IADR Abstract Archives
bMSCs-Osteogenesis/osteoclasia Toward Bone-implant Interaction is Manipulated By Macrophages On Nanostructured-Ti-surfaces
Objectives: The interaction among biomaterials, macrophages, and bMSCs play a vital role which contributes to the clinical outcome of implant. Although it has been well reported that bMSC osteogenic differentiation or macrophage osteoclastic differentiation can be manipulated by the biomaterial surface nanostructure respectively, the interaction among them has not been well elucidated. The objective of this study is to clarify the the mutual influence of implant surface nanostructure, macrophage inflammatory response and bMSCs osteogenic differentiation as well as bMSCs retro-regulative effects toward macrophage osteoclastic differentiation
Methods: F+-based anodization method was used to construct TiO2 nano-structured surfaces and specimens were grouped by anodization voltages(polished Ti, 5V and 20V) and labeled as P, NT5 and NT20 respectively, which were examed by field emission scanning electronic microscopy(FE-SEM). Human macrophages were seeded on NTs surfaces.The macrophages culture supernatent on NTs surfaces of were collected and used for conditioned medium(NTs-CMs).Using a co-culture system and a set of methods, the osteogenic behaviors and osteoclastogenesis-related secretions(sRANKL/OPG/M-CSF) of human bMSCs on NTs surfaces in presence/absence of NTs-CMs were analyzed.The formation of multi-nuclei gaint cells(MGCs) and osteoclasts were also inspected with the stimulation of bMSCs-derived sRANKL/OPG/M-CSF.
