IADR Abstract Archives
Biomechanical Analysis of Clear Aligners With Different Designs and Properties
Objectives: This study used finite element methods to investigate the biomechanical effects of varying power-ridge depths and material elastic properties on tooth movement patterns.
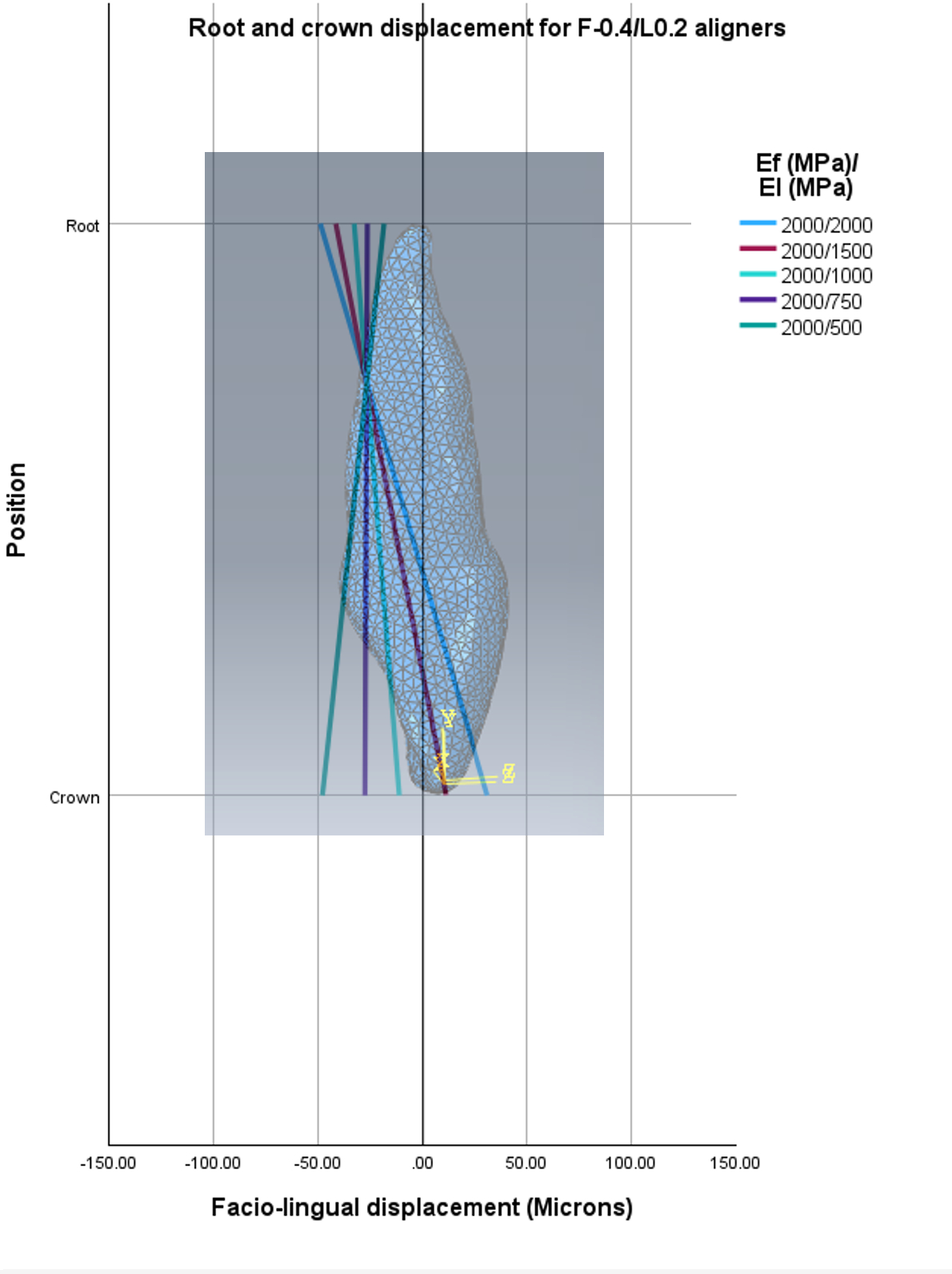
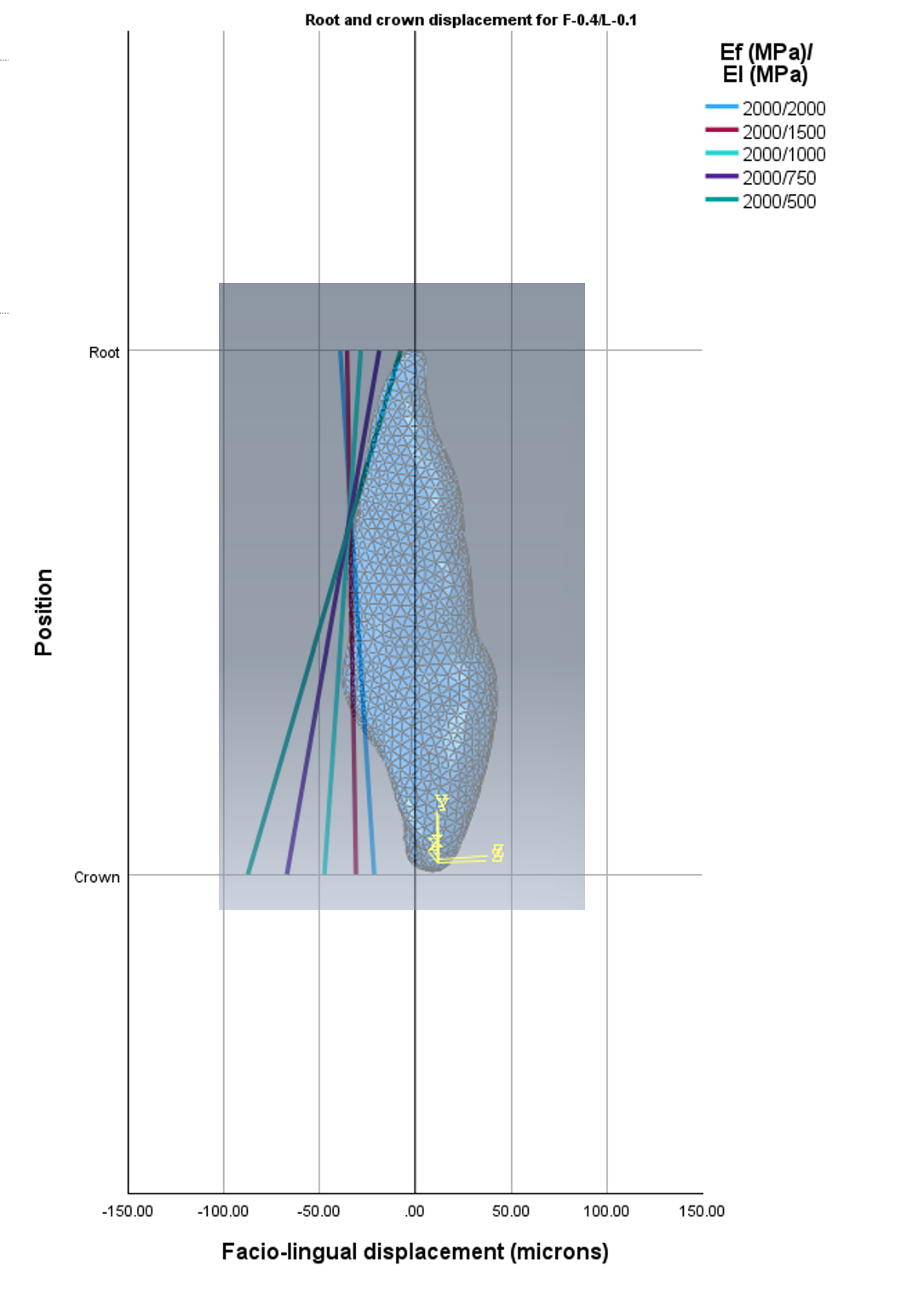
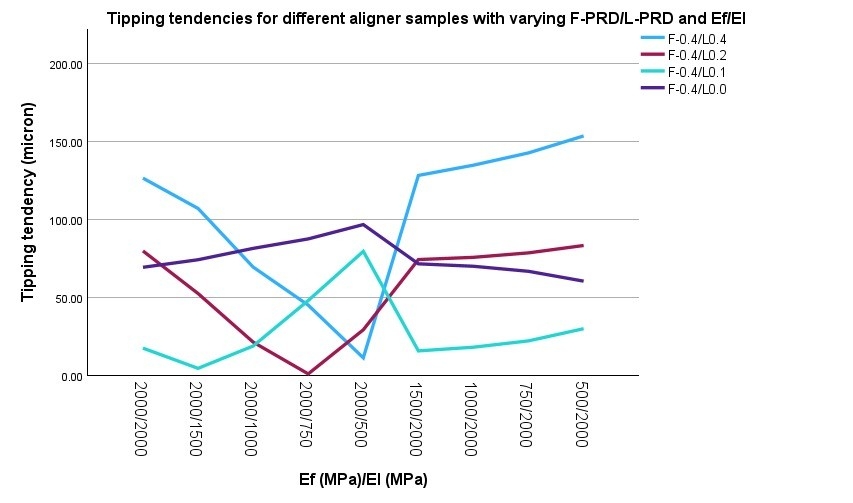
Methods: A three-dimensional model from a cone-beam computerized tomography of a 36-year-old individual was obtained. The maxillary teeth, bone and periodontal ligaments were segmented, and clear aligners (CA) were designed using computer-aided design. Power ridges were designed to apply a force couple on the facial and lingual surfaces of the maxillary right central incisor. CAs with a constant facial power-ridge depth (F-PRD) of 0.4-mm and varying lingual power-ridge depths (L-PRD) of 0.4-mm, 0.2-mm, 0.1-mm and 0.0-mm were designed. Elastic moduli for the facial (Ef) and lingual (El) parts of a CA ranged from 500 to 2000 MPa. All parts were later assembled and analyzed in finite element software to obtain crown displacements (UC), root (UR) displacements and tipping tendencies |UC-UR|.
