IADR Abstract Archives
Gloss Retention of CAD/CAM and Conventional Materials After Chemical/Mechanical Degradation
Objectives: Three-dimensional (3D) printed composite resins have recently become a topic of interest for permanent restoration in clinical settings with its advantage in terms of production efficiency and cost-effectiveness. However, the evidence of their surface gloss retention after exposure to chemical and mechanical degradation in the oral environment is still missing. Thus, this study aims to evaluate the surface gloss of 3D-printed composite resin, CAD/CAM materials and light-curing composite resins for direct restoration after the in vitro degradation simulation by chemical and mechanical methods.
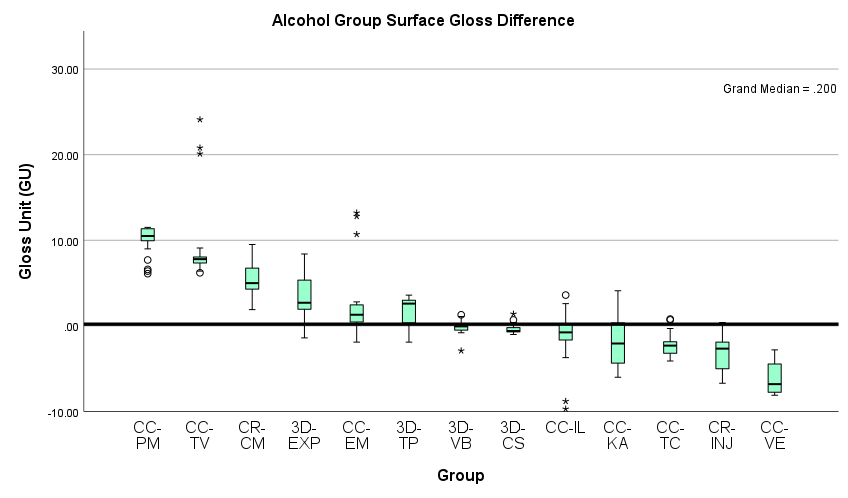
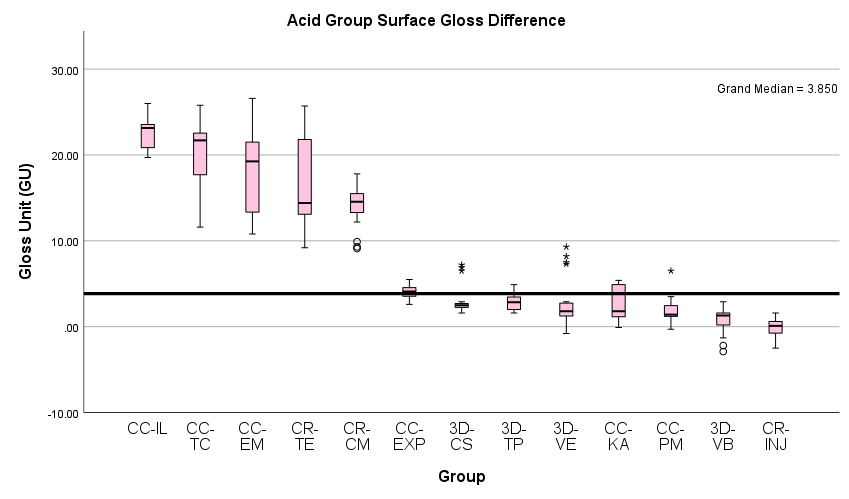
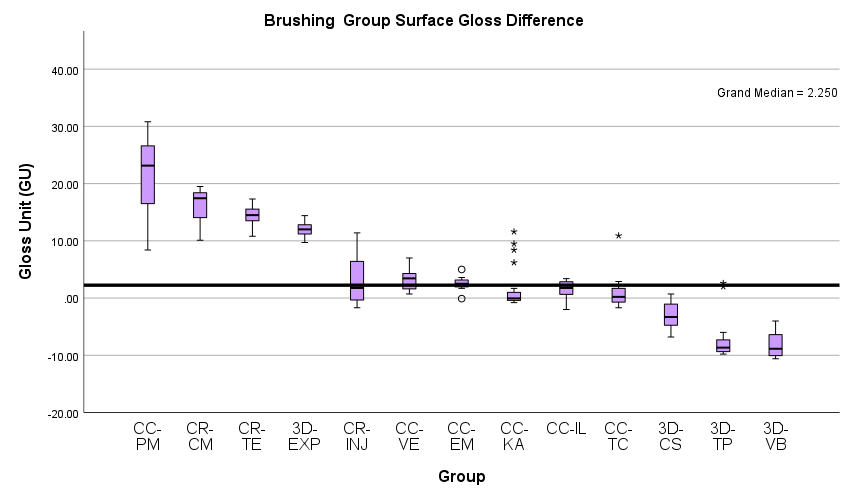
Methods: 416 specimens were prepared from 4 different 3D-printed composite resins (Brilliant-Print-Experimental, Crowntec and VarseoSmile-Crown-Plus, Temp-PRINT), 6 subtractive CAD/CAM materials (Tetric-CAD, Katana-Avencia, Vita-Enamic, Telio-CAD, IPS-e.max-CAD, Initial-Lisi-Block) and 3 light-curing composites for direct restoration (Tetric-EvoCeram, Clearfill-Majesty-ES-2-Classic and G-ænial-Universal-Injectable) and polished with abrasive paper (600,1200,2400,4000). The samples were then measured for gloss value (Novo-Curve) with 3 points per 1 sample, at the same point, each time turning 120 degrees. Four surface treatments including water, 75% Alcohol, Acid (Elmex-Gelée) and Mechanical Brushing were applied to the specimens for an hour. They were then measured for gloss value and the ΔGU data were statistically analyzed between each surface treatment group and then between each material group (Independent-Samples Kruskal-Wallis One-way ANOVA Test).
Results: Initial result demonstrates that the e.max-CAD, Initial-Lisi-Block and Tetric-CAD from acid aging and Telio-CAD from brushing group show ΔGU above 17.6 (gloss value difference detectable by at least 50% of observers). The rest of experiment groups present ΔGU value below 17.6. Statistical tests show significant differences between initial and final gloss value for all materials and aging groups.
