IADR Abstract Archives
Mathematical, Numerical and biomechanical analysis using final element method (FEM) of mandible after treatment with bone substitute materials and loading with implant-supported prostheses
Objectives: The aim of the study was to describe mineralized bone structures of the mandible with use of wavelet application and perform biomechanical analysis with final element method (FEM) in individuals that have been treated with bone substitute materials: Algipore, Bio-Gran, Bio-Oss, Cerasorb, Chron-Os, HA-Biocer and loaded with implant-supported prostheses.
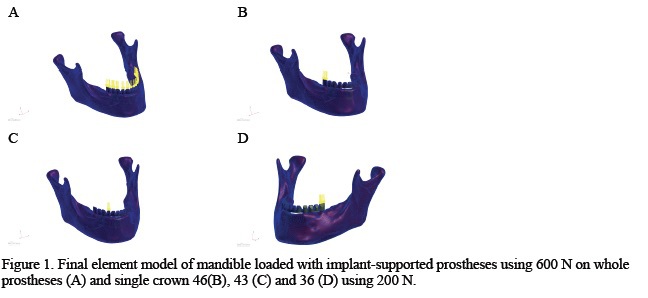
Methods: 70 patients were included to the study, 60 were treated using six different bone substitute materials: Algipore (ALG), Bio-Oss (BVB), Bio-Gran (BAG), HA-Biocer (SHA), Cerasorb (CER), Chron-Os (CHR) and 10 patients, where bone regeneration process was followed without using bone substitute material (NON). The control patient group was mandible bone without defect (REF). The structure of mineralized bone of mandible in surgical area was examined on 490 digital radiological images using discrete wavelet transform for mathematical distribution of radiotexture. This method has been applied to estimate the physical properties of bone (e.g. Young’s modulus) during the period of healing (3, 6, 9, 12, 18, 24 months) of the bony lesion following the use of bone substitute material. A three-dimensional FEM of a mandible with a prostheses supported by four implants was developed (Figure 1). The biomechanical analysis of mandible was performed using MD PATRAN.
Results: The studies helped to estimate physical properties (Youngs' modulus) during a period of healing of bony lesion following the use of biomaterial.
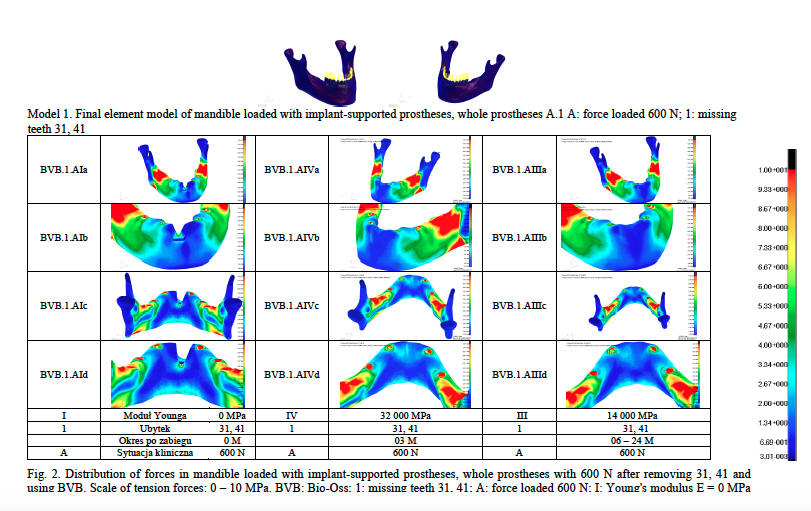
Numerical and biomechanical analysis of mandible after surgical operation with use of six bone substitute materials showed diverse distribution of tension forces compared with control patient group (REF). Bio-Oss (BVB) (Fig. 2) showed already after 3 months (03 M) distribution of forces, which was similar to the one observed in control group (REF). Significant differences in stress, strain, and strain energy densities were found in the comparison of models with bone substitute materials treatment and without (NON). It was observed that loading with implant-supported prostheses leads to high stress concentrations in bone without bone substitute treatment (NON).
Conclusions: In conclusion the numerical analysis might be promising alternative method for selection of treatment material and promising tool for planning of surgical procedure.
Methods: 70 patients were included to the study, 60 were treated using six different bone substitute materials: Algipore (ALG), Bio-Oss (BVB), Bio-Gran (BAG), HA-Biocer (SHA), Cerasorb (CER), Chron-Os (CHR) and 10 patients, where bone regeneration process was followed without using bone substitute material (NON). The control patient group was mandible bone without defect (REF). The structure of mineralized bone of mandible in surgical area was examined on 490 digital radiological images using discrete wavelet transform for mathematical distribution of radiotexture. This method has been applied to estimate the physical properties of bone (e.g. Young’s modulus) during the period of healing (3, 6, 9, 12, 18, 24 months) of the bony lesion following the use of bone substitute material. A three-dimensional FEM of a mandible with a prostheses supported by four implants was developed (Figure 1). The biomechanical analysis of mandible was performed using MD PATRAN.
Results: The studies helped to estimate physical properties (Youngs' modulus) during a period of healing of bony lesion following the use of biomaterial.
Numerical and biomechanical analysis of mandible after surgical operation with use of six bone substitute materials showed diverse distribution of tension forces compared with control patient group (REF). Bio-Oss (BVB) (Fig. 2) showed already after 3 months (03 M) distribution of forces, which was similar to the one observed in control group (REF). Significant differences in stress, strain, and strain energy densities were found in the comparison of models with bone substitute materials treatment and without (NON). It was observed that loading with implant-supported prostheses leads to high stress concentrations in bone without bone substitute treatment (NON).
Conclusions: In conclusion the numerical analysis might be promising alternative method for selection of treatment material and promising tool for planning of surgical procedure.