IADR Abstract Archives
The influence of Infantile Thiamine Deficiency on primary dentition
Objectives: The present study explored the histological and chemical effects of Infantile Thiamine Deficiency (ITD) on enamel development through the examination of exfoliated deciduous teeth from a patient who had been fed during his first year of life with a thiamine-deficient milk substitute.
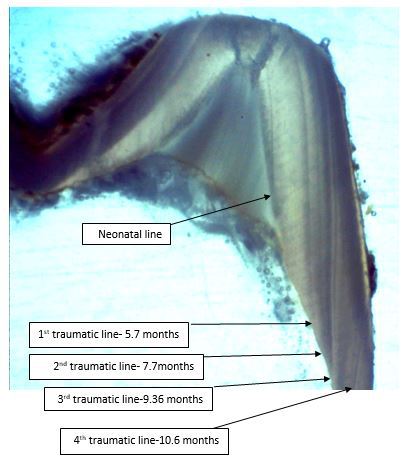
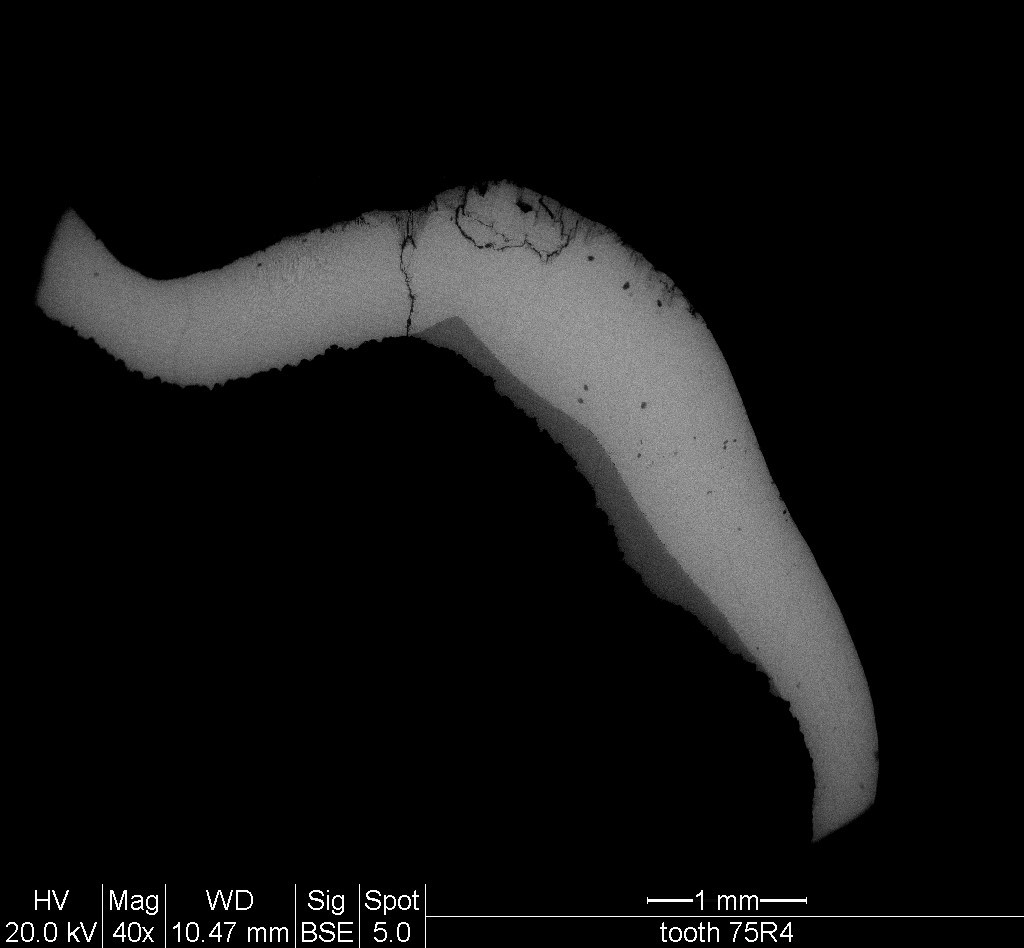
Methods: Ground sections derived from six exfoliated primary teeth of a patient who suffered from ITD were examined. Slices from a light microscope were photographed for histological analysis. We calculated the time when the amelogenesis insults occurred and the data were cross- examined with the patient's medical history. We then measured the enamel content of calcium, phosphate, oxygen, carbon and magnesium on two lines from the Dentino-Enamel Junction (DEJ) to the outer surface using an energy dispersive X-ray spectrometer.
Results: Carbon (organic matter) concentration in postnatal enamel was 2.37 times higher in ITD, phosphate levels were lower and magnesium and calcium levels tended to be higher in ITD teeth.
Conclusions: Chemical and histological analysis enabled us to confirm that thiamine deficiency in infancy impaired postnatal amelogenesis and resulted in less calcified enamel with a higher level of organic matter. The higher postnatal enamel carbon and magnesium concentration found in ITD may derive from either impaired mineralization caused by thiamine deficiency and disturbed cellular metabolism or indirect damage to the ameloblasts due to the physical condition of the patient. Ca/P mean ratio in ITD teeth was higher than the mean ratio in the control displaying a damaged mineralization process.
Methods: Ground sections derived from six exfoliated primary teeth of a patient who suffered from ITD were examined. Slices from a light microscope were photographed for histological analysis. We calculated the time when the amelogenesis insults occurred and the data were cross- examined with the patient's medical history. We then measured the enamel content of calcium, phosphate, oxygen, carbon and magnesium on two lines from the Dentino-Enamel Junction (DEJ) to the outer surface using an energy dispersive X-ray spectrometer.
Results: Carbon (organic matter) concentration in postnatal enamel was 2.37 times higher in ITD, phosphate levels were lower and magnesium and calcium levels tended to be higher in ITD teeth.
Conclusions: Chemical and histological analysis enabled us to confirm that thiamine deficiency in infancy impaired postnatal amelogenesis and resulted in less calcified enamel with a higher level of organic matter. The higher postnatal enamel carbon and magnesium concentration found in ITD may derive from either impaired mineralization caused by thiamine deficiency and disturbed cellular metabolism or indirect damage to the ameloblasts due to the physical condition of the patient. Ca/P mean ratio in ITD teeth was higher than the mean ratio in the control displaying a damaged mineralization process.