 male rats, divided into the Veh+ Ti group (Vehicle-treated rat, with Titanium (Ti) implant), BP+Ti group (Bisphosphonate (BP)-treated rat, with Ti implant), BP+Mg group (BP-treated rat, with Mg implant), BP+Mg+SU5416 group (BP-treated rat, with Mg implant and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) receptor-2 inhibitor), BP+Mg+BIBN group (BP-treated rat, with Mg implant and calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) receptor antagonist), and BP+Mg+SU5416+BIBN group (BP-treated rat, with Mg implant and VEGF receptor-2 inhibitor and CGRP receptor antagonist). The occurrence of MRONJ, alveolar bone necrosis, new bone formation and vessel formation were assessed by histomorphometry, immunohistochemistry, and micro-CT analysis.
Results: Eight weeks after surgery, the BP+Mg group had significantly reduced occurrence of MRONJ-like lesion and histological osteonecrosis, increased bone microstructural parameters, and increased expressions of VEGFA and CGRP, than the BP+Ti group. By simultaneously blocking VEGF receptor-2 and CGRP receptor, the vessel volume and new bone formation in the BP+Mg group were significantly decreased, meanwhile the occurrence of MRONJ-like lesion and histological bone necrosis were significantly increased.
Conclusions: Biodegradable Mg implant could alleviate the development of MRONJ-like lesion, possibly via upregulating VEGF- and CGRP-mediated angiogenesis. Mg-based implants have the potential to be developed as a novel internal fixation device for patients with the risk of MRONJ.
Methods: MRONJ model was established in 50 male rats, divided into the Veh+ Ti group (Vehicle-treated rat, with Titanium (Ti) implant), BP+Ti group (Bisphosphonate (BP)-treated rat, with Ti implant), BP+Mg group (BP-treated rat, with Mg implant), BP+Mg+SU5416 group (BP-treated rat, with Mg implant and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) receptor-2 inhibitor), BP+Mg+BIBN group (BP-treated rat, with Mg implant and calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) receptor antagonist), and BP+Mg+SU5416+BIBN group (BP-treated rat, with Mg implant and VEGF receptor-2 inhibitor and CGRP receptor antagonist). The occurrence of MRONJ, alveolar bone necrosis, new bone formation and vessel formation were assessed by histomorphometry, immunohistochemistry, and micro-CT analysis.
Results: Eight weeks after surgery, the BP+Mg group had significantly reduced occurrence of MRONJ-like lesion and histological osteonecrosis, increased bone microstructural parameters, and increased expressions of VEGFA and CGRP, than the BP+Ti group. By simultaneously blocking VEGF receptor-2 and CGRP receptor, the vessel volume and new bone formation in the BP+Mg group were significantly decreased, meanwhile the occurrence of MRONJ-like lesion and histological bone necrosis were significantly increased.
Conclusions: Biodegradable Mg implant could alleviate the development of MRONJ-like lesion, possibly via upregulating VEGF- and CGRP-mediated angiogenesis. Mg-based implants have the potential to be developed as a novel internal fixation device for patients with the risk of MRONJ.