IADR Abstract Archives
Epoxy-tiglianes Stimulate Keratinocyte Proliferative and Migratory Responses, Enhancing Wound Re-epithelialisation.
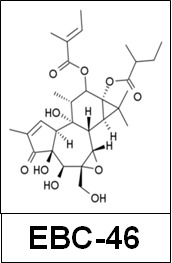
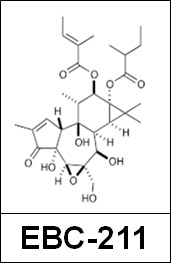
Objectives: The novel epoxy-tiglianes, EBC-46 and EBC-211, occur within seeds of the Fontain’s Blushwood Tree (Fontainea picrosperma), indigenous to Queensland’s tropical rainforest. EBC-46 is being developed by biotechnology company, QBiotics (www.qbiotics.com/), as an anti-cancer pharmaceutical. In clinical studies, EBC-46 stimulates exceptional dermal wound healing responses following tumour destruction, manifested as accelerated wound re-epithelialisation and closure; reminiscent of preferential healing in oral mucosal wounds. As little is known on how epoxy-tiglianes induce this reponse, this study examined their effects on epidermal keratinocyte wound healing responses and the underlying mechanisms of action.
Methods: Immortalized human epidermal keratinocytes (HACATs) were cultured with EBC-46 or EBC-211 (0-100µg/ml). HACAT proliferation and cell cycle analysis were assessed by MTT assay and Draq5/FACS. Migration was assessed using in vitro scratch wounds and Time-Lapse Microscopy. Global gene expression analyses were performed by Microarrays (Human HT-12 v4 Expression BeadChips), with significant differences identified using GeneSpring, and Ingenuity Pathway Analysis elucidating the key pathways involved. Differentially expressed genes were confirmed by protein level analysis (Western blotting, ELISAs, activity assays).
Results: Both EBC-46 and EBC-211 induced significant HACAT cytotoxicity at 100µg/ml, but stimulated significant HACAT proliferation at 0.001-10µg/ml. These epoxy-tiglianes also induced significant HACAT scratch wound closure at 0.001-0.1µg/ml (EBC-46) and 0.001-10µg/ml (EBC-211). Microarray analyses identified key genes differentially expressed in EBC-46 and EBC-211-treated HACATs, which contribute to the stimulatory effects on keratinocyte proliferation and migration. Up-regulated genes included certain keratins (KRT9, KRT13, KRT15, KRT81), positive cell cycle/proliferation regulatory genes (CCNB2, CDKN3, CDCA7, GINS2, KIAA0101); and proteinases (MMP-1, MMP-7, MMP-10). Other keratins were down-regulated (KRT6B, KRT16, KRT17) and many cytokine/growth factor/chemokine-related genes.
Conclusions: These findings provide evidence to explain the enhanced re-epithelialisation responses in epoxy-tigliane-treated skin; and their potential as novel therapeutics for impaired dermal wound healing situations.
Methods: Immortalized human epidermal keratinocytes (HACATs) were cultured with EBC-46 or EBC-211 (0-100µg/ml). HACAT proliferation and cell cycle analysis were assessed by MTT assay and Draq5/FACS. Migration was assessed using in vitro scratch wounds and Time-Lapse Microscopy. Global gene expression analyses were performed by Microarrays (Human HT-12 v4 Expression BeadChips), with significant differences identified using GeneSpring, and Ingenuity Pathway Analysis elucidating the key pathways involved. Differentially expressed genes were confirmed by protein level analysis (Western blotting, ELISAs, activity assays).
Results: Both EBC-46 and EBC-211 induced significant HACAT cytotoxicity at 100µg/ml, but stimulated significant HACAT proliferation at 0.001-10µg/ml. These epoxy-tiglianes also induced significant HACAT scratch wound closure at 0.001-0.1µg/ml (EBC-46) and 0.001-10µg/ml (EBC-211). Microarray analyses identified key genes differentially expressed in EBC-46 and EBC-211-treated HACATs, which contribute to the stimulatory effects on keratinocyte proliferation and migration. Up-regulated genes included certain keratins (KRT9, KRT13, KRT15, KRT81), positive cell cycle/proliferation regulatory genes (CCNB2, CDKN3, CDCA7, GINS2, KIAA0101); and proteinases (MMP-1, MMP-7, MMP-10). Other keratins were down-regulated (KRT6B, KRT16, KRT17) and many cytokine/growth factor/chemokine-related genes.
Conclusions: These findings provide evidence to explain the enhanced re-epithelialisation responses in epoxy-tigliane-treated skin; and their potential as novel therapeutics for impaired dermal wound healing situations.