IADR Abstract Archives
Effect of Buccal Cusp Coverage on Restored Non-Vital Premolars
Objectives: When restoring root-canal treated premolars, the decision of the position of the buccal margin and the amount of cusp reduction is often driven by esthetic considerations. However, the impact of the cavity configurationon on mechanical strength should also be considered. Therefore, this study assessed the effect of different levels of buccal cusp reduction on marginal adaptation and fracture strength of root-canal treated premolars restored with CAD/CAM composite endocrowns, a direct composite restoration being used as control.
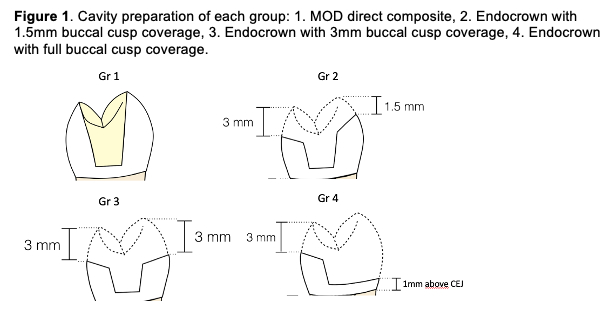
Methods: 40 endodontically-treated premolars were restored and divided into four groups (n=10): 1) MOD direct resin composite restoration with no cusp reduction, 2) Endocrown with buccal cusp coverage of 1.5 mm, 3) endocrown with buccal cusp coverage of 3 mm and 4) endocrown with full buccal cusp coverage (Figure 1). The materials used were a micro hybrid resin composite (Brilliant Everglow) for direct restoration and a CAD/CAM composite block for the endocrowns, (Brilliant Crios) combined with a universal adhesive system (One Coat 7 Universal) as luting agent. Marginal adaptation of the restorations before and after thermo-mechanical loading was evaluated by semi-quantitative SEM analysis. Samples were then subjected to static loading until fracture. The results were statistically evaluated by non-parametric tests, significance level set at 0.05.
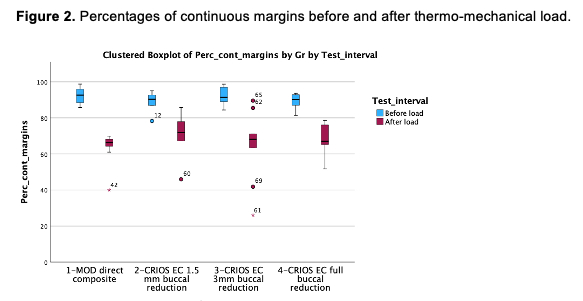
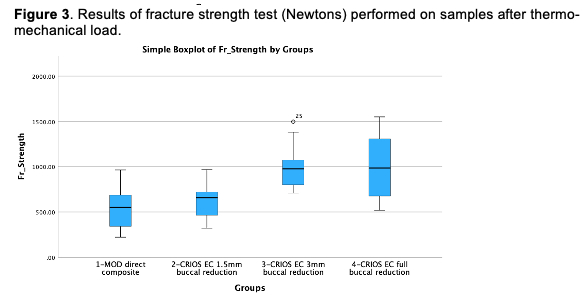
Results: No significant differences in marginal adaptation were observed between groups both before and after loading (Figure 2). MOD direct composites (Median 552.5 N) and endocrowns with buccal cusp coverage of 1.5 mm (Median 658.5 N) presented significantly lower values of fracture strength than endocrowns with 3mm (Median 977 N) or full cuspal reduction (Median 985.5 N) (Figure 3).
Conclusions: Although marginal adaptation of MOD direct restorations was not significantly different than endocrowns, resistance to fracture was directly related to the level of cusp coverage. 3mm or full cusp reduction appear to improve the fracture strength. On the contrary, comparable fracture strength were observed between a buccal cusp reduction of 1.5mm and a direct composite without cusp reduction.
We thank Mrs Isaline Rossier and Mrs Luciana Caseiro for their valuable help.
Methods: 40 endodontically-treated premolars were restored and divided into four groups (n=10): 1) MOD direct resin composite restoration with no cusp reduction, 2) Endocrown with buccal cusp coverage of 1.5 mm, 3) endocrown with buccal cusp coverage of 3 mm and 4) endocrown with full buccal cusp coverage (Figure 1). The materials used were a micro hybrid resin composite (Brilliant Everglow) for direct restoration and a CAD/CAM composite block for the endocrowns, (Brilliant Crios) combined with a universal adhesive system (One Coat 7 Universal) as luting agent. Marginal adaptation of the restorations before and after thermo-mechanical loading was evaluated by semi-quantitative SEM analysis. Samples were then subjected to static loading until fracture. The results were statistically evaluated by non-parametric tests, significance level set at 0.05.
Results: No significant differences in marginal adaptation were observed between groups both before and after loading (Figure 2). MOD direct composites (Median 552.5 N) and endocrowns with buccal cusp coverage of 1.5 mm (Median 658.5 N) presented significantly lower values of fracture strength than endocrowns with 3mm (Median 977 N) or full cuspal reduction (Median 985.5 N) (Figure 3).
Conclusions: Although marginal adaptation of MOD direct restorations was not significantly different than endocrowns, resistance to fracture was directly related to the level of cusp coverage. 3mm or full cusp reduction appear to improve the fracture strength. On the contrary, comparable fracture strength were observed between a buccal cusp reduction of 1.5mm and a direct composite without cusp reduction.
We thank Mrs Isaline Rossier and Mrs Luciana Caseiro for their valuable help.