IADR Abstract Archives
Surface-Finish Effect of Carbide-Burs and Diamond-Instruments on Four-Classes of Composite-Materials
Objectives: The objective of this study was to characterize the surface finish of four classes of resin-based-composite-materials (RBCM) after finishing with either multi-fluted tungsten carbide burs or fine particle diamond instruments.
Methods: Four classes of RBCM(Table1) were formed and cured into twelve cylindrical specimens per-class(48-specimens, d=15.87mm,h=4mm). An initial surface roughness (1.9µm≤Ra≤3.5µm) was applied to each specimen. An electric handpiece(BienAir) was used to apply a finishing pass(depth=0.1mm,width~3mm) to each specimen using ultrafine particle diamond rotary instruments(30,000RPM) and 30-fluted carbide burs(200,000RPM) at a 2mm/s feed-rate and 50ml/min chip water-spray using a motorized stage(Table2). Surface roughness (Surtronic3+profilometer) and gloss (NovoCurve-Glossmeter) measurements were taken before and after finishing. SEM images(JCM6000,JEOL) were taken after finishing for 16 random-specimens(4-per-class). Two-way ANOVAs(SigmaPlot) were used to compare both surface-roughness and gloss with respect to class of RBCM and instrument-type.
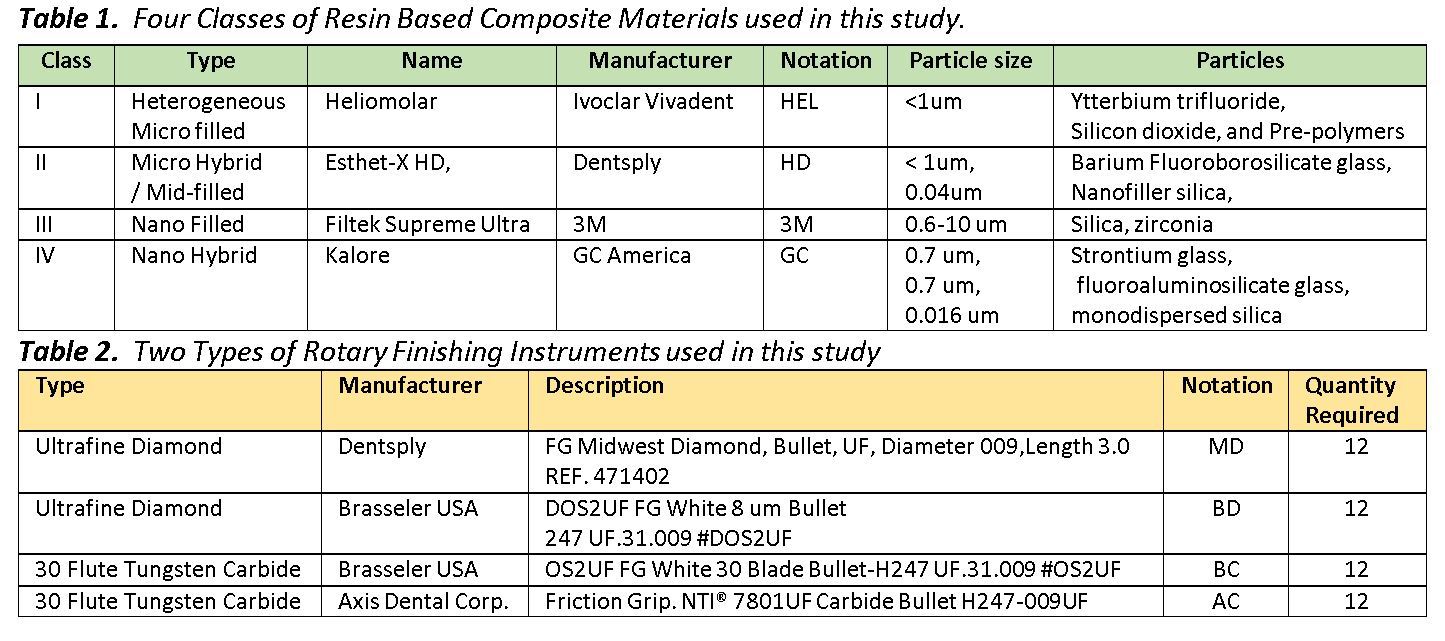
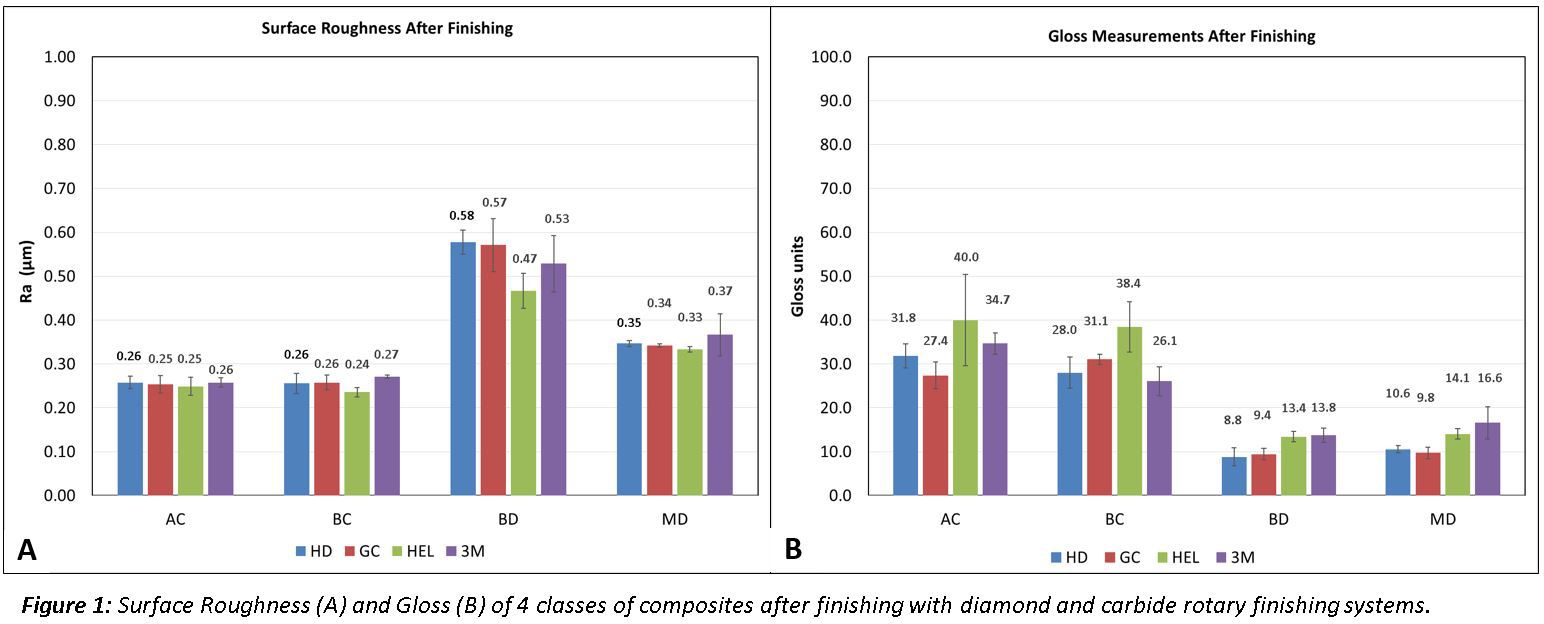
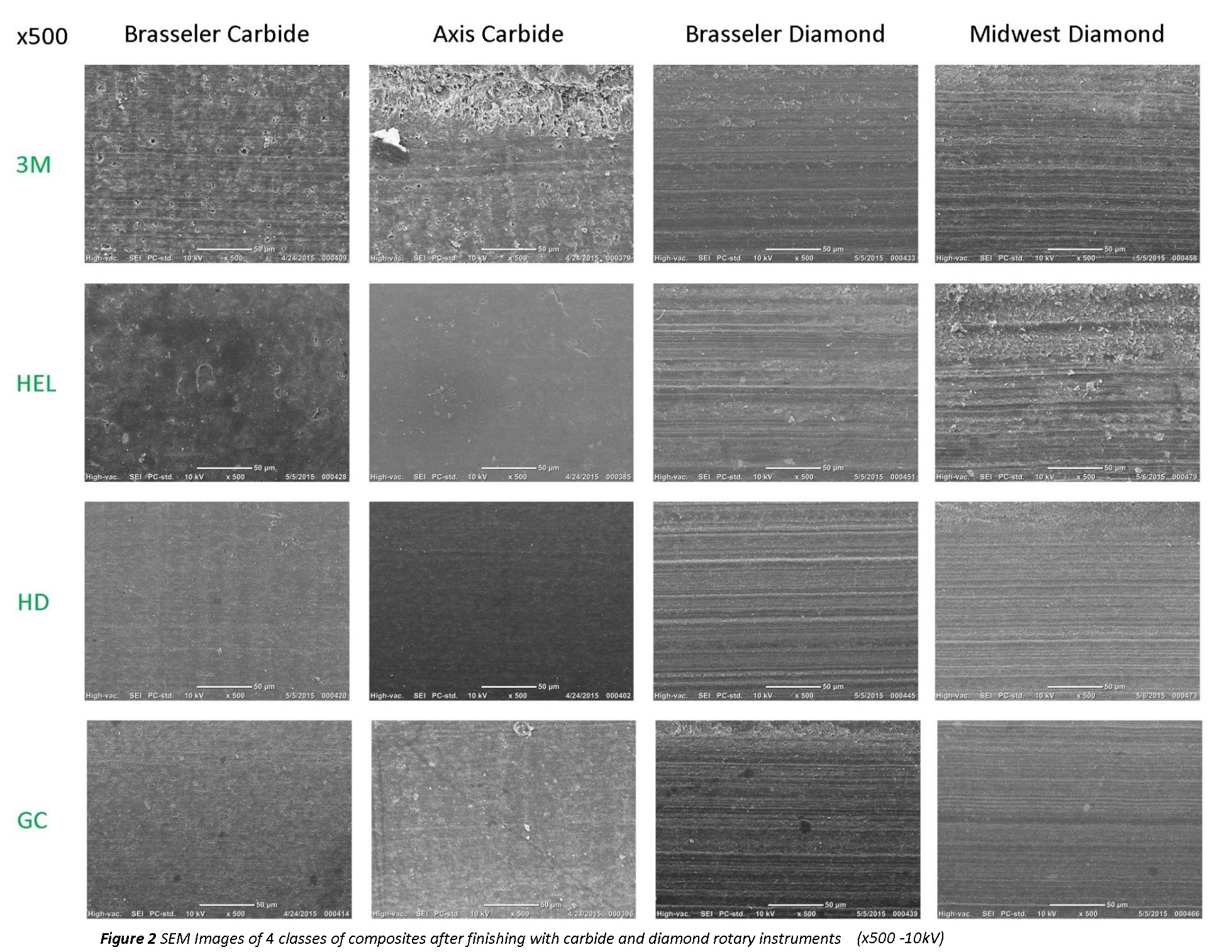
