IADR Abstract Archives
Flexible Pinpoint Electrolysis Unit for Electrochemical Disinfection of Root-canal
Objectives: Invention of flexible pinpoint electrolysis unit for electrochemical disinfection of root-canals by using of conductive diamond-powder/polymer composites or platinum-modified titanium (Pt/Ti) electrodes.
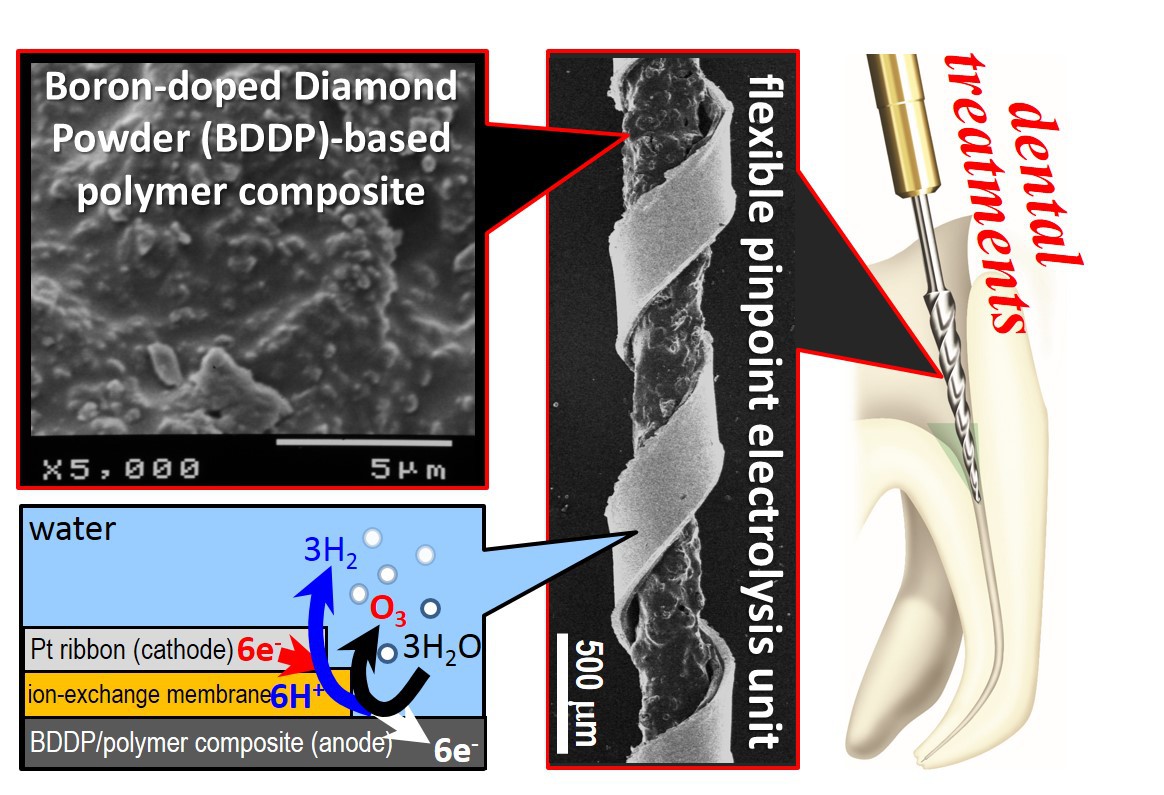
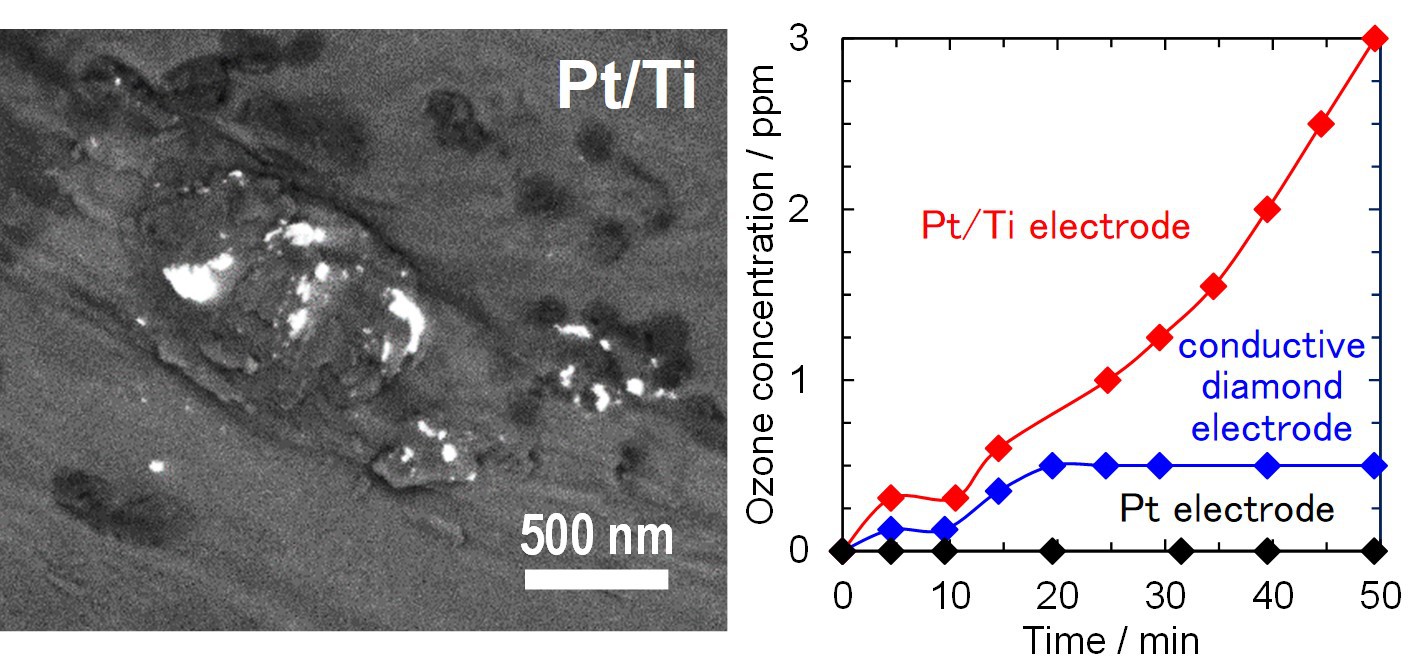
Methods: The unit with conductive diamond-powder/polymer composites was prepared as descrived previously (Electrochemistry Communications 2016, 68, 49-53, image 1). When DC 7.5V was applied between the Ti-wire and the Pt-ribbon in the root canal, ozone and oxidative intermediates were generated by electrolysis. Typical in vitro assessment of the unit was also carried out as descrived previously. On the other hand, The Pt/Ti electrode was prepared by our original method, multiple electrostrike method as follows. A vibrating Pt wire was rubbed over a titanium electrode surface with a potential of 7.5 V. Molten Pt metal particles ranging from several nanometers to submicrometers were sprayed onto the Ti surface (image 2 left, bright spots). Electrochemical ozone generation activities of the electrodes were evaluated in an acryl sealed 36 L box. Ozone gas was generated potentiostatically (5 V) in H2SO4 and dispersed in the box by a fan.
Results: Electrolysis by the unit with conductive diamond-powder/polymer composites showed almost the same sterilization ability as conventional treatment in in vitro assessment in the root-canal of human teeth. However, SEM images indicated that though conventional treatment decalcifies dentin and exposes collagen tissues, the electrolysis cause no damage against root-canal surface. On the other hand, ozone generation activity of the Pt/Ti electrode was found to be much higher than that of the conductive diamond or the Pt electrode (image 2 right).
