IADR Abstract Archives
Comparison of the factors associated with the adhesion of Candida albicans on heat cure denture base acrylic material subjected to conventional polishing. in-vitro experimental study
Objectives: 1. To compare different surface properties i.e. surface roughness (μm), hydrophobicity and free surface energy or zeta potential (mV), in mechanically polished acrylic surfaces compared to chemically polished acrylic surfaces using finished only acrylic surface as negative control.
2. To assess the influence of surface roughness, hydrophobicity, and free surface energy (mV) of mechanically polished acrylic surfaces on the adherence of Candida albicans compared to chemically polished acrylic surface using finished only acrylic surface as negative control.
Methods: Thirty (20x20x2mm3) Polymethylmethacrylate specimens will be fabricated from heat polymerization. After finishing acrylic specimens will be randomly divided into two groups using the lottery method. The two groups included 15 samples of mechanically polished acrylic surface specimen and 15 samples of chemically polished acrylic surface specimen.
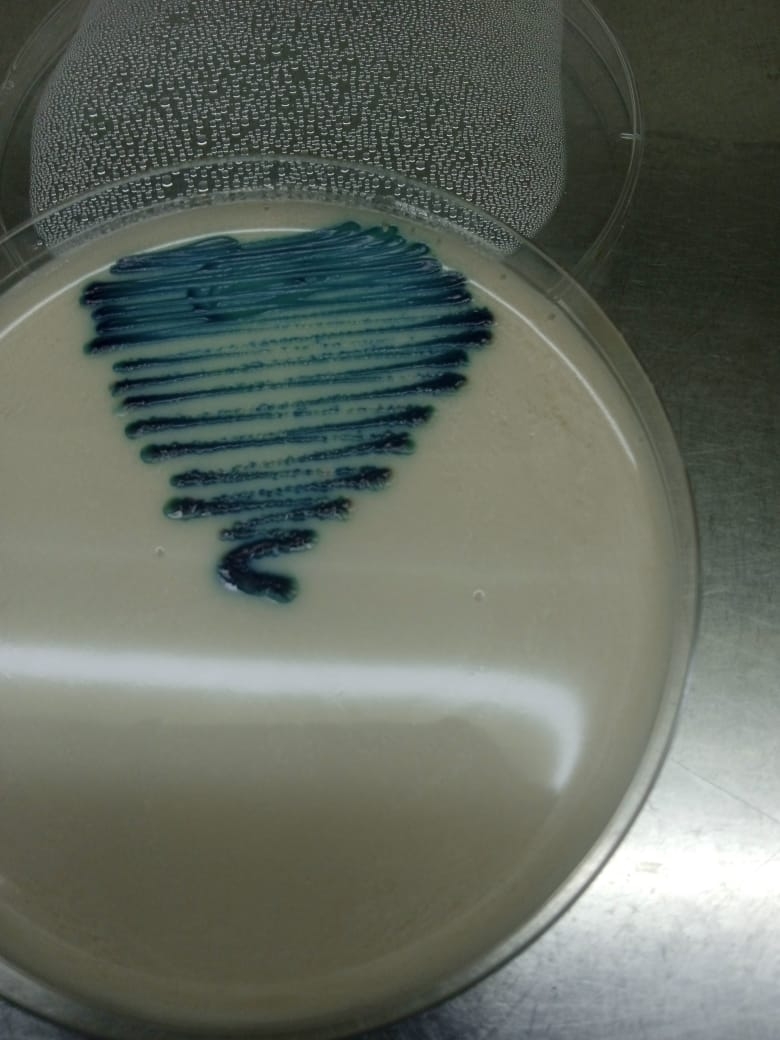
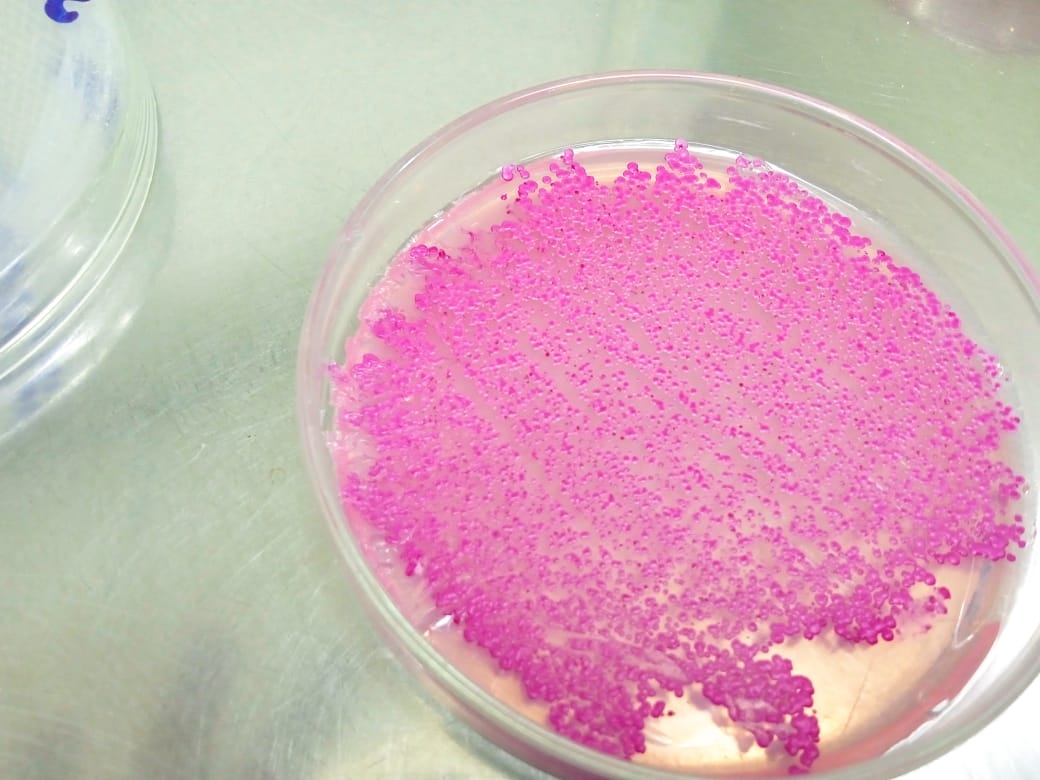
The present study was based on three clinical isolates and one control strain of C Albicans. Initially, subject isolates were grown on Dichloran Rose-Bengal Chloramphenicol agar (DRBC) and chocolate agar and incubated at 25 C for five (5) days. ATCC # control was run along the test samples for the confirmation of Candida albicans on Chrome agar.
