IADR Abstract Archives
Comparison Between Three Scan Abutments and the Effect on Determining the Implant Axis Using an Intraoral Digital Scanner
Objectives: The purpose of this study is to evaluate the differences in the digitally derived longitudinal axis of the implant between three types of scan abutments.
Methods: Three different standard scanning bodies (MIS, Alpha bio, Zirkonzahn) were used.
For every scanning body, one extraoral scan was performed on a TRIOS (E2) laboratory desktop scanner. This scanner and the resulting scans are considered the gold standard in terms of accuracy.17 The intraoral scans were performed 30 times with a CEREC AC Omnicam (Dentsply Sirona) scanner.
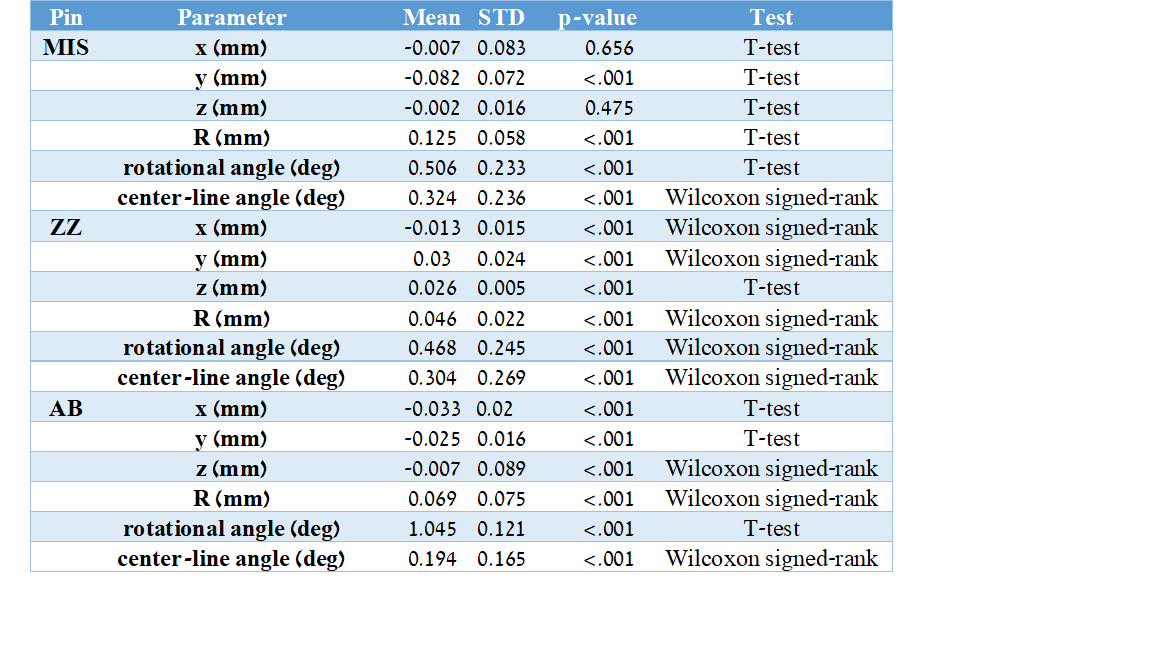
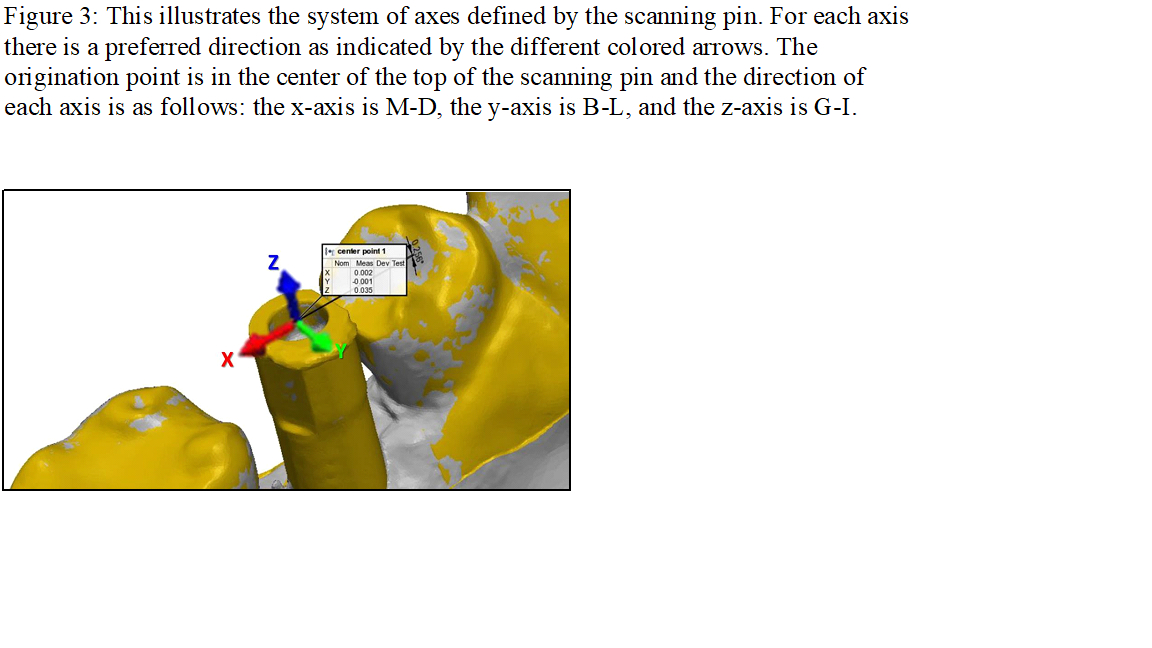
For each abutment, several spatial parameters were defined to enable comparison between the digital scans: 1) 3D position of the upper face center – indicating the movement of the scan abutment’s head compared to the gold standard in each axis (x axis representing the M-D axis, y axis representing the B-L axis, z axis representing the I-G axis). 2) Central line angle – 3D angle between the gold standard central axis to the intra-oral central axis. 3) Rotation angle – 3D angle of the scan abutment rotation around the central axis.
For each of those spatial parameters a statistical analysis was conducted to test the trueness and the precision of our results.
Results: We examined the location of the center point of the occlusal surface.
The geometrical shape of the scan body effects the intra-oral scan quality. The standard deviation from the MIS pin was higher than the maximum threshold set for clinical bone tolerance around the implant.
The rotational angle has the most profound clinical impact on the entire scan. In the AB pin, which is cylindrical, there is the largest rotational angle of the scan pins (about one degree), with low trueness and high precision relative to the other two pins, which can cause problems in passive seating.