Conclusions: The investigated commercially-available 3D-printed composite resins may present acceptable gloss retention after in vitro chemical and mechanical degradation. Their gloss retention property are similar to CAD/CAM materials and light-curing composite resins for direct restoration.
Methods: 416 specimens were prepared from 4 different 3D-printed composite resins (Brilliant-Print-Experimental, Crowntec and VarseoSmile-Crown-Plus, Temp-PRINT), 6 subtractive CAD/CAM materials (Tetric-CAD, Katana-Avencia, Vita-Enamic, Telio-CAD, IPS-e.max-CAD, Initial-Lisi-Block) and 3 light-curing composites for direct restoration (Tetric-EvoCeram, Clearfill-Majesty-ES-2-Classic and G-ænial-Universal-Injectable) and polished with abrasive paper (600,1200,2400,4000). The samples were then measured for gloss value (Novo-Curve) with 3 points per 1 sample, at the same point, each time turning 120 degrees. Four surface treatments including water, 75% Alcohol, Acid (Elmex-Gelée) and Mechanical Brushing were applied to the specimens for an hour. They were then measured for gloss value and the ΔGU data were statistically analyzed between each surface treatment group and then between each material group (Independent-Samples Kruskal-Wallis One-way ANOVA Test).
Results: Initial result demonstrates that the e.max-CAD, Initial-Lisi-Block and Tetric-CAD from acid aging and Telio-CAD from brushing group show ΔGU above 17.6 (gloss value difference detectable by at least 50% of observers). The rest of experiment groups present ΔGU value below 17.6. Statistical tests show significant differences between initial and final gloss value for all materials and aging groups.
Conclusions: The investigated commercially-available 3D-printed composite resins may present acceptable gloss retention after in vitro chemical and mechanical degradation. Their gloss retention property are similar to CAD/CAM materials and light-curing composite resins for direct restoration.