IADR Abstract Archives
Chlorhexidine- vs. Sodium Chloride-mouthrinse for Periodontal Surgery. A Randomized Clinical Trial
Objectives: The aim of this study was to compare the efficacy of a sodium chloride- and a 0.12% chlorhexidine mouthwash (CHX) in patients undergoing periodontal surgery.
Methods: Twenty patients with chronic periodontitis and indication for access flap were randomly selected. A sodium chloride water-based mouthwash (test) or a 0.12% CHX (control) administered after surgery in a randomized blinded way. Patients were instructed to use 15ml mouthwash (2x/day for one week). Subsequently, patients were evaluated in the whole mouth and in the surgical site at baseline (T1), one week (T2) and twelve weeks (T3) after treatment using O’Leary Plaque Index (PI), Gingival Index (GI), probing depth (PD), postoperative pain- and satisfaction-index. Changes were compared for T1/T2/T3 using repeated ANOVA-test.
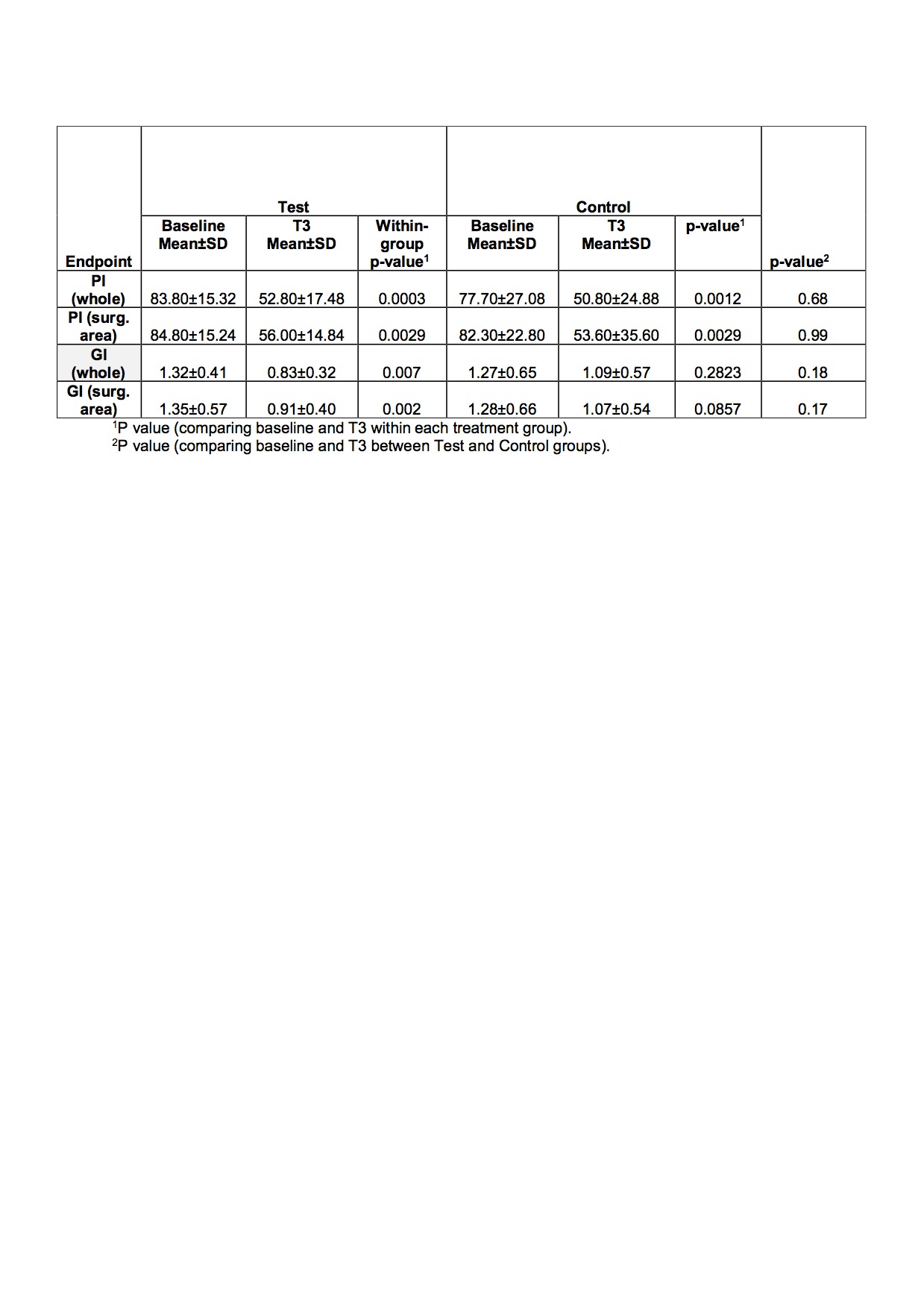
Results: The results showed significant reduction of PI (p<0.005) from baseline for test in the whole mouth, and in the surgical site between T1/T3 but not for the control group. No statistical differences (p>0.05) were found between test and control groups for GI, PD, postoperative pain and satisfaction index (see Table).
Conclusions: The effect of sodium chloride-mouthrinse seems to have beneficial effects on periodontal wound healing and is comparable with the standard treatment for postoperative care.
Methods: Twenty patients with chronic periodontitis and indication for access flap were randomly selected. A sodium chloride water-based mouthwash (test) or a 0.12% CHX (control) administered after surgery in a randomized blinded way. Patients were instructed to use 15ml mouthwash (2x/day for one week). Subsequently, patients were evaluated in the whole mouth and in the surgical site at baseline (T1), one week (T2) and twelve weeks (T3) after treatment using O’Leary Plaque Index (PI), Gingival Index (GI), probing depth (PD), postoperative pain- and satisfaction-index. Changes were compared for T1/T2/T3 using repeated ANOVA-test.
Results: The results showed significant reduction of PI (p<0.005) from baseline for test in the whole mouth, and in the surgical site between T1/T3 but not for the control group. No statistical differences (p>0.05) were found between test and control groups for GI, PD, postoperative pain and satisfaction index (see Table).
Conclusions: The effect of sodium chloride-mouthrinse seems to have beneficial effects on periodontal wound healing and is comparable with the standard treatment for postoperative care.