Conclusions: Our conclusion is that, at the level of a single unit scan, there is probably no clinical impact on which scan pin we will use. Nevertheless, it is worthwhile to further research and examine whether a digital intraoral scan of two or more pins will create too much distortion in fabrication and clinically affect the final prosthetic result.
Methods: Three different standard scanning bodies (MIS, Alpha bio, Zirkonzahn) were used.
For every scanning body, one extraoral scan was performed on a TRIOS (E2) laboratory desktop scanner. This scanner and the resulting scans are considered the gold standard in terms of accuracy.17 The intraoral scans were performed 30 times with a CEREC AC Omnicam (Dentsply Sirona) scanner.
For each abutment, several spatial parameters were defined to enable comparison between the digital scans: 1) 3D position of the upper face center – indicating the movement of the scan abutment’s head compared to the gold standard in each axis (x axis representing the M-D axis, y axis representing the B-L axis, z axis representing the I-G axis). 2) Central line angle – 3D angle between the gold standard central axis to the intra-oral central axis. 3) Rotation angle – 3D angle of the scan abutment rotation around the central axis.
For each of those spatial parameters a statistical analysis was conducted to test the trueness and the precision of our results.
Results: We examined the location of the center point of the occlusal surface.
The geometrical shape of the scan body effects the intra-oral scan quality. The standard deviation from the MIS pin was higher than the maximum threshold set for clinical bone tolerance around the implant.
The rotational angle has the most profound clinical impact on the entire scan. In the AB pin, which is cylindrical, there is the largest rotational angle of the scan pins (about one degree), with low trueness and high precision relative to the other two pins, which can cause problems in passive seating.
Conclusions: Our conclusion is that, at the level of a single unit scan, there is probably no clinical impact on which scan pin we will use. Nevertheless, it is worthwhile to further research and examine whether a digital intraoral scan of two or more pins will create too much distortion in fabrication and clinically affect the final prosthetic result.