IADR Abstract Archives
Anatomical and mechanical properties of the midpalatal suture
Objectives: Rapid maxillary expansion (RME) is based on sutural distraction osteogenesis (SDO) of the midpalatal suture. It consists of load application in order to divide the maxillary halves while inducing osteogenesis through the sutural ligament. Anatomical and mechanical properties of the midpalatal suture were assessed.
Methods: Soft tissues were removed from ten swine heads (12-month-old). Samples were obtained by slicing the hard palate (automatic cutting machine, water irrigation, 2500rpm) perpendicular to the midpalatal suture. Thirteen specimens were collected from each palate, with length according to anatomy (22.5~40.0mm) and standardised width (2.5mm). One hundred and thirty specimens were scanned with micro-CT (25μm pixel) and tested in four-point-bending (1.00mm/min) within 48h (storage in 0.9%NaCl at 4°C). Fracture type (Ft), linear interdigitation index (LII), linear obliteration index (LOI), ultimate stress (σf), and elastic modulus (E), were calculated. Kruskal-Wallis one-way ANOVA with Mann-Whitney’s post hoc test and Fisher’s exact test (α=0.05) were applied to compare values among anterior, median, and posterior region.
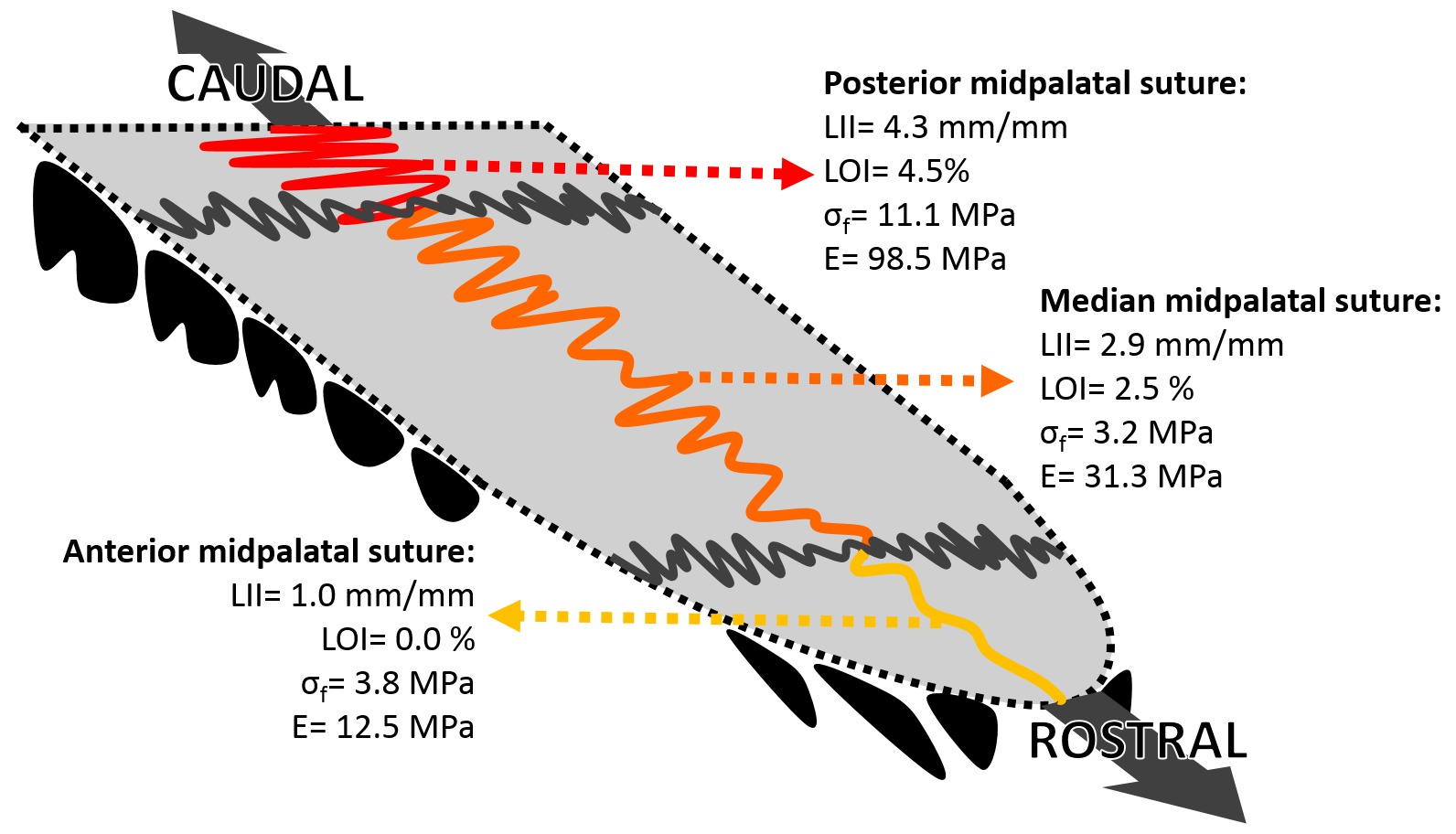
Results: Anterior (95.0%) and median (85.6%) regions exhibited higher prevalence of fracture within the suture, compared to the posterior one (30.0%) (p<0.001). LII had values of 1.0 (IQR=0.0) anteriorly, 2.9 (IQR=1.5) medially, and 4.3 (IQR=1.0) posteriorly. LOI had values of 0.0% (IQR=0.0%) anteriorly, 2.5% (IQR=2.6%) medially, and 4.5% (IQR=2.3%) posteriorly. E had values of 12.5MPa (IQR=11.2MPa) anteriorly, 31.3MPa (IQR=29.6MPa) medially, and 98.5MPa (IQR=250.3MPa) posteriorly. σf had values of 3.8MPa (IQR=1.7MPa) anteriorly, 3.2MPa (IQR=2.2MPa) medially, and 11.1MPa (IQR=10.7MPa) posteriorly. Apart for σf between anterior and median regions, all values showed significant differences (p<0.05).