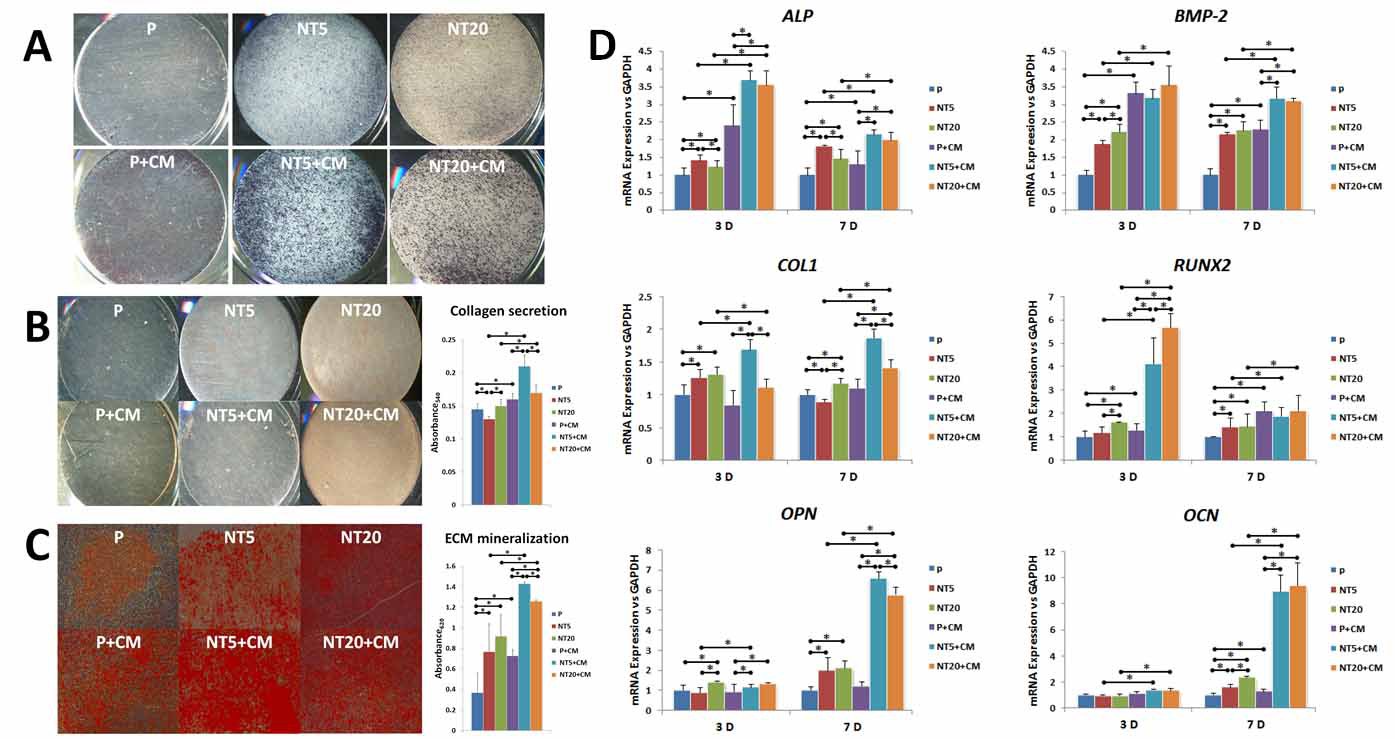
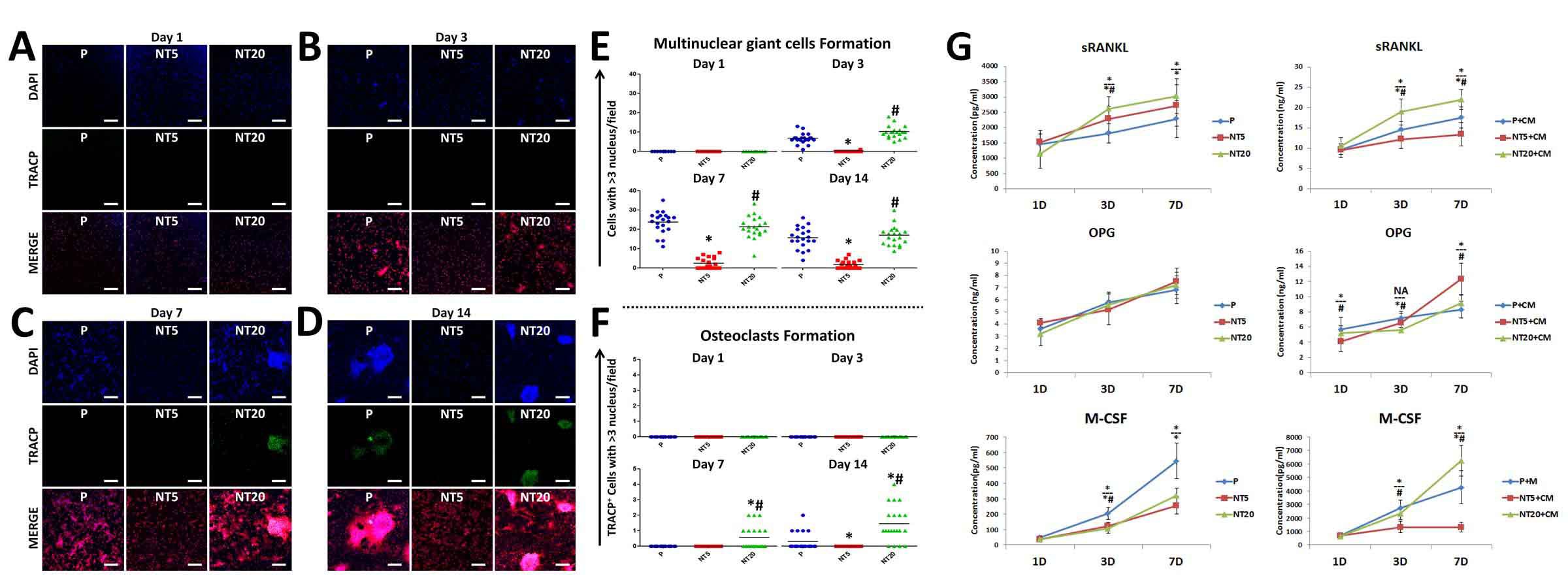
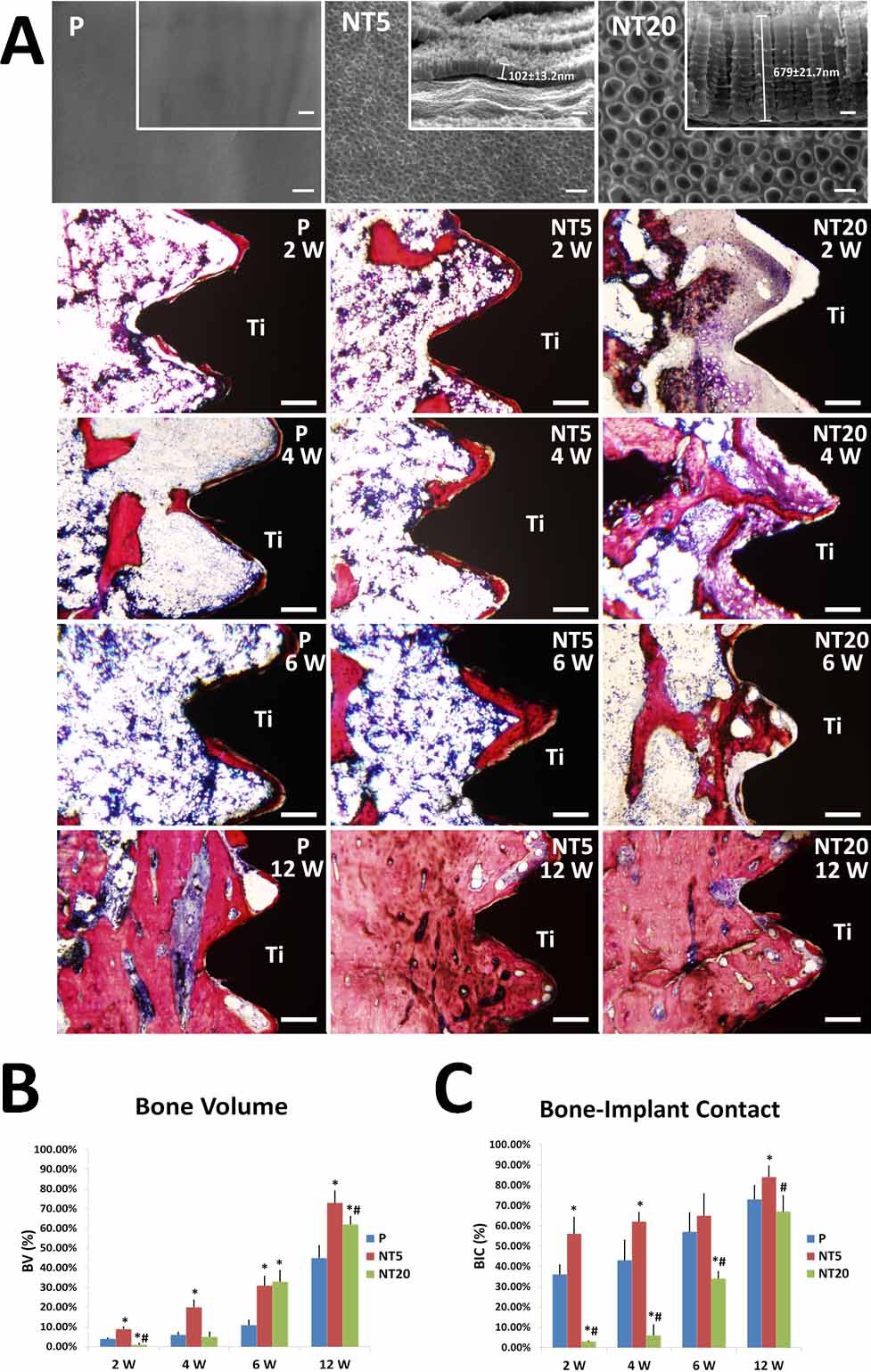
Results: Macrophages on NT5 and NT20 surface showed divergent secretion profiles of cytokines.Though bMSCs showed similar osteogenic behaviors on NT5 and NT20 surfaces in both blank medium and NTs-CMs, the collagen synthesis and ECM mineralization were partly impeded on NT20 in NT20-CM(Fig.1), and the bMSCs secretions on NT20 in NT20-CM elicited remarkable MGCs and osteoclasts formation compared to their counterpart on NT5 in NT5-CM with almost no osteoclast formation(Fig.2).In vivo evidence showed that the mineralized bone formation was significantly delayed around NT20 implant compared to NT5 implant(Fig.3).
Conclusions: The profile of macrophage secretions and bMSCs osteoclastic retroegulative cytokines provide a systemic framework for analyzing and predicting the performance of implant, as well as a prospective approach for improving implant osseointegration via immuno-regulation.
Methods: F+-based anodization method was used to construct TiO2 nano-structured surfaces and specimens were grouped by anodization voltages(polished Ti, 5V and 20V) and labeled as P, NT5 and NT20 respectively, which were examed by field emission scanning