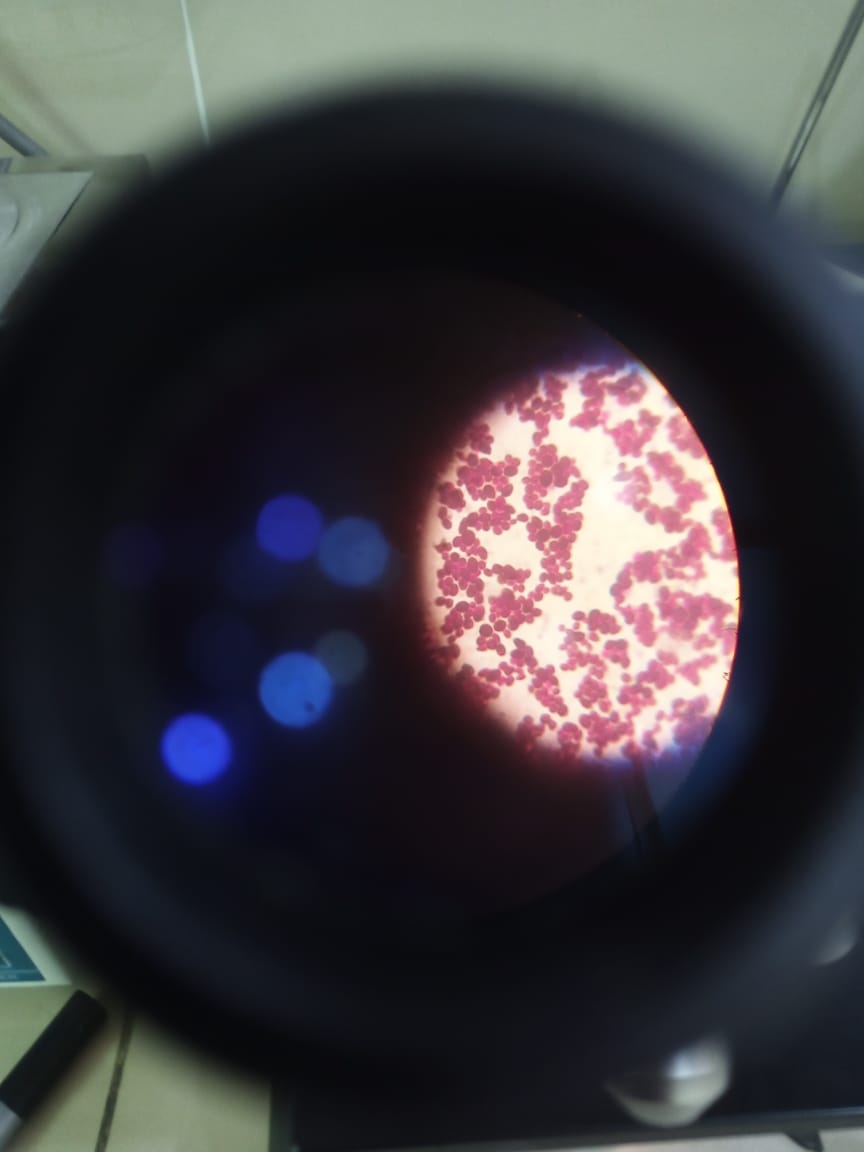
Overnight cultures of subjected isolates of C. albicans were inoculated (0.1 mL=2.5x105) in 100 mL TSB flasks having (pH =7.0) and incubated at 35 °C for 7 days for biofilm assay. Images were acquired using JSM IT 100 JEOL (Japan) Electron Microscope. Aqueous phase absorbance was measured (ABS 2) at 578 nm and the percentage of adhesion was expressed as %adhesion= (1–ABS 2/ ABS 1) × 100.
Zeta potential of the mechanically polished and chemically polished acrylic surface can be calculated with the Smoluchowski's formula.
Results: For both initial adherence and biofilm formation, no statistically-significant differences were observed among both groups, as determined by c.f.u./mm. SEM analysis showed the presence of scratches and valleys on the non polsihed acrylic specimens and densely-packed yeast cells covering the entire surface. Free surface energy for non polished acrylic surface was -32 mV where as for mechanical and chemcial polsihed specimens, it is -34mV and -38mV respectively. Non Polished Control 7.9x10 6 candidal counts.
Conclusions: ..
2. To assess the influence of surface roughness, hydrophobicity, and free surface energy (mV) of mechanically polished acrylic surfaces on the adherence of Candida albicans compared to chemically polished acrylic surface using finished only acrylic surface as negative control.
Methods: Thirty (20x20x2mm3) Polymethylmethacrylate specimens will be fabricated from heat polymerization. After finishing acrylic specimens will be randomly divided into two groups using the lottery method. The two groups included 15 samples of mechanically polished acrylic surface specimen and 15 samples of chemically polished acrylic surface specimen.
