IADR Abstract Archives
Nano-hydroxyapatite from Pink Salmon Fish Bone as a Direct Pulp Capping Material
Objectives: In the contemporary period, patients and dental practitioners are becomingly mindful with preservation of tooth rather than pulp extirpation or tooth extraction. Direct pulp capping (DPC) is a procedure by which a biocompatible medicament is placed over the exposed pulp to induce reparative dentinogenesis. This study aimed to evaluate both the physico-chemical properties and biologic response of the nano-Hydroxyapatite (nHa) from Pink Salmon (Oncorhynchus gorbuscha) fish bone as a viable alternative DPC-material, and to compare with Calcium hydroxide (Ca(OH)2).
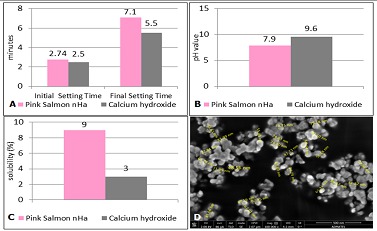
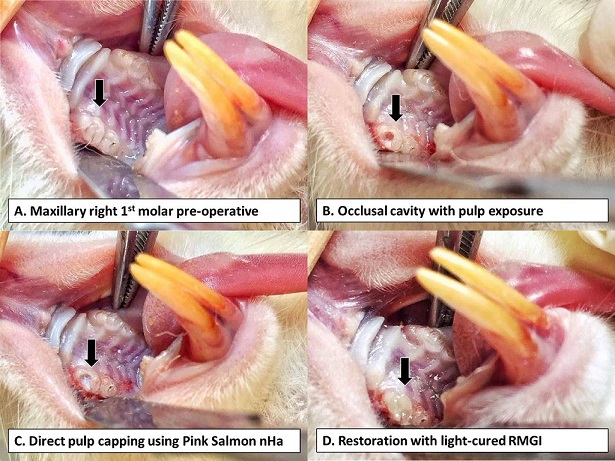
Methods: The properties that were measured and compared were setting time, pH, solubility and particle size. The protocol for the study was approved by CEU-Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee (CEU-IACUC). The study utilized a combination of completely-randomized block design and single-blinded controlled in-vivo design. Thirty maxillary right first molars of 30 Sprague-dawley rats (n=10/gp) were selected, prepared using sterile slow-speed ¼ round bur, capped with nHa, Ca(OH)2, and no DPC-material, and restored using light-cured restorative glass ionomer cement. The samples (n=10/gp) were subjected to histologic evaluation after 2nd and 4th week, and statistically analyzed (Independent t-test, ANOVA, Fisher’s Exact test and Bonferroni test, p<0.05).
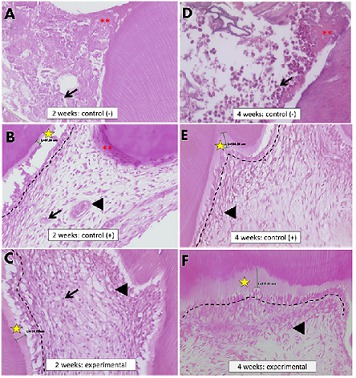
Results: There was no significant difference between the physico-chemical properties of nHa and Ca(OH)2, except on solubility. Histologic evaluation showed that there was a significant difference to the effect of nHa, Ca(OH)2, and group without any DPC-material on inflammatory cells infiltration and presence of necrotic areas after 4 weeks, and tertiary dentin thickness at 2 weeks in favor of nHa. However, there was no significant difference on vascularization, tertiary dentin (bridge) formation and odontoblasts proliferation. n=10/gp) were subjected to histologic examination after 2nd and 4th week, and statistically analyzed (Independent t-test, ANOVA, Fisher’s Exact test and Bonferroni test, p<0.05).
Conclusions: It can be concluded that Pink nano-Hydroxyapatite, with its favourable physico-chemical properties, can be used as an alternative direct pulp capping material that is biocompatible with pulp tissues and is capable of remineralization of compromised dentin-pulp complex.
Methods: The properties that were measured and compared were setting time, pH, solubility and particle size. The protocol for the study was approved by CEU-Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee (CEU-IACUC). The study utilized a combination of completely-randomized block design and single-blinded controlled in-vivo design. Thirty maxillary right first molars of 30 Sprague-dawley rats (n=10/gp) were selected, prepared using sterile slow-speed ¼ round bur, capped with nHa, Ca(OH)2, and no DPC-material, and restored using light-cured restorative glass ionomer cement. The samples (n=10/gp) were subjected to histologic evaluation after 2nd and 4th week, and statistically analyzed (Independent t-test, ANOVA, Fisher’s Exact test and Bonferroni test, p<0.05).
Results: There was no significant difference between the physico-chemical properties of nHa and Ca(OH)2, except on solubility. Histologic evaluation showed that there was a significant difference to the effect of nHa, Ca(OH)2, and group without any DPC-material on inflammatory cells infiltration and presence of necrotic areas after 4 weeks, and tertiary dentin thickness at 2 weeks in favor of nHa. However, there was no significant difference on vascularization, tertiary dentin (bridge) formation and odontoblasts proliferation. n=10/gp) were subjected to histologic examination after 2nd and 4th week, and statistically analyzed (Independent t-test, ANOVA, Fisher’s Exact test and Bonferroni test, p<0.05).
Conclusions: It can be concluded that Pink nano-Hydroxyapatite, with its favourable physico-chemical properties, can be used as an alternative direct pulp capping material that is biocompatible with pulp tissues and is capable of remineralization of compromised dentin-pulp complex.