Results: Materials finished with carbide burs and diamond instruments had average Ra values of 0.25(±0.02)µm and 0.44(±0.11)µm, respectively(Figure1A). Gloss-measurements showed that materials finished with carbide burs and diamond instruments had average gloss values of 32.2(±6.4) and 12.1(±3.1) gloss units, respectively(Figure1B). Surface roughness showed no statistically significant difference for class of RBCM(p=0.148), but did show significance for instrument-type(p=<0.001). Gloss measurements showed a statistically significant difference for both class of RBCM(p=0.043) and instrument-type(p=<0.001). SEM images(Figure2) show grooves on all material-classes finished with ultrafine diamond instruments(diamond particle size=8-10µm), and images of materials finished with 30-fluted carbide burs demonstrate a smoother surface, but also show the existence of surface voids.
Conclusions: Surface roughness and gloss measurements show that multi-fluted tungsten-carbide burs and ultrafine diamond instruments produced significantly different surface finishes on four classes of RBCM. SEM images showed surface grooves and voids associated with diamond instruments and carbide burs, respectively.
Methods: Four classes of RBCM(Table1) were formed and cured into twelve cylindrical specimens per-class(48-specimens, d=15.87mm,h=4mm). An initial surface roughness (1.9µm≤Ra≤3.5µm) was applied to each specimen. An electric handpiece(BienAir) was used to apply a finishing pass(depth=0.1mm,width~3mm) to each specimen using ultrafine particle diamond rotary instruments(30,000RPM) and 30-fluted carbide burs(200,000RPM) at a 2mm/s feed-rate and 50ml/min chip water-spray using a motorized stage(Table2). Surface roughness (Surtronic3+profilometer) and gloss (NovoCurve-Glossmeter) measurements were taken before and after finishing. SEM images(JCM6000,JEOL) were taken after finishing for 16 random-specimens(4-per-class). Two-way ANOVAs(SigmaPlot) were used to compare both surface-roughness and gloss with respect to class of RBCM and instrument-type.
Results: Materials finished with carbide burs and diamond instruments had average Ra values of 0.25(±0.02)µm and 0.44(±0.11)µm, respectively(Figure1A). Gloss-measurements showed that materials finished with carbide burs and diamond instruments had average gloss values of 32.2(±6.4) and 12.1(±3.1) gloss units, respectively(Figure1B). Surface roughness showed no statistically significant difference for class of RBCM(p=0.148), but did show significance for instrument-type(p=<0.001). Gloss measurements showed a statistically significant difference for both class of RBCM(p=0.043) and instrument-type(p=<0.001). SEM images(Figure2) show grooves on all material-classes finished with ultrafine diamond instruments(diamond particle size=8-10µm), and images of materials finished with 30-fluted carbide burs demonstrate a smoother surface, but also show the existence of surface voids.
Conclusions: Surface roughness and gloss measurements show that multi-fluted tungsten-carbide burs and ultrafine diamond instruments produced significantly different surface finishes on four classes of RBCM. SEM images showed surface grooves and voids associated with diamond instruments and carbide burs, respectively.