The present study was based on three clinical isolates and one control strain of C Albicans. Initially, subject isolates were grown on Dichloran Rose-Bengal Chloramphenicol agar (DRBC) and chocolate agar and incubated at 25 C for five (5) days. ATCC # control was run along the test samples for the confirmation of Candida albicans on Chrome agar.
Overnight cultures of subjected isolates of C. albicans were inoculated (0.1 mL=2.5x105) in 100 mL TSB flasks having (pH =7.0) and incubated at 35 °C for 7 days for biofilm assay. Images were acquired using JSM IT 100 JEOL (Japan) Electron Microscope. Aqueous phase absorbance was measured (ABS 2) at 578 nm and the percentage of adhesion was expressed as %adhesion= (1–ABS 2/ ABS 1) × 100.
Zeta potential of the mechanically polished and chemically polished acrylic surface can be calculated with the Smoluchowski's formula.
Results: For both initial adherence and biofilm formation, no statistically-significant differences were observed among both groups, as determined by c.f.u./mm. SEM analysis showed the presence of scratches and valleys on the non polsihed acrylic specimens and densely-packed yeast cells covering the entire surface. Free surface energy for non polished acrylic surface was -32 mV where as for mechanical and chemcial polsihed specimens, it is -34mV and -38mV respectively. Non Polished Control 7.9x10 6 candidal counts.
Conclusions: ..