Results: Variations in L-PRD, Ef and El influenced the amount and pattern of tooth movement. While all aligners with uniform elastic moduli [Ef-2000/El-2000] caused tipping tendencies, bodily lingual movement occurred with reduced L-PRD (0.1 and 0.2 mm) and certain elastic modulus combinations (Ef-2000/El-1500 and Ef-2000/El-750, respectively). Lowering El and L-PRD minimized labial crown tipping and enhanced root torque control, while reducing Ef decreased lingual displacement with minimal effect on movement patterns. Lingual crown tipping occurred in all samples with L-0.0.
Conclusions: Modifying power-ridge depth and elastic modulus on the lingual of an aligner influenced tooth movement patterns. Reducing L-PRD and El relative to the facial side improved root torque control, while specific L-PRD and elastic moduli combinations enabled bodily movement. These findings provide insights for optimizing CA designs to improve controlled tooth movement.
Methods: A three-dimensional model from a cone-beam computerized tomography of a 36-year-old individual was obtained. The maxillary teeth, bone and periodontal ligaments were segmented, and clear aligners (CA) were designed using computer-aided design. Power ridges were designed to apply a force couple on the facial and lingual surfaces of the maxillary right central incisor. CAs with a constant facial power-ridge depth (F-PRD) of 0.4-mm and varying