IADR Abstract Archives
In Vitro Biocompatibility Evaluation of Dental Cements With Titanium Components
Objectives: Residual cement accumulation in subgingival tissue triggers peri-implantitis, which results in bone loss and implant failure. Thus, cement biocompatibility is a critical factor that ensures implant success. The goal of this study was to investigate the cytotoxicity of different dental cement compositions after directly exposing human gingival fibroblast (HGF) and MC3T3-E1 pre-osteoblast cell lines to (i) cement alone and (ii) cement applied on commercially pure titanium (cpTi) specimens.
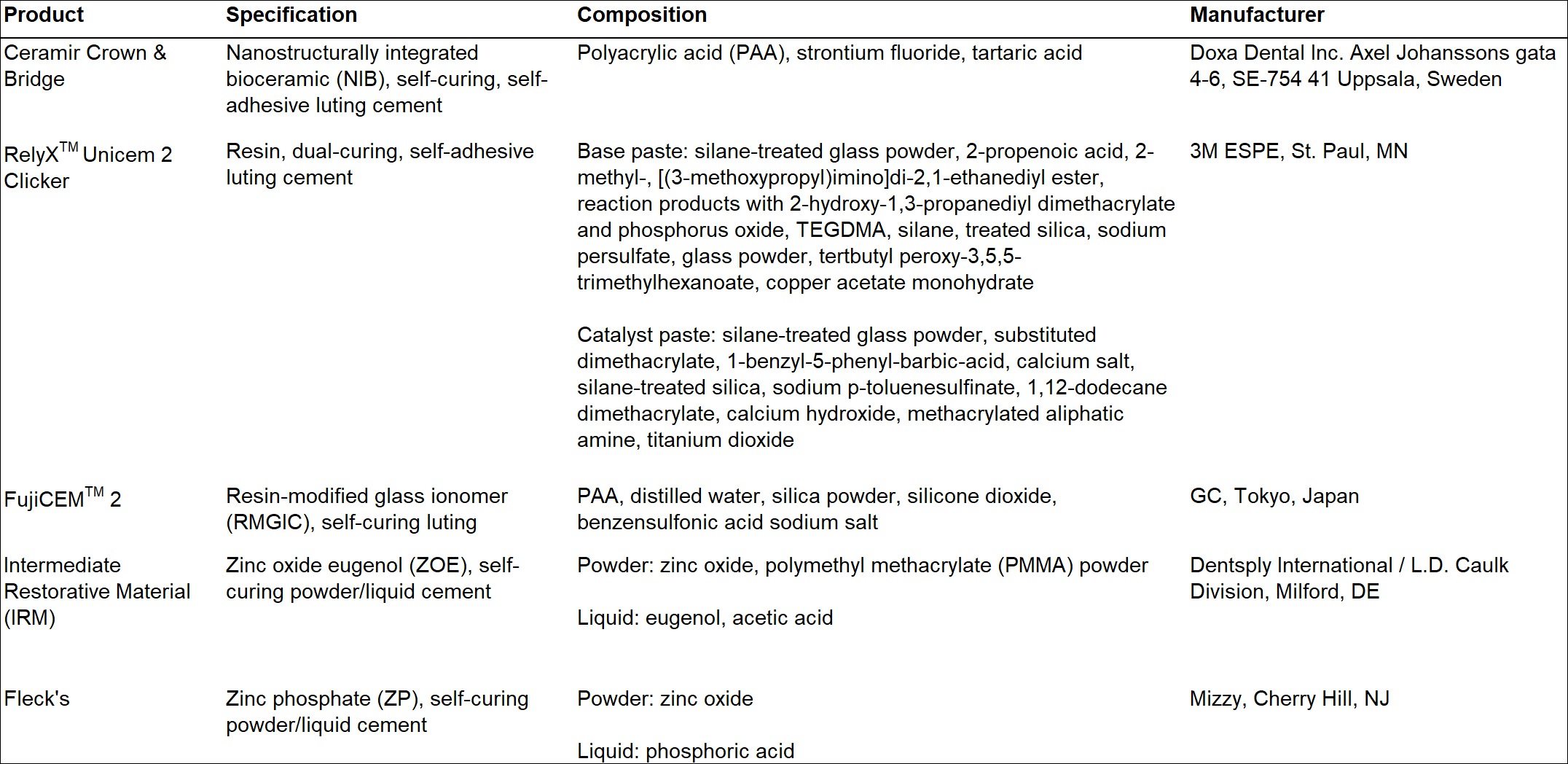
Methods: NIB, R, RMGIC, ZOE, and ZP compositions were prepared according to the respective manufacturer’s instructions (Table 1). Samples were prepared in cylindrical Teflon molds (d=11mm, thickness=1.6mm) or applied over the entire surface of polished cpTi discs (d=11mm, thickness=3–3.5mm). All samples were cured for 0.5h or 24h post-mixing. Direct contact testing was conducted according to ISO 10993 by seeding 6-well plates at 350,000 cells/well. Plates were incubated (37°C, 5% CO2, 24h) before individually plating samples and cpTi control discs (at least n=3/gp). Plates were then incubated for an additional 24h. Microtetrazolium (MTT) assays were used to measure cell viability. Statistical analysis was performed using unpaired, nonparametric Student’s t-tests (α=0.05).
