IADR Abstract Archives
Evaluation of pharyngeal airway volume subsequent to treatment of skeletal Class II patients via a skeletally anchored distalizer assisted with rapid palatal expansion: A retrospective CBCT study
Objectives: To evaluate pharyngeal airway volume changes after treatment of skeletal Class II patients using a skeletally anchored distalizer assisted by rapid palatal expansion (RPE) via Cone Beam Computed Tomography (CBCT).
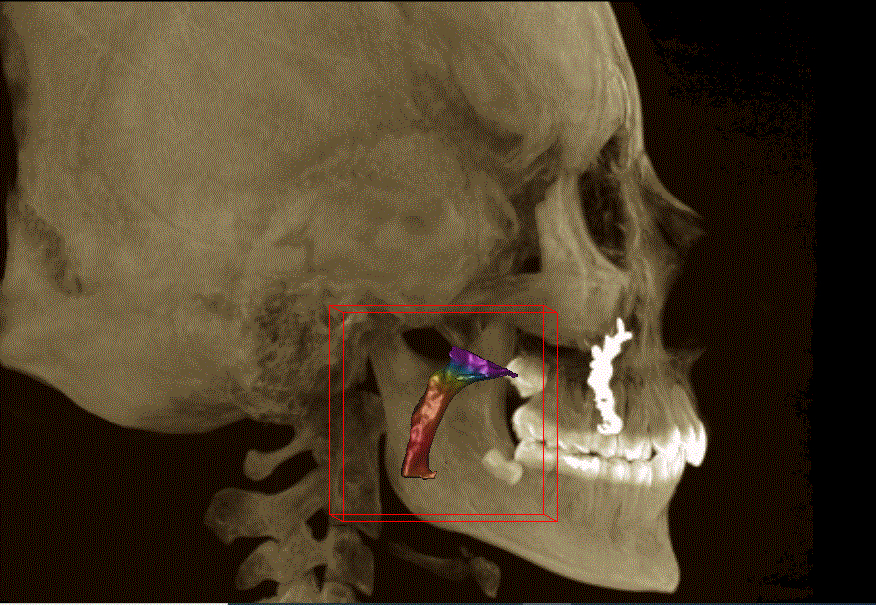
Methods: Ten Class II patients (8 females and 2 males), with a mean age, 13.22 ± 1.39 years were treated by a skeletally anchored distalizer, Zygoma Anchorage System (ZAS), following a conventional protocol of RPE. ZAS consisted of two zygomatic miniplates, a heavy arch wire, and a closed Nickel Titanium (NiTi) coil spring attached between a power hook on 0.018 × 0.025-inch stainless steel arch wire that stepped on the six anterior teeth mesial to the maxillary 1st premolar. The miniplate's hook was supported to zygomatic buttress of each side and the NiTi spring delivered a 450 gm distalizing continuous force. Pharyngeal air way volumes were analyzed via CBCT images before and after distalization of maxillary buccal segments. Moreover, sagittal dentoskeletal parameters were also evaluated and compared and the significance level was set at p≤ 0.05.
Results: Subsequent to correction of Class II malocclusion, there are statistically significant increases (p≤0.01) in total pharyngeal,retroglossal, and nasal airway volumes by 4.36 cm3 , 1.19cm3 , 8.96 cm3 , respectively. While nasopharynx and retropalatal airway volumes showed significant (p≤0.05) increases by 1.73 cm3 and 1.85 cm3 , respectively. Moreover, an improvement in Class II relation was evident as demonstrated by significant (p≤0.01) positive changes regarding the sagittal dental parameters of maxillary permanent molars.
Conclusions: The current treatment protocol of skeletal Class II malocclusion with skeletally anchored distalizer assisted by RPE revealed a considerable augmentation of pharyngeal airway volumes. Indeed, this approach can be a helpful option for skeletal Class II patients with breathing disorders.
Methods: Ten Class II patients (8 females and 2 males), with a mean age, 13.22 ± 1.39 years were treated by a skeletally anchored distalizer, Zygoma Anchorage System (ZAS), following a conventional protocol of RPE. ZAS consisted of two zygomatic miniplates, a heavy arch wire, and a closed Nickel Titanium (NiTi) coil spring attached between a power hook on 0.018 × 0.025-inch stainless steel arch wire that stepped on the six anterior teeth mesial to the maxillary 1st premolar. The miniplate's hook was supported to zygomatic buttress of each side and the NiTi spring delivered a 450 gm distalizing continuous force. Pharyngeal air way volumes were analyzed via CBCT images before and after distalization of maxillary buccal segments. Moreover, sagittal dentoskeletal parameters were also evaluated and compared and the significance level was set at p≤ 0.05.
Results: Subsequent to correction of Class II malocclusion, there are statistically significant increases (p≤0.01) in total pharyngeal,retroglossal, and nasal airway volumes by 4.36 cm3 , 1.19cm3 , 8.96 cm3 , respectively. While nasopharynx and retropalatal airway volumes showed significant (p≤0.05) increases by 1.73 cm3 and 1.85 cm3 , respectively. Moreover, an improvement in Class II relation was evident as demonstrated by significant (p≤0.01) positive changes regarding the sagittal dental parameters of maxillary permanent molars.
Conclusions: The current treatment protocol of skeletal Class II malocclusion with skeletally anchored distalizer assisted by RPE revealed a considerable augmentation of pharyngeal airway volumes. Indeed, this approach can be a helpful option for skeletal Class II patients with breathing disorders.