Conclusions: The superiority of simple and easy-to-handle pinpoint electrolysis units, in terms of the flexibility, durability, and disinfection activity was demonstrated. This research is attractive to develop a practical unit for dental treatment. We are grateful to Dr. T. Kondo (Tokyo University of Science) for the experiments, suggestions for developing research ideas, and helpful advices.
Methods: The unit with conductive diamond-powder/polymer composites was prepared as descrived previously (Electrochemistry Communications 2016, 68, 49-53, image 1). When DC 7.5V was applied between the Ti-wire and the Pt-ribbon in the root canal, ozone and oxidative intermediates were generated by electrolysis. Typical in vitro assessment of the unit was also carried out as descrived previously. On the other hand, The Pt/Ti electrode was prepared by our original method, multiple electrostrike method as follows. A vibrating Pt wire was rubbed over a titanium electrode surface with a potential of 7.5 V. Molten Pt metal particles ranging from several nanometers to submicrometers were sprayed onto the Ti surface (image 2 left, bright spots). Electrochemical ozone generation activities of the electrodes were evaluated in an acryl sealed 36 L box. Ozone gas was generated potentiostatically (5 V) in H2SO4 and dispersed in the box by a fan.
Results: Electrolysis by the unit with conductive diamond-powder/polymer composites showed almost the same sterilization ability as conventional treatment in in vitro assessment in the root-canal of human teeth. However, SEM images indicated that though conventional treatment decalcifies dentin and exposes collagen tissues, the electrolysis cause no damage against root-canal surface. On the other hand, ozone generation activity of the Pt/Ti electrode was found to be much higher than that of the conductive diamond or the Pt electrode (image 2 right).
Conclusions: The superiority of simple and easy-to-handle pinpoint electrolysis units, in terms of the flexibility, durability, and disinfection activity was demonstrated. This research is attractive to develop a practical unit for dental treatment. We are grateful to Dr. T. Kondo (Tokyo University of Science) for the experiments, suggestions for developing research ideas, and helpful advices.