IADR Abstract Archives
New Method to Measure Angle of Convergence in Dental Preparations
Objectives: Compare the Convergence Angle (CA) measurements of dental preparations (DP) between a new dental instrument that measures CA in situ versus the measurement obtained indirectly with digital angle measurement software (AutoCad®).
Methods: A correlational experimental descriptive study was carried out in adult patients who attended the Undergraduate Dental Clinic of the Universidad de La Frontera, in the city of Temuco (Chile), with indication of crowns. The sample obtained is non-probabilistic for the convenience of consecutive cases that meets the eligibility criteria. The total collected were 108 dental preparations obtained from 66 patients.
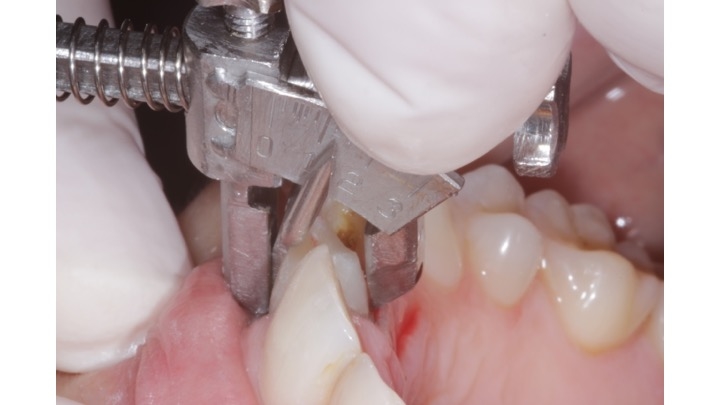
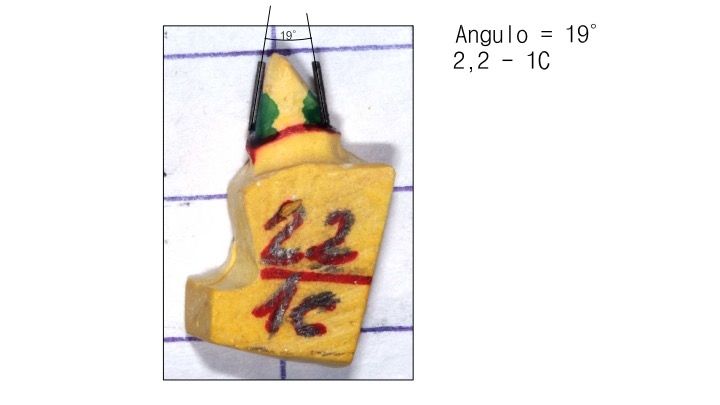
The investigator in charge measured the dental instrument (created at the University of La Frontera) clinically on 2 different occasions, the same DP (in situ). These measurements were compared with digital measurements from AutoCad® software to measure angles using an indirect DP method (DP printing and dies). An intraclass correlation coefficient test (ICC) was applied with its conceptual evaluation to determine the reliability of the measurements.
Results: The average CA of all the preparations obtained (n = 108) by the instrument was 16.9 ± 5.9 (1st measurement); 17.1 ± 5.7 (2nd measurement) and by the AutoCad 18.9 ± 6.2. When comparing the measurements of the dental instrument versus the measurement with AutoCad®, a good ICC was observed (0.79 to 0.78, respective first and second measurement with the instrument). The comparative ICC between 1st and 2nd measurement with the dental instrument had a very good conceptual evaluation (ICC = 0.95).
Conclusions: The study reported that the new dental instrument measures reliable values of the Convergence Angle of dental preparation, immediately (in situ); and it constitutes an advantageous tool that will allow the clinician to obtain objective values of the convergence angle for a correct dental preparation in an immediate, economic and effective way.
Methods: A correlational experimental descriptive study was carried out in adult patients who attended the Undergraduate Dental Clinic of the Universidad de La Frontera, in the city of Temuco (Chile), with indication of crowns. The sample obtained is non-probabilistic for the convenience of consecutive cases that meets the eligibility criteria. The total collected were 108 dental preparations obtained from 66 patients.
The investigator in charge measured the dental instrument (created at the University of La Frontera) clinically on 2 different occasions, the same DP (in situ). These measurements were compared with digital measurements from AutoCad® software to measure angles using an indirect DP method (DP printing and dies). An intraclass correlation coefficient test (ICC) was applied with its conceptual evaluation to determine the reliability of the measurements.
Results: The average CA of all the preparations obtained (n = 108) by the instrument was 16.9 ± 5.9 (1st measurement); 17.1 ± 5.7 (2nd measurement) and by the AutoCad 18.9 ± 6.2. When comparing the measurements of the dental instrument versus the measurement with AutoCad®, a good ICC was observed (0.79 to 0.78, respective first and second measurement with the instrument). The comparative ICC between 1st and 2nd measurement with the dental instrument had a very good conceptual evaluation (ICC = 0.95).
Conclusions: The study reported that the new dental instrument measures reliable values of the Convergence Angle of dental preparation, immediately (in situ); and it constitutes an advantageous tool that will allow the clinician to obtain objective values of the convergence angle for a correct dental preparation in an immediate, economic and effective way.