IADR Abstract Archives
Accelerated Dental-Dedicated MRI at 0.55T Using Deep-Learning Based Image Reconstruction
Objectives: MR image quality is often hampered by long scan durations, reducing patient comfort and leading to motion artefacts. New MRI reconstruction methods employ deeplearning (DL)-based reconstruction to enhance image quality at shorter scan times. Using a dental-dedicated MRI (ddMRI) scanner, we assessed image quality parameters in volumes reconstructed with and without DL.
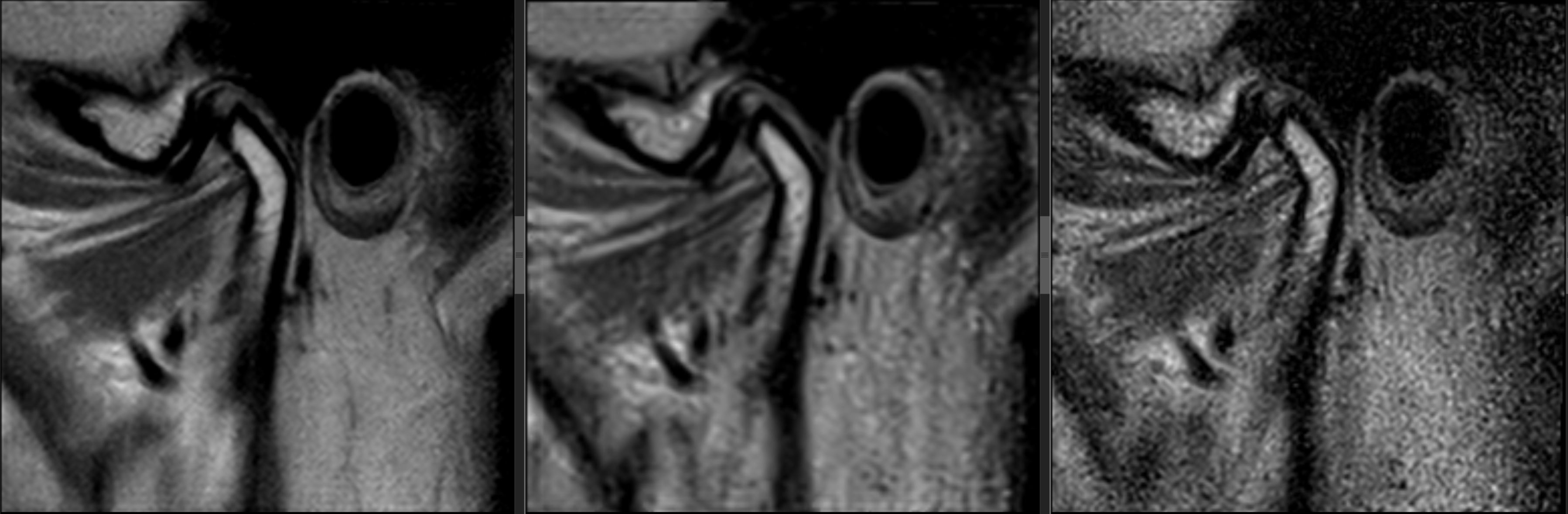
Methods: One oral radiologist evaluated 27 image stacks from 9 healthy volunteers, in a blinded randomized fashion, obtained on a 0.55T scanner (MAGNETOM Free.Max, Siemens Healthineers, Erlangen, Germany) equipped with a custom-built surface coil tailored for dentomaxillofacial imaging (i.e., ddMRI). One TMJ from each participant was imaged with a proton density-weighted TSE sequence in the parasagittal plane, with 2.5mm slice thickness using 3 different scan techniques: 2:38min duration accelerated with DL reconstruction at 0.24mmx0.24mm in plane resolution (test), 4:32min duration with conventional acquisition (CQ) at 0.31mmx0.35mm in plane resolution (reference with similar quality), and 2:38min duration with conventional acceleration (CD) at 0.24mmx0.24mm in plane resolution (reference with similar scan duration). Various hard and soft tissue anatomical components of the TMJ, and selected image quality parameters (noise, resolution, contrast, artifacts), were assessed using a 3-point scale (0=unacceptable, 1=acceptable, 2=excellent). Chi-square tests determined differences between techniques (significance set at ≤0.05).
Results: No difference between DL and CQ were observed when scoring hard and soft tissue anatomy (p=1,00; p=1.00 respectively), while all CD images were judged unacceptable when compared to DL and CQ (p<0.001, p<0.001 respectively). All images were judged as acceptable/excellent regarding resolution and artifacts. There was no preference of scans with regards to contrast (p=0.28). All CD images were rated as having unacceptable noise.
Conclusions: DL based image reconstruction enables shorter (-42%) scan times with comparable signal-to-noise at higher nominal resolution when compared to conventional imaging. Robustness and preservation of sensitivity in detecting pathologies of the new approach must be further investigated.
Methods: One oral radiologist evaluated 27 image stacks from 9 healthy volunteers, in a blinded randomized fashion, obtained on a 0.55T scanner (MAGNETOM Free.Max, Siemens Healthineers, Erlangen, Germany) equipped with a custom-built surface coil tailored for dentomaxillofacial imaging (i.e., ddMRI). One TMJ from each participant was imaged with a proton density-weighted TSE sequence in the parasagittal plane, with 2.5mm slice thickness using 3 different scan techniques: 2:38min duration accelerated with DL reconstruction at 0.24mmx0.24mm in plane resolution (test), 4:32min duration with conventional acquisition (CQ) at 0.31mmx0.35mm in plane resolution (reference with similar quality), and 2:38min duration with conventional acceleration (CD) at 0.24mmx0.24mm in plane resolution (reference with similar scan duration). Various hard and soft tissue anatomical components of the TMJ, and selected image quality parameters (noise, resolution, contrast, artifacts), were assessed using a 3-point scale (0=unacceptable, 1=acceptable, 2=excellent). Chi-square tests determined differences between techniques (significance set at ≤0.05).
Results: No difference between DL and CQ were observed when scoring hard and soft tissue anatomy (p=1,00; p=1.00 respectively), while all CD images were judged unacceptable when compared to DL and CQ (p<0.001, p<0.001 respectively). All images were judged as acceptable/excellent regarding resolution and artifacts. There was no preference of scans with regards to contrast (p=0.28). All CD images were rated as having unacceptable noise.
Conclusions: DL based image reconstruction enables shorter (-42%) scan times with comparable signal-to-noise at higher nominal resolution when compared to conventional imaging. Robustness and preservation of sensitivity in detecting pathologies of the new approach must be further investigated.