IADR Abstract Archives
Effect of storage media on material properties in extracted human teeth – A systematic review
Objectives: To study the effects of storage media on the results of materials being tested in an invitro studies on extracted teeth.
Methods: An electronic search was in four databases PubMed , CINAHL Plus, Dent & Oral Science and Cochrane databases along with manual searching. The PICO was kept as following; Population- Extracted Human Teeth, Intervention: Different Storage media, Comparison: Comparison of storage media amongst themselves , Outcome(s): Material property testing , Setting : In-vitro experimental studies.
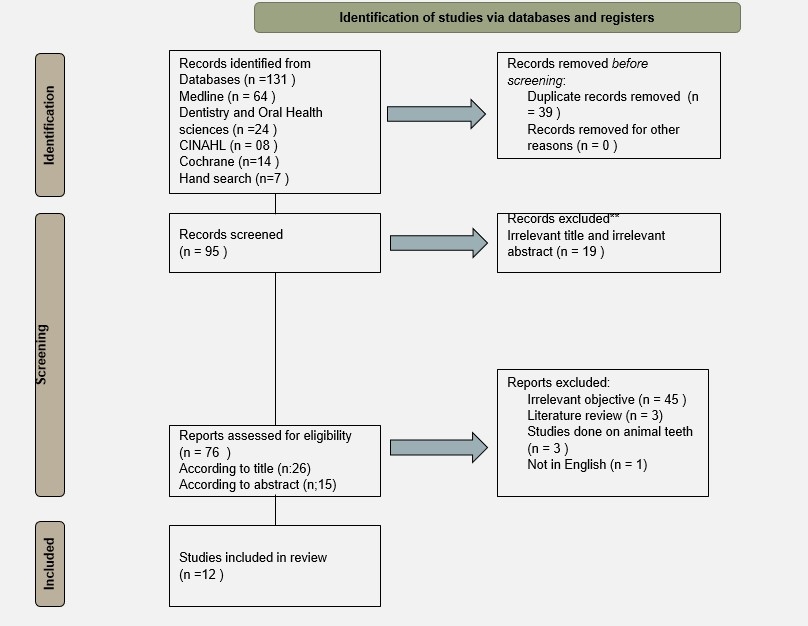
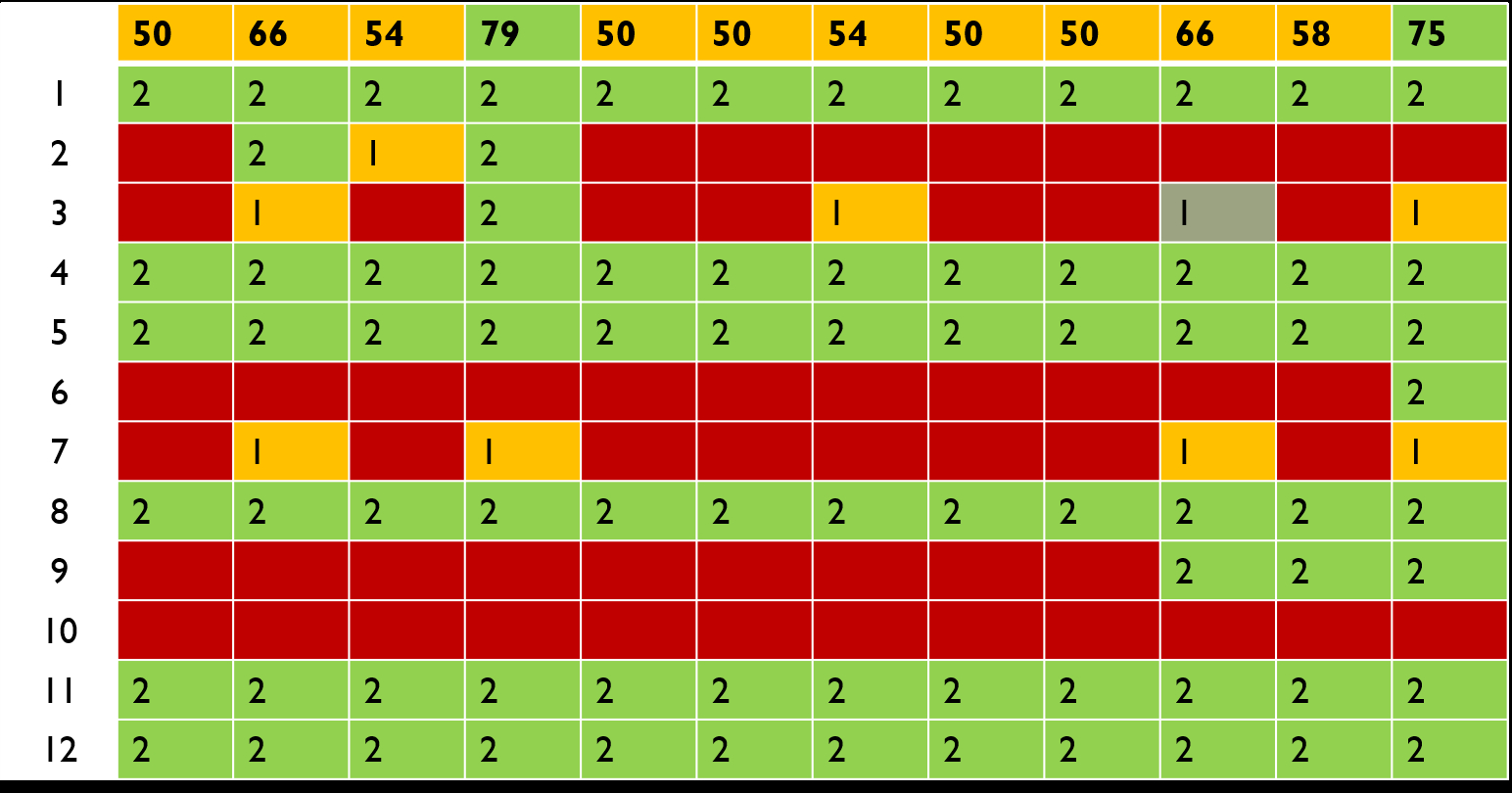
Results: A total of 131 articles were found out of which 39 duplicates were removed. 95 articles were then screened from which 19 articles were shortlisted based on title .A total of 13 articles were then shortlisted based on title from which 12 articles were included in the systematic review process. Quinn tool was utilised to assess the risk of bias of invidual invitro studies , which revealed 2 studies out of 12 to be of low risk whereas remaining were of unclear risk
Conclusions: So far relatively fewer high quality studies are done which focus on the effect that storage media has on dental material properties. This review indicated that no material has yet found to be superior in terms of maintaining or improving the properties of tested materials.However, dry storage , formalin and cryopreservation were found out to be least affecting the properties of dental materials. Properly designed and controlled studies of higher quality are recommended to be conducted.
Methods: An electronic search was in four databases PubMed , CINAHL Plus, Dent & Oral Science and Cochrane databases along with manual searching. The PICO was kept as following; Population- Extracted Human Teeth, Intervention: Different Storage media, Comparison: Comparison of storage media amongst themselves , Outcome(s): Material property testing , Setting : In-vitro experimental studies.
Results: A total of 131 articles were found out of which 39 duplicates were removed. 95 articles were then screened from which 19 articles were shortlisted based on title .A total of 13 articles were then shortlisted based on title from which 12 articles were included in the systematic review process. Quinn tool was utilised to assess the risk of bias of invidual invitro studies , which revealed 2 studies out of 12 to be of low risk whereas remaining were of unclear risk
Conclusions: So far relatively fewer high quality studies are done which focus on the effect that storage media has on dental material properties. This review indicated that no material has yet found to be superior in terms of maintaining or improving the properties of tested materials.However, dry storage , formalin and cryopreservation were found out to be least affecting the properties of dental materials. Properly designed and controlled studies of higher quality are recommended to be conducted.