IADR Abstract Archives
A New Device to Distalize Maxillary Molar With High Pseudoelastic Forces.
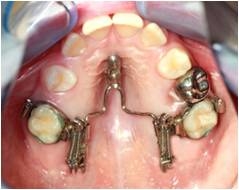
Objectives: Distalization of upper molars, followed by maximal anchorage, belong to the most important orthodontic objectives. Various non-compliance devices have been developed to solve this therapeutic problem without the risk of inverse forces, based on skeletal anchoring. These requirements characterise the Longslider, a modification of the Beneslider, by two mini-implants placed along the median palatine suture (Figure 1). The active elements are pseudoelastic NiTi springs with high constant forces up to gf 600 (5,88N) to overcome slider friction and automatic deactivation at the end of the desired distalization extent. The present study explores the sagittal dental movement of the first and second molars within an orthodontic treatment with fixed appliances (vestibular technique).
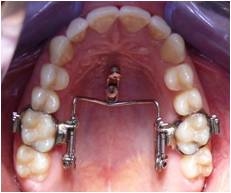
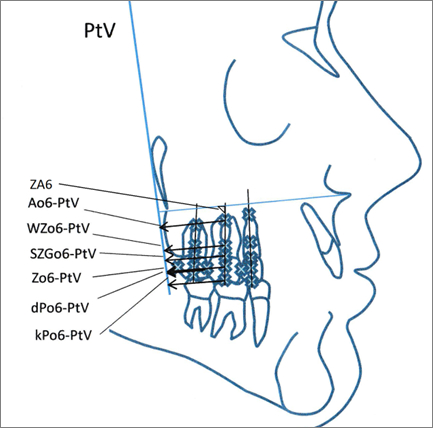
Methods: 38 patients with symmetric class II malocclusion (24 female, 14 male; age 10,3 to 53,8, mean: 17,4 years) were collected for clinical evaluation. The facial type of 73,7% was moderate retrognathic and of 26,3% orthognathic. Cephalograms were taken before and after orthodontic treatment, all including molar distalization. Two groups were divided refered to the eruption stage of the second molar: Group 1 include patients before his eruption (mean age: 13,2 years) (Figure 1), group 2 after his eruption (mean age: 19,5 years) (Figure 2). The extend of distal movements of the upper molars were evaluated with six linear measurements from distal dental points to the pterygoid vertical (Figure 3); statistical evaluation were carried out with the shapiro-wilk-test.
Results: The intended treatment goal was achieved with a class I occlusion between the first upper and lower molars. Distalization of the first molars could be achieved from 1,0 up to 4,8 mm; the desired translational movement differ with a minor distal tipping of 0,9°, bodiliy translation predominates. Between the two groups no significant differences were evident.
Conclusions: The Longslider is a clinically comfortable, safe and effective non-compliance devise for maxillary molar distalization. The high and constant pseudoelastic forces overcome high frictional forces and seems to optimize translatory tooth movement.
Methods: 38 patients with symmetric class II malocclusion (24 female, 14 male; age 10,3 to 53,8, mean: 17,4 years) were collected for clinical evaluation. The facial type of 73,7% was moderate retrognathic and of 26,3% orthognathic. Cephalograms were taken before and after orthodontic treatment, all including molar distalization. Two groups were divided refered to the eruption stage of the second molar: Group 1 include patients before his eruption (mean age: 13,2 years) (Figure 1), group 2 after his eruption (mean age: 19,5 years) (Figure 2). The extend of distal movements of the upper molars were evaluated with six linear measurements from distal dental points to the pterygoid vertical (Figure 3); statistical evaluation were carried out with the shapiro-wilk-test.
Results: The intended treatment goal was achieved with a class I occlusion between the first upper and lower molars. Distalization of the first molars could be achieved from 1,0 up to 4,8 mm; the desired translational movement differ with a minor distal tipping of 0,9°, bodiliy translation predominates. Between the two groups no significant differences were evident.
Conclusions: The Longslider is a clinically comfortable, safe and effective non-compliance devise for maxillary molar distalization. The high and constant pseudoelastic forces overcome high frictional forces and seems to optimize translatory tooth movement.