IADR Abstract Archives
Comparative Evaluation of Wettability Between Alginate and Silicone Impression Materials
Objectives: In Japan, Aroma Injection (ARI), paste-type alginate impression material filled in a cartridge, is available for combined impressions that can take precise impressions. Silicone impression materials are generally used for obtaining a precise impression to make a prosthesis. An impression taken by silicone impression materials has high accuracy, but because they are hydrophobic, there is a risk of re-impression if moisture protection is neglected. On the other hand, ARI has the same accuracy as silicone impression material and is hydrophilic. The aim of this study was to evaluate the wettability of ARI and silicone impression materials.
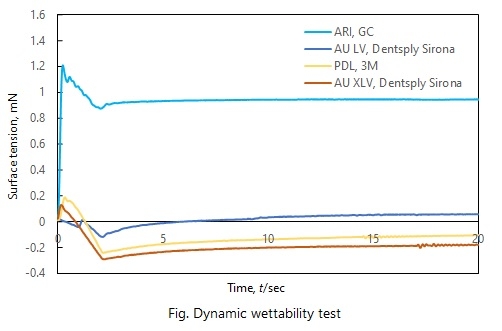
Methods: ARI (GC, Japan), Paradigm Light Body (PDL: 3M, USA), Aquasil Ultra LV, XLV (AU LV, AU XLV: Dentsply Sirona, USA) were used. Dynamic wettability and contact angle were measured by the following methods. For the dynamic wettability, the surface tension before setting was measured 1 minute after the start of mixing of the pastes. Regarding the contact angle, each material was flattened and 2.0 μL of distilled water was dropped onto the surface of the material 1 minute after the start of mixing of the pastes, and the contact angle was measured 10, 30 and 60 seconds after the dropping.
Results: From the results of dynamic wettability evaluation, it was clarified that ARI had the highest hydrophilicity before setting of the material. In addition, from the results of the contact angle evaluation, ARI showed the smallest contact angle, and it was clarified that the hydrophilicity of ARI was significantly higher than that of silicone impression materials evaluated in this study.
Conclusions: ARI is more hydrophilic than the silicone impression materials and can take a precise impression even if exudate remains, suggesting that the risk of clinical failure is reduced by using ARI.
Methods: ARI (GC, Japan), Paradigm Light Body (PDL: 3M, USA), Aquasil Ultra LV, XLV (AU LV, AU XLV: Dentsply Sirona, USA) were used. Dynamic wettability and contact angle were measured by the following methods. For the dynamic wettability, the surface tension before setting was measured 1 minute after the start of mixing of the pastes. Regarding the contact angle, each material was flattened and 2.0 μL of distilled water was dropped onto the surface of the material 1 minute after the start of mixing of the pastes, and the contact angle was measured 10, 30 and 60 seconds after the dropping.
Results: From the results of dynamic wettability evaluation, it was clarified that ARI had the highest hydrophilicity before setting of the material. In addition, from the results of the contact angle evaluation, ARI showed the smallest contact angle, and it was clarified that the hydrophilicity of ARI was significantly higher than that of silicone impression materials evaluated in this study.
Conclusions: ARI is more hydrophilic than the silicone impression materials and can take a precise impression even if exudate remains, suggesting that the risk of clinical failure is reduced by using ARI.