lingual power-ridge depths (L-PRD) of 0.4-mm, 0.2-mm, 0.1-mm and 0.0-mm were designed. Elastic moduli for the facial (Ef) and lingual (El) parts of a CA ranged from 500 to 2000 MPa. All parts were later assembled and analyzed in finite element software to obtain crown displacements (UC), root (UR) displacements and tipping tendencies |UC-UR|.
Results: Variations in L-PRD, Ef and El influenced the amount and pattern of tooth movement. While all aligners with uniform elastic moduli [Ef-2000/El-2000] caused tipping tendencies, bodily lingual movement occurred with reduced L-PRD (0.1 and 0.2 mm) and certain elastic modulus combinations (Ef-2000/El-1500 and Ef-2000/El-750, respectively). Lowering El and L-PRD minimized labial crown tipping and enhanced root torque control, while reducing Ef decreased lingual displacement with minimal effect on movement patterns. Lingual crown tipping occurred in all samples with L-0.0.
Conclusions: Modifying power-ridge depth and elastic modulus on the lingual of an aligner influenced tooth movement patterns. Reducing L-PRD and El relative to the facial side improved root torque control, while specific L-PRD and elastic moduli combinations enabled bodily movement. These findings provide insights for optimizing CA designs to improve controlled tooth movement.