IADR Abstract Archives
Doped Magnesium and Strontium Affect Enamel Remineralized Crystal Morphology
Objectives: To investigate the effect of various levels of doped Mg and Sr ions with F ion on the morphology and elemental compositions of calcium phosphate crystals growth on acid-etched enamel.
Methods: Human teeth were sectioned into 0.5 mm thick slices. Samples were etched with a 5% HNO3 solution for 20 seconds, rinsed with distilled water, and placed into 20 mL scintillation vials. Biomimetic mineralization solution (BMS) was prepared using supersaturated CaCl2, and KH2PO4 with a neutral pH 7.1. After adding BMS in each vial, doped F, Mg, and Sr ions were added at various desired concentrations. Specimens were incubated for 8 hours at 37 °C to initiate crystal growth on the etched enamel surfaces. The remineralized crystal morphology on enamel surfaces and the crystal elemental composition were assayed by FE-SEM and EDS, respectively. Three sets of solutions containing different F, Sr, and Mg levels that led to promising crystal growth and density were selected for 9 days of treatment on etched tooth specimens, and assayed by FE-SEM, EDS, and microhardness test.
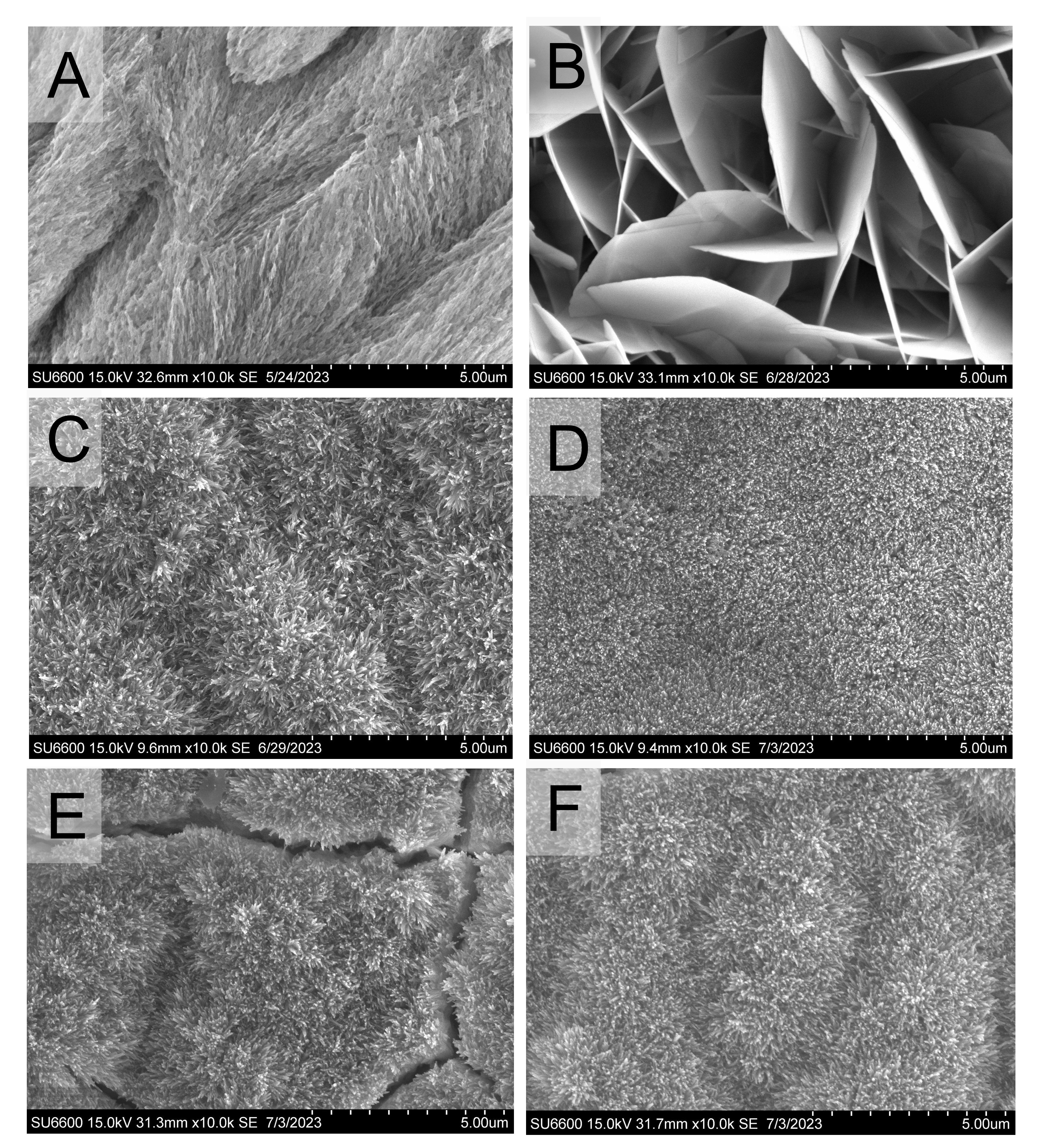
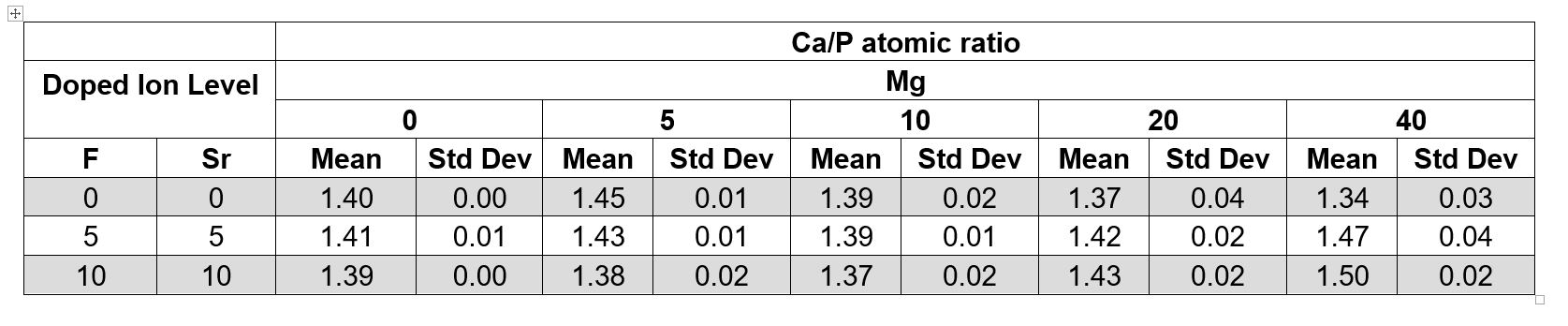
Results: In the presence of fluoride, the morphology of crystals was needle-like. In the presence of magnesium, the crystals were distorted plate-like and the growth rate was obviously supressed. In the coexisting of magnesium, strontium, and fluoride, morphology became needle-like with greater packing density. The Vicker's microhardness test values for the 9-day experimental specimens in the presence of Mg, Sr, and F are 180.65 kg/mm2, 125.58 kg/mm2, and 159.78 kg/mm2. In the presence of increased fluoride, strontium, and magnesium, needle-like crystals grew faster, but the crystal layer showed lower hardness than that without Mg.
Conclusions: Fluoride, magnesium, and strontium ions have a synergistic effect on enamel crystal growth by changing crystal morphology, density, composition, and potentially enamel-like crystallographic