Conclusions: Ultimate stress and rigidity of the midpalatal suture increased from rostral to caudal, according to greater interdigitation and obliteration. These anatomical and mechanical differences may contribute to the non-parallel opening during RME.
Methods: Soft tissues were removed from ten swine heads (12-month-old). Samples were obtained by slicing the hard palate (automatic cutting machine, water irrigation, 2500rpm) perpendicular to the midpalatal suture. Thirteen specimens were collected from each palate, with length according to anatomy (22.5~40.0mm) and standardised width (2.5mm). One hundred and thirty specimens were scanned with micro-CT (25μm pixel) and tested in four-point-bending (1.00mm/min) within 48h (storage in 0.9%NaCl at 4°C). Fracture type (Ft), linear interdigitation index (LII), linear obliteration index (LOI), ultimate stress (σf), and elastic modulus (E), were calculated. Kruskal-Wallis one-way ANOVA with Mann-Whitney’s post hoc test and Fisher’s exact test (α=0.05) were applied to compare values among anterior, median, and posterior region.
Results: Anterior (95.0%) and median (85.6%) regions exhibited higher prevalence of fracture within the suture, compared to the posterior one (30.0%) (p<0.001). LII had values of 1.0 (IQR=0.0) anteriorly, 2.9 (IQR=1.5) medially, and 4.3 (IQR=1.0) posteriorly. LOI had values of 0.0% (IQR=0.0%) anteriorly, 2.5% (IQR=2.6%) medially, and 4.5% (IQR=2.3%) posteriorly. E had values of 12.5MPa (IQR=11.2MPa) anteriorly, 31.3MPa (IQR=29.6MPa) medially, and 98.5MPa (IQR=250.3MPa) posteriorly. σf had values of 3.8MPa (IQR=1.7MPa) anteriorly, 3.2MPa (IQR=2.2MPa) medially, and 11.1MPa (IQR=10.7MPa) posteriorly. Apart for σf between anterior and median regions, all values showed significant differences (p<0.05).
Conclusions: Ultimate stress and rigidity of the midpalatal suture increased from rostral to caudal, according to greater interdigitation and obliteration. These anatomical and mechanical differences may contribute to the non-parallel opening during RME.