IADR Abstract Archives
Pairwise Comparison of the Initial Hydrophilicity of Impression Materials
Objectives: To investigate whether two newly developed experimental super-quick set polyether materials (one light and one medium bodied) are more hydrophilic than vinyl polysiloxane (VPS) materials in the unset stage.
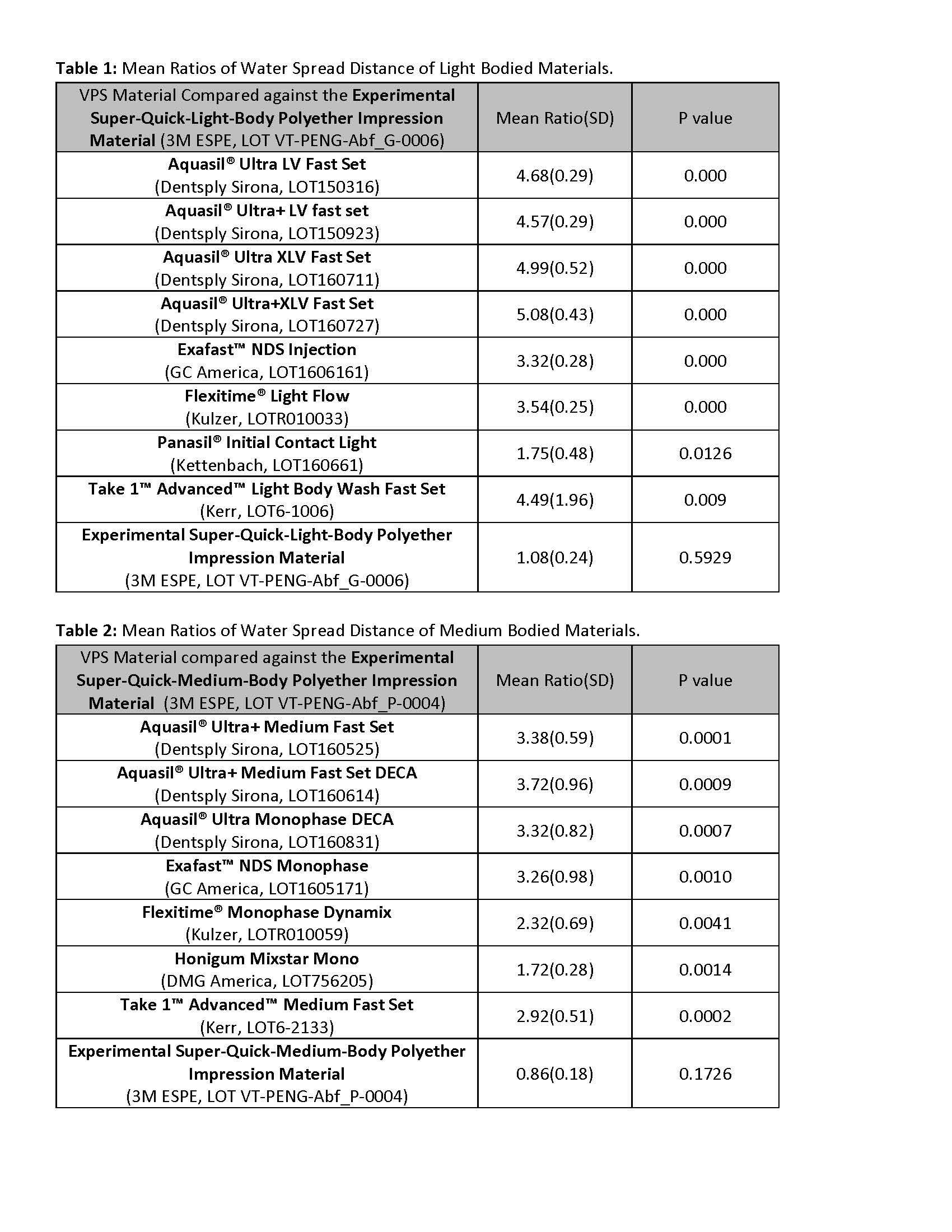
Methods: Using pairwise comparisons, eight light bodied VPS materials were tested against the experimental Super-Quick-Light-Body polyether material (n=5) (Table 1). Seven medium bodied VPS materials were compared against the experimental Super-Quick-Medium-Body polyether material (n=5) (Table 2). The experimental polyether materials were tested against themselves as controls (n=5). Each pair of samples was created simultaneously by: mixing both materials at once, and then smearing a 0.2mm layer of each material across the surface of two separate glass slides. The slides are subsequently placed side-by-side, creating an interface between the two impression materials. 45s after the start of mixing of both materials, a 5µl drop of water was placed on the interface of the two materials by a DropShape-Analysis-System (DSA-30, Kruess). 2s after the drop touched the surface of the impression materials, the horizontal spreading distance of water on both materials was measured. A standard ratio was calculated using the formula: ratio=experimental polyether material water spread distance/VPS material water spread distance (ratio=1, represents equal water spread distance). The one sample t-test was used to compare the log of the ratios to the log of 1.
Results: Mean ratios of water spread distance of all material combinations, except for the controls, were statistically significantly different than 1 (p<0.05) (Table 1, Table 2).
Conclusions: The experimental Super-Quick-Light-Body polyether impression material is more hydrophilic in the unset stage than the VPS light body impression materials tested (ratios>1, p<0.05). The experimental Super-Quick-Medium-Body polyether impression material is more hydrophilic in the unset stage than the VPS medium body impression materials tested (ratios>1, p<0.05).
Methods: Using pairwise comparisons, eight light bodied VPS materials were tested against the experimental Super-Quick-Light-Body polyether material (n=5) (Table 1). Seven medium bodied VPS materials were compared against the experimental Super-Quick-Medium-Body polyether material (n=5) (Table 2). The experimental polyether materials were tested against themselves as controls (n=5). Each pair of samples was created simultaneously by: mixing both materials at once, and then smearing a 0.2mm layer of each material across the surface of two separate glass slides. The slides are subsequently placed side-by-side, creating an interface between the two impression materials. 45s after the start of mixing of both materials, a 5µl drop of water was placed on the interface of the two materials by a DropShape-Analysis-System (DSA-30, Kruess). 2s after the drop touched the surface of the impression materials, the horizontal spreading distance of water on both materials was measured. A standard ratio was calculated using the formula: ratio=experimental polyether material water spread distance/VPS material water spread distance (ratio=1, represents equal water spread distance). The one sample t-test was used to compare the log of the ratios to the log of 1.
Results: Mean ratios of water spread distance of all material combinations, except for the controls, were statistically significantly different than 1 (p<0.05) (Table 1, Table 2).
Conclusions: The experimental Super-Quick-Light-Body polyether impression material is more hydrophilic in the unset stage than the VPS light body impression materials tested (ratios>1, p<0.05). The experimental Super-Quick-Medium-Body polyether impression material is more hydrophilic in the unset stage than the VPS medium body impression materials tested (ratios>1, p<0.05).