IADR Abstract Archives
Impact of malocclusions on oral health-related quality of life of adolescents assessed with Parent assessment and Child perception Questionnaires
Objectives: The study objectives were to evaluate the impact of malocclusions specifically increased overjet and crowding, on children and their parents, on the oral health–related quality of life (OHRQOL) of adolescents aged 11 to 14 years old in Jordan.
Methods: Three hundred and twenty-four adolescents and their parents completed both the Child Perceptions Questionnaire (CPQ) and the Parent assessment Questionnaire (PAQ). Participants were examined and divided into controls, increased overjet, and crowding. The effect of sociodemographis factors on OHRQOL were determined with the Mann-Whitney U test, Kruskal-Wallis H test, and correlation analysis using SPSS (version 29.0; IBM). Statistical significance was set at P <0.05.
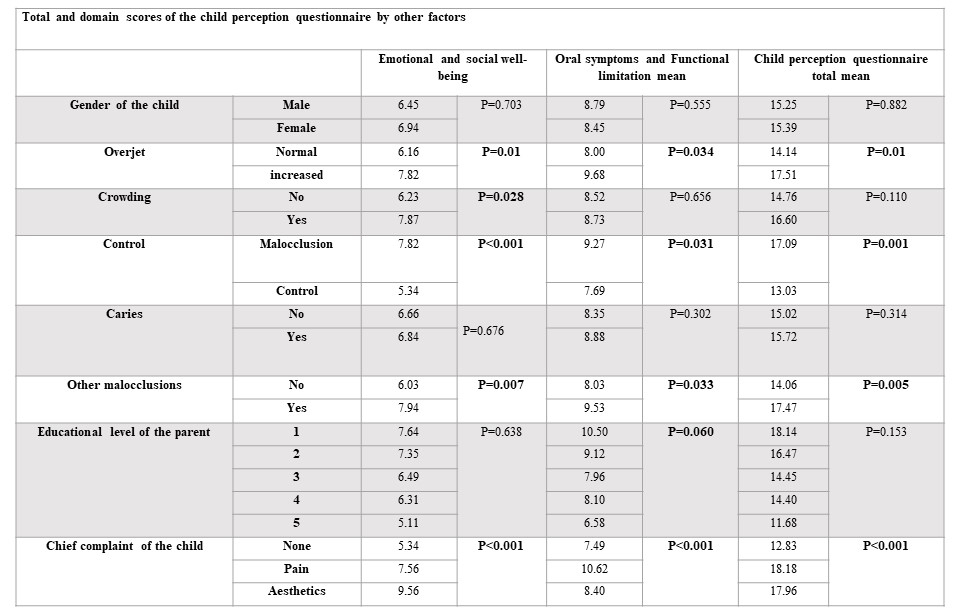
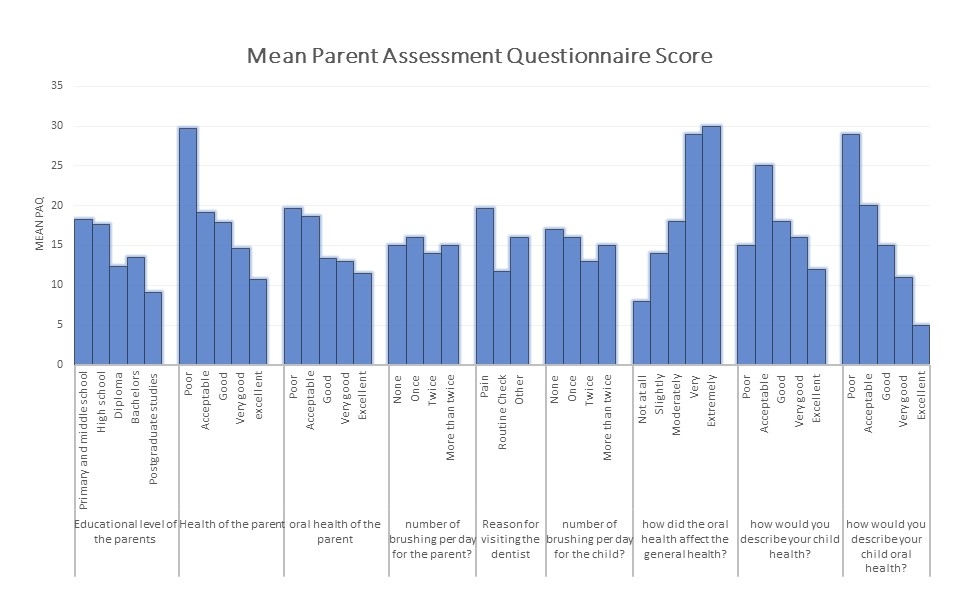
Results: Participants were divided as follows: increased overjet (114) ranging from 3 mm to 13 mm, crowding (101) grouped into mild, moderate, and severe, and controls (109). Mean PAQ score increased among participants with increased overjet (17.1 vs. 13.9, P=0.027). The mean CPQ score increased among participants with increased overjet (14.15 vs. 17.51, P=0.01). Additionally, the PAQ and the CPQ both increased significantly according to the patients chief complaint; the results showed a mean PAQ score of 18.7 for pain, 16.1 for aesthetics, and 12.5 for no chief complaint (P<0.0001). Similarly the mean CPQ score was highest for pain and aesthetics compared to none (18.2 vs.18.0 vs. 12.8, P<0.0001). Finally, there was a positive correlation between the CPQ and the PAQ (r=0.647, P<0.001).
Conclusions: Children and adolescents with increased overjet in comparison to the norm are associated with significant limitations of the OHRQoL from the children’s as well as the parents perception. As the PAQ increased so did the CPQ, indicating a true and non-coincidental effect of these malocclusions on the children as well as how their parents perceive the malocclusion affects them. The implications of the complex perception of malocclusion and its effect on children and their parents might lead to difficulty in orthodontic treatment planning. Thus, by understanding the emotional, social, economic, cultural, and psychological aspects of malocclusion and its effect on the quality of patients’ life, this might influence the decision for orthodontic treatment needs.
