IADR Abstract Archives
Biocompatibility and Biomineralization Assessment of Iodoform and Calcium Hydroxide Pastes
Objectives: The aim of this study was to evaluate, in vivo, the inflammatory response and the biomineralization capacity of iodoform and calcium hydroxide pastes in subcutaneous tissue of rats. Eighteen Wistar rats (n=6) received implanted polyethylene tubes filled with the following materials: calcium hydroxide + propylene glycol; calcium hydroxide + propylene glycol + iodoform; iodoform + Carbowax; and Carbowax.
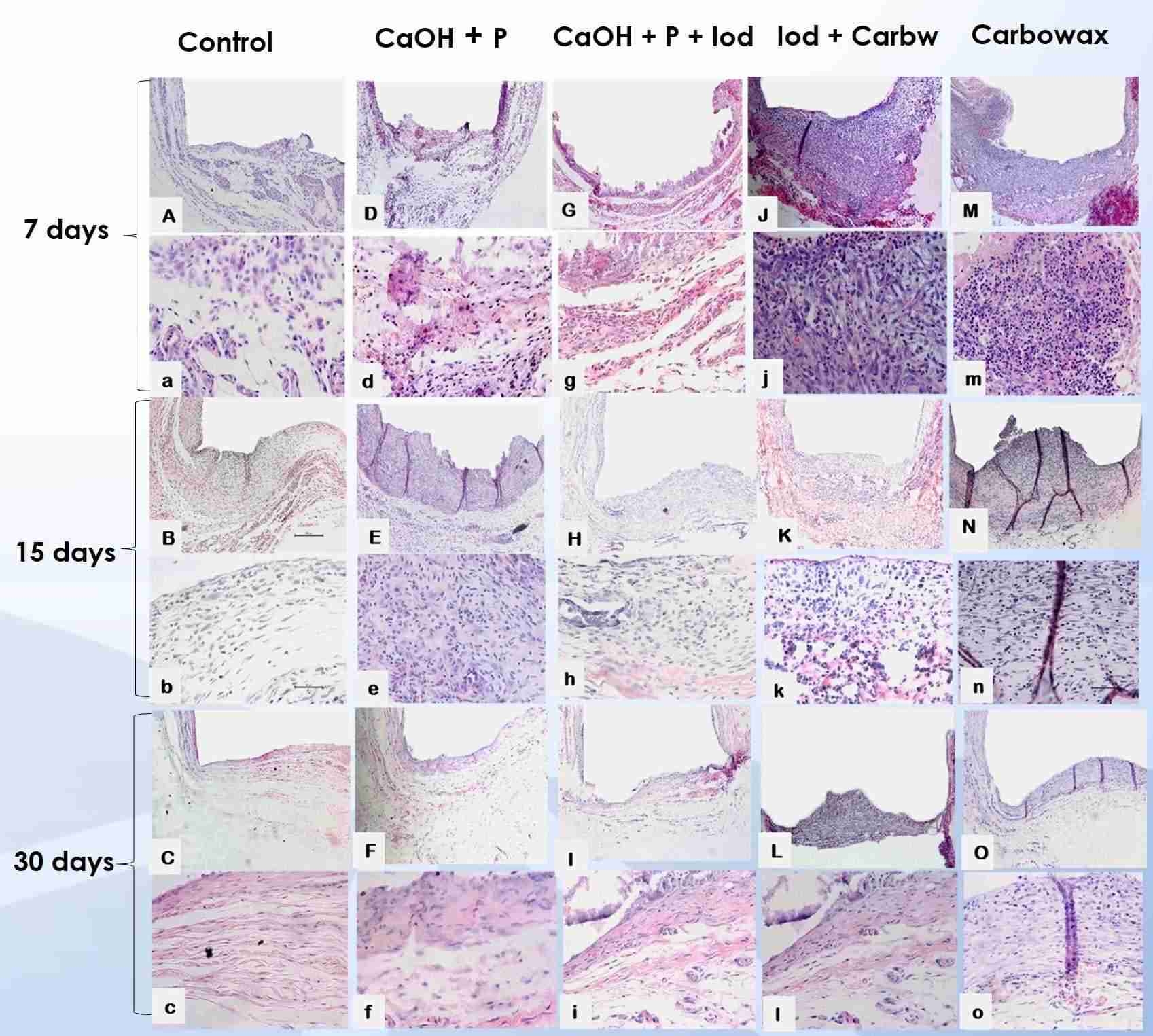
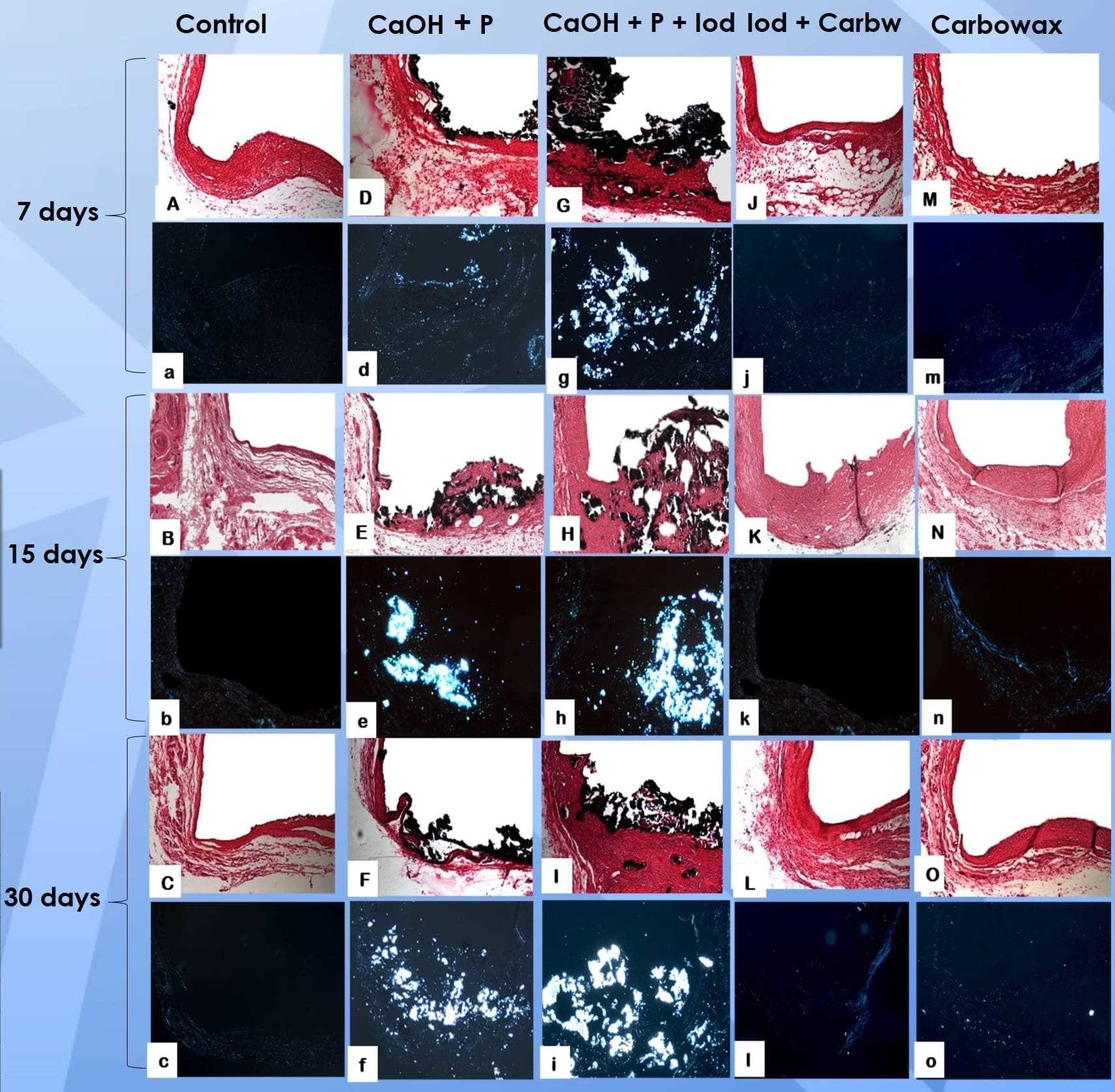
Methods: Empty tubes were used as control. After 7, 15 and 30 days, the animals were euthanized and the polyethylene tubes were removed with the surrounding tissues. Inflammatory infiltrate and thickness of the fibrous capsule were histologically evaluated via hematoxylin-eosin (HE) staining, attributing the following scores: 0 (few inflammatory cells); 1 (less than 25 cells); 2 (between 25 and 125 cells); and 3 (125 or more inflammatory cells). The fibrous capsule was classified as thin (<150μm) or thick (>150μm). Mineralization was assessed by Von Kossa (VK) staining and under polarized light (PL) as positive or negative. After tabulated, data were analyzed via Kruskal-Wallis and Dunn’s test with a significance level set at 5%.
Results: After 7 days, all groups showed similarity to control with inflammatory score 2, except Carbowax, which showed score 3. All groups showed initial thick fibrous capsule, similar to control. After 15 days all groups, except control, showed a decrease in the inflammatory infiltrate and fibrous capsule thickness. After 30 days, all groups presented score 1 and thin fibrous capsule. Regarding biomineralization, the groups containing calcium hydroxide were positive for VK and PL in all experimental periods, in contrast to the other groups, which showed no signs of mineralization in any period, similar to control.