electronic microscopy(FE-SEM). Human macrophages were seeded on NTs surfaces.The macrophages culture supernatent on NTs surfaces of were collected and used for conditioned medium(NTs-CMs).Using a co-culture system and a set of methods, the osteogenic behaviors and osteoclastogenesis-related secretions(sRANKL/OPG/M-CSF) of human bMSCs on NTs surfaces in presence/absence of NTs-CMs were analyzed.The formation of multi-nuclei gaint cells(MGCs) and osteoclasts were also inspected with the stimulation of bMSCs-derived sRANKL/OPG/M-CSF.
Results: Macrophages on NT5 and NT20 surface showed divergent secretion profiles of cytokines.Though bMSCs showed similar osteogenic behaviors on NT5 and NT20 surfaces in both blank medium and NTs-CMs, the collagen synthesis and ECM mineralization were partly impeded on NT20 in NT20-CM(Fig.1), and the bMSCs secretions on NT20 in NT20-CM elicited remarkable MGCs and osteoclasts formation compared to their counterpart on NT5 in NT5-CM with almost no osteoclast formation(Fig.2).In vivo evidence showed that the mineralized bone formation was significantly delayed around NT20 implant compared to NT5 implant(Fig.3).
Conclusions: The profile of macrophage secretions and bMSCs osteoclastic retroegulative cytokines provide a systemic framework for analyzing and predicting the performance of implant, as well as a prospective approach for improving implant osseointegration via immuno-regulation.