IADR Abstract Archives
Prevalence of bad occlusion and orthodontic treatment need in 12-year-old adolescents from SSVQ.
Objectives: To determine the prevalence of bad occlusion and analyze the index of orthodontic treatment need in definitive dentition in 12-year-old adolescents beneficiary of Servicio de Salud Viña del Mar-Quillota (SSVQ).
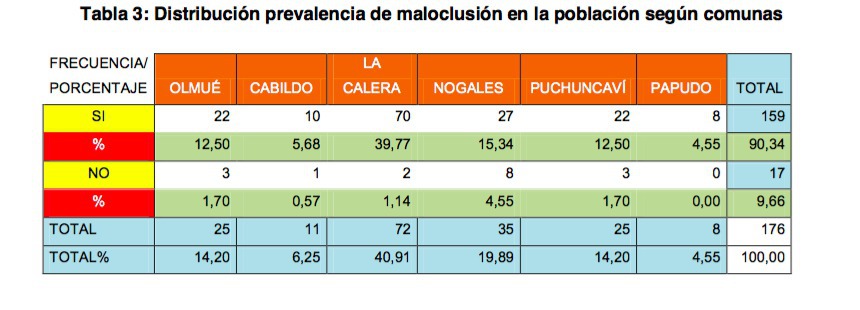
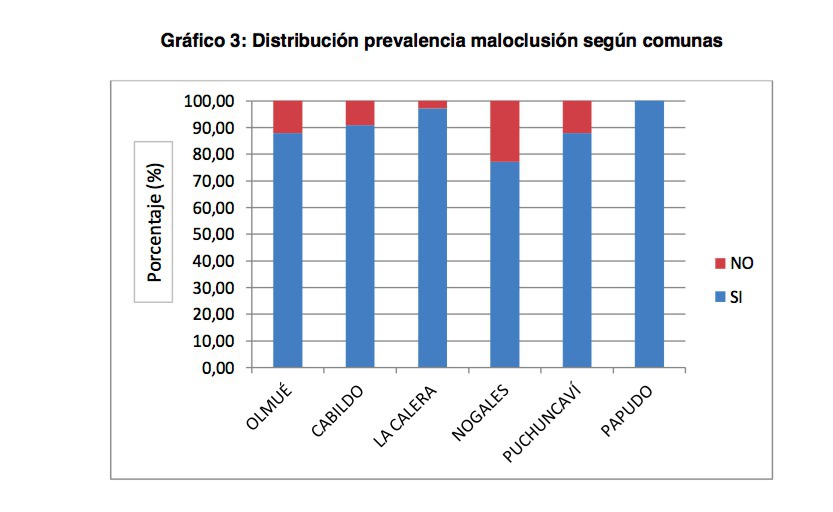
Methods: Observational - Transversal Study. We studied 12-year-old adolescents beneficiary of SSVQ. Inclusion criteria: To have complete definitive dentition and 12 years of age, exclusion criteria: They do not have to be beneficiary of SSVQ, previous or current orthodontic treatment and to present any type of syndrome. A stratified sampling was carried out with proportional allocation by districts studying with the Index of orthodontic treatment need (IOTN) a total of 176 adolescents belonging to 6 districts of the SSVQ (Olmué, Cabildo, La Calera, Nogales, Puchuncaví and Papudo).
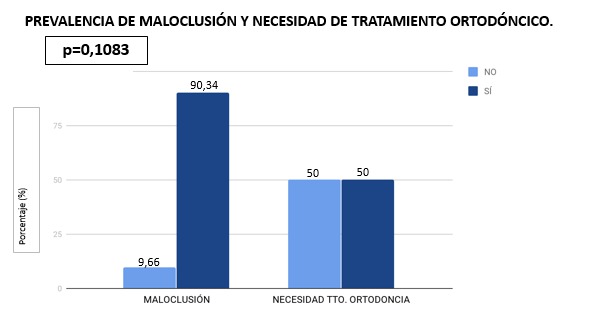
Results: The prevalence of bad occlusion and orthodontic treatment need, according to IOTN is 90.34% and 50%, respectively.
- The clinical priority of adolescents who present a need for orthodontic treatment, according to IOTN is: High 86.36%, intermediate 7.95% and low 5.68%.
- The most common WMDs are: presence of gyroversions (86.93%), ectopic teeth (42.05%), deviation of the upper and lower line to the left (18.75% and 30.68%, respectively) decreasing bite (18.18%), Edge to edge bite uni or posterior bilateral 11.33%, overbite (7.95%) and posterior cross bite uni or bilateral 6.25%.
Conclusions: There is a high prevalence of bad occlusion and orthodontic treatment in 12-year-old adolescents belonging to the SSVQ beneficiary districts, the latter being 1: 1. In relation to bad occlusion, although not all need treatment of corrective orthodontics, may require an interceptive orthodontic treatment. The results obtained should serve as a concern to the SSVQ, being able to extend the coverage of orthodontists due to the large number of patients requiring priority treatment and, at the same time, to promote the interception of bad occlusion and preventive actions to reduce the need for treatment optimizing public resources.
Methods: Observational - Transversal Study. We studied 12-year-old adolescents beneficiary of SSVQ. Inclusion criteria: To have complete definitive dentition and 12 years of age, exclusion criteria: They do not have to be beneficiary of SSVQ, previous or current orthodontic treatment and to present any type of syndrome. A stratified sampling was carried out with proportional allocation by districts studying with the Index of orthodontic treatment need (IOTN) a total of 176 adolescents belonging to 6 districts of the SSVQ (Olmué, Cabildo, La Calera, Nogales, Puchuncaví and Papudo).
Results: The prevalence of bad occlusion and orthodontic treatment need, according to IOTN is 90.34% and 50%, respectively.
- The clinical priority of adolescents who present a need for orthodontic treatment, according to IOTN is: High 86.36%, intermediate 7.95% and low 5.68%.
- The most common WMDs are: presence of gyroversions (86.93%), ectopic teeth (42.05%), deviation of the upper and lower line to the left (18.75% and 30.68%, respectively) decreasing bite (18.18%), Edge to edge bite uni or posterior bilateral 11.33%, overbite (7.95%) and posterior cross bite uni or bilateral 6.25%.
Conclusions: There is a high prevalence of bad occlusion and orthodontic treatment in 12-year-old adolescents belonging to the SSVQ beneficiary districts, the latter being 1: 1. In relation to bad occlusion, although not all need treatment of corrective orthodontics, may require an interceptive orthodontic treatment. The results obtained should serve as a concern to the SSVQ, being able to extend the coverage of orthodontists due to the large number of patients requiring priority treatment and, at the same time, to promote the interception of bad occlusion and preventive actions to reduce the need for treatment optimizing public resources.