Methods: Three hundred and twenty-four adolescents and their parents completed both the Child Perceptions Questionnaire (CPQ) and the Parent assessment Questionnaire (PAQ). Participants were examined and divided into controls, increased overjet, and crowding. The effect of sociodemographis factors on OHRQOL were determined with the Mann-Whitney U test, Kruskal-Wallis H test, and correlation analysis using SPSS (version 29.0; IBM). Statistical significance was set at P <0.05.
Results: Participants were divided as follows: increased overjet (114) ranging from 3 mm to 13 mm, crowding (101) grouped into mild, moderate, and severe, and controls (109). Mean PAQ score increased among participants with increased overjet (17.1 vs. 13.9, P=0.027). The mean CPQ score increased among participants with increased overjet (14.15 vs. 17.51, P=0.01). Additionally, the PAQ and the CPQ both increased significantly according to the patients chief complaint; the results showed a mean PAQ score of 18.7 for pain, 16.1 for aesthetics, and 12.5 for no chief complaint (P<0.0001). Similarly the mean CPQ score was highest for pain and aesthetics compared to none (18.2 vs.18.0 vs. 12.8, P<0.0001). Finally, there was a positive correlation between the CPQ and the PAQ (r=0.647, P<0.001).
Conclusions: Children and adolescents with increased overjet in comparison to the norm are associated with significant limitations of the OHRQoL from the children’s as well as the parents perception. As the PAQ increased so did the CPQ, indicating a true and non-coincidental effect of these malocclusions on the children as well as how their parents perceive the malocclusion affects them. The implications of the complex perception of malocclusion and its effect on children and their parents might lead to difficulty in orthodontic treatment planning. Thus, by understanding the emotional, social, economic, cultural, and psychological aspects of malocclusion and its effect on the quality of patients’ life, this might influence the decision for orthodontic treatment needs.