Conclusions: At the end of the experiment, all materials showed biocompatibility but only the groups containing calcium hydroxide induced biomineralization.
Methods: Empty tubes were used as control. After 7, 15 and 30 days, the animals were euthanized and the polyethylene tubes were removed with the surrounding tissues. Inflammatory infiltrate and thickness of the fibrous capsule were histologically evaluated via hematoxylin-eosin (HE) staining, attributing the following scores: 0 (few inflammatory cells); 1 (less than 25 cells); 2 (between 25 and 125 cells); and 3 (125 or more inflammatory cells). The fibrous capsule was classified as thin (<150μm) or thick (>150μm). Mineralization was assessed by Von Kossa (VK) staining and under polarized light (PL) as positive or negative. After tabulated, data were analyzed via Kruskal-Wallis and Dunn’s test with a significance level set at 5%.
Results: After 7 days, all groups showed similarity to control with inflammatory score 2, except Carbowax, which showed score 3. All groups showed initial thick fibrous capsule, similar to control. After 15 days all groups, except control, showed a decrease in the inflammatory infiltrate and fibrous capsule thickness. After 30 days, all groups presented score 1 and thin fibrous capsule. Regarding biomineralization, the groups containing calcium hydroxide were positive for VK and PL in all experimental periods, in contrast to the other groups, which showed no signs of mineralization in any period, similar to control.
Conclusions: At the end of the experiment, all materials showed biocompatibility but only the groups containing calcium hydroxide induced biomineralization.