IADR Abstract Archives
EFFECTIVENESS OF DEXAMETHASONE IN TREATMENT OF ORAL MUCOCELE: A CASE SERIES.
Objectives: We evaluated the effectiveness of dexamethasone injections in treatment of oral mucocele.
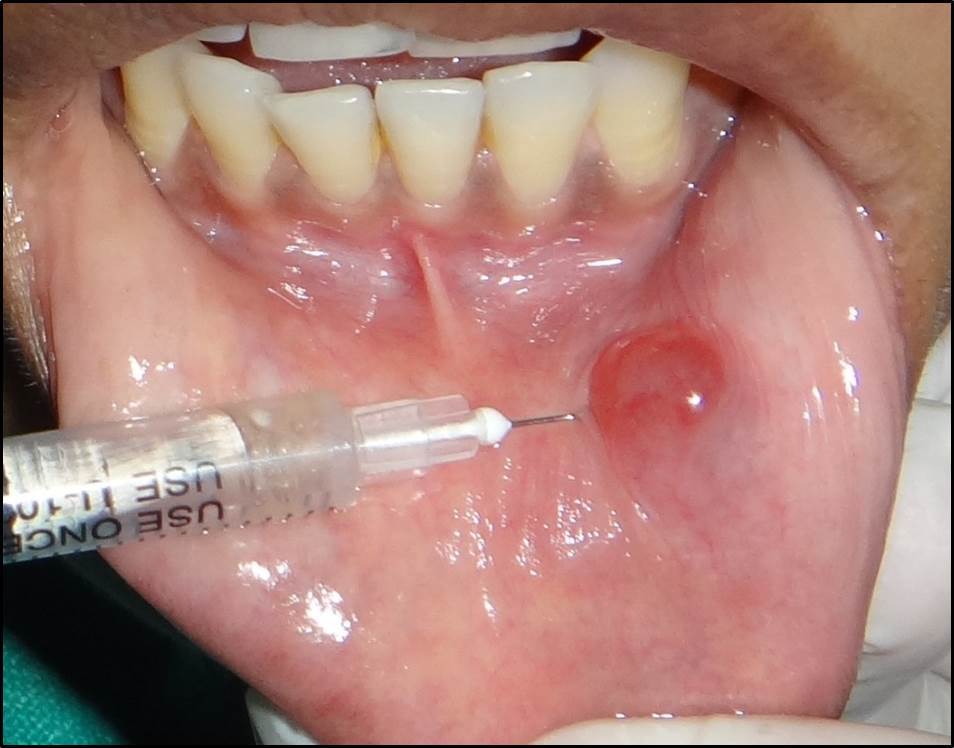
Methods: Nine patients with mucocele and one with ranula were treated with two having reoccurrence after surgery in our department. Diagnosing was made by on and off lesion, non progressing, history of trauma, dome-shaped, smooth surface, soft to firm consistency, non reducible and non pulsatile with mucus fluid on aspiration and sent for cytopatholigical examination.Eight were treated with intralesional and ranula was treated with combination of micromarsupialization and intralesional injection.
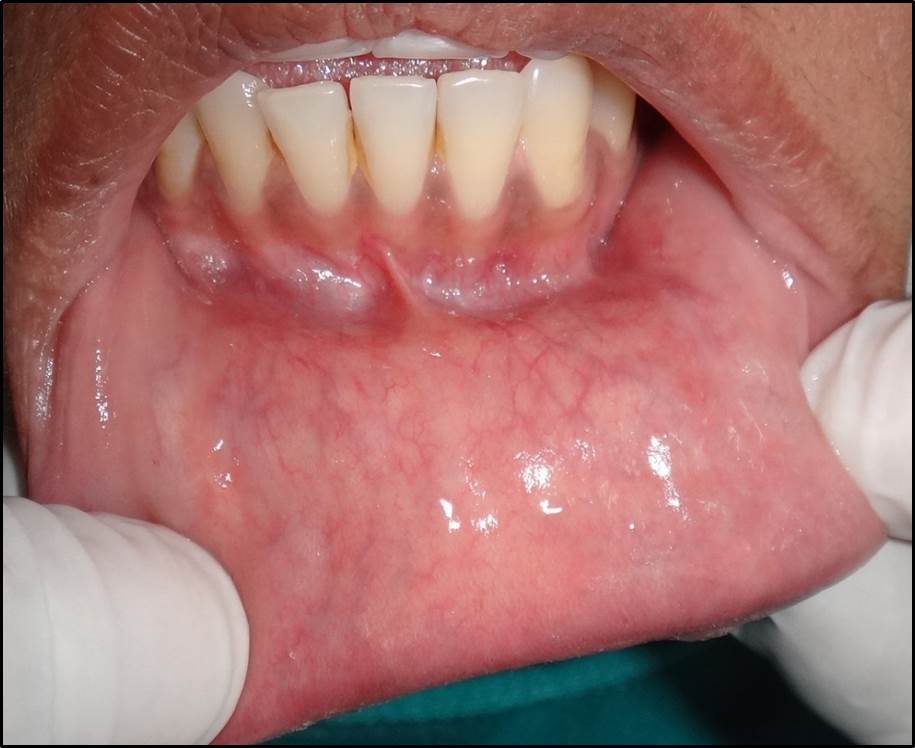
Results: Intalesional dexamethasone 4mg/ml 0.2 to 1 ml on weekly under topical anesthesia. We injected 2 to 4 sessions over 14 or 28 days, depending on the clinical response. Complete healing was seen in seven patients, without recurrences for a mean time of 8 months (range, 4-12 months) one patient choosed to under go surgey and one was lost to follow up after 1 month.
Conclusions: Intralesional dexamethasone can be used as an alternative to surgery in patients who are anxious about surgery procedure and in case of reccurence after surgery. The patient compliance is good, as the treatment is done under topical anesthesia specially in pediatric patient. The multiple follow up is one of the disadvantage.
Methods: Nine patients with mucocele and one with ranula were treated with two having reoccurrence after surgery in our department. Diagnosing was made by on and off lesion, non progressing, history of trauma, dome-shaped, smooth surface, soft to firm consistency, non reducible and non pulsatile with mucus fluid on aspiration and sent for cytopatholigical examination.Eight were treated with intralesional and ranula was treated with combination of micromarsupialization and intralesional injection.
Results: Intalesional dexamethasone 4mg/ml 0.2 to 1 ml on weekly under topical anesthesia. We injected 2 to 4 sessions over 14 or 28 days, depending on the clinical response. Complete healing was seen in seven patients, without recurrences for a mean time of 8 months (range, 4-12 months) one patient choosed to under go surgey and one was lost to follow up after 1 month.
Conclusions: Intralesional dexamethasone can be used as an alternative to surgery in patients who are anxious about surgery procedure and in case of reccurence after surgery. The patient compliance is good, as the treatment is done under topical anesthesia specially in pediatric patient. The multiple follow up is one of the disadvantage.