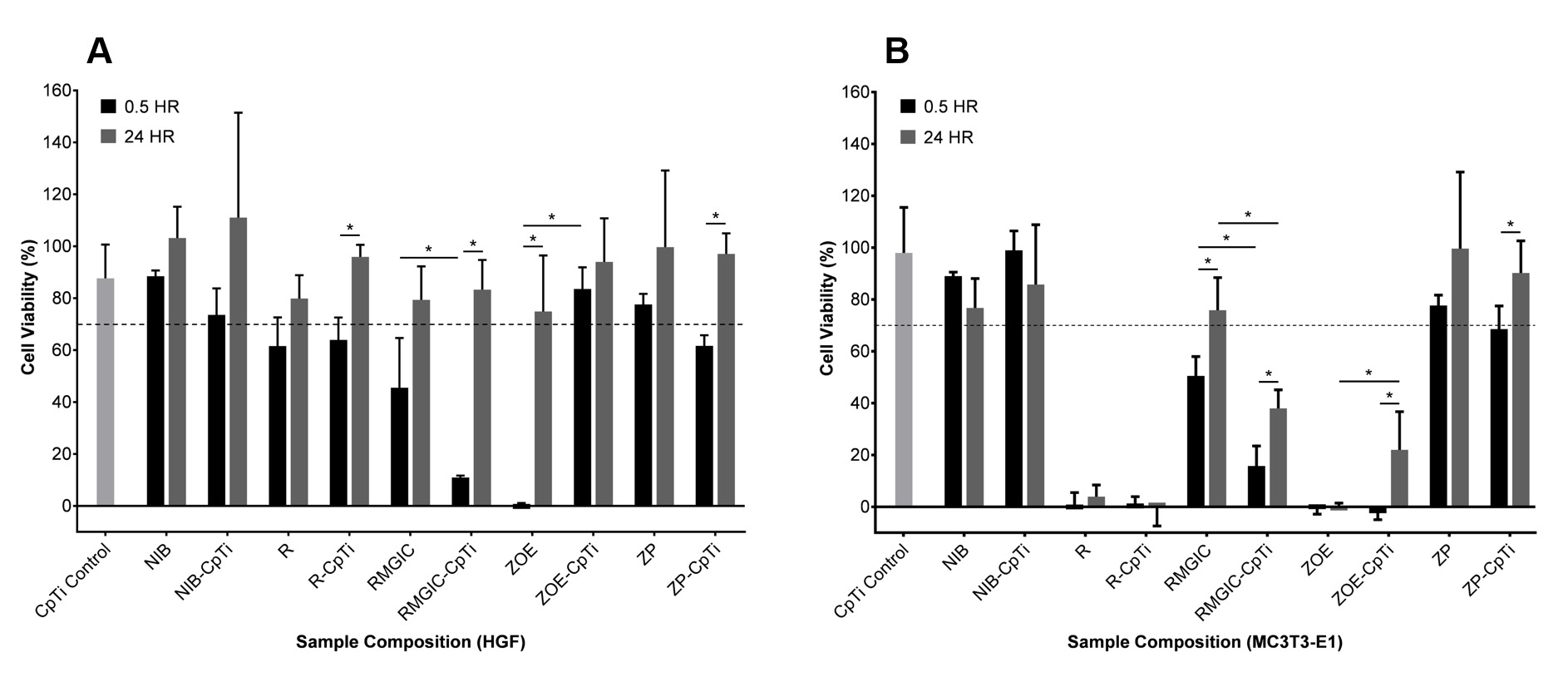
Results: At the 24h setting time point, only NIB and ZP compositions exhibited cell viability ≥ 70%. MC3T3-E1 cell viability decreased drastically after exposure to ZOE and R samples, indicating high levels of cytotoxicity to pre-osteoblast cells. For HGF cells, ZOE cemented-cpTi specimens exhibited significantly decreased cytotoxicity, whereas RMGIC cemented-cpTi specimens exhibited significantly increased cytotoxicity. Overall, HGF cells were less sensitive than MC3T3-E1 cells to dental cements.
Conclusions: Despite previous studies that showed enhanced cpTi corrosion activity for fluoride-containing compositions (NIB and ZP), there was no significant difference in cell viability between cement alone and cemented-cpTi for these two compositions. NIB and ZP were the most biocompatible compositions, ZOE was the least biocompatible composition, and both R and RMGIC compositions demonstrated moderate to severe cytotoxicity.
Methods: NIB, R, RMGIC, ZOE, and ZP compositions were prepared according to the respective manufacturer’s instructions (Table 1). Samples were prepared in cylindrical Teflon molds (d=11mm, thickness=1.6mm) or applied over the entire surface of polished cpTi discs (d=11mm, thickness=3–3.5mm). All samples were cured for 0.5h or 24h post-mixing. Direct contact testing was conducted according to ISO 10993 by seeding 6-well plates at 350,000 cells/well. Plates were incubated (37°C, 5% CO2, 24h) before individually plating samples and cpTi control discs (at least n=3/gp). Plates were then incubated for an additional 24h. Microtetrazolium (MTT) assays were used to measure cell viability. Statistical analysis was performed using unpaired, nonparametric Student’s t-tests (α=0.05).
Results: At the 24h setting time point, only NIB and ZP compositions exhibited cell viability ≥ 70%. MC3T3-E1 cell viability decreased drastically after exposure to ZOE and R samples, indicating high levels of cytotoxicity to pre-osteoblast cells. For HGF cells, ZOE cemented-cpTi specimens exhibited significantly decreased cytotoxicity, whereas RMGIC cemented-cpTi specimens exhibited significantly increased cytotoxicity. Overall, HGF cells were less sensitive than MC3T3-E1 cells to dental cements.
Conclusions: Despite previous studies that showed enhanced cpTi corrosion activity for fluoride-containing compositions (NIB and ZP), there was no significant difference in cell viability between cement alone and cemented-cpTi for these two compositions. NIB and ZP were the most biocompatible compositions, ZOE was the least biocompatible composition, and both R and RMGIC compositions demonstrated moderate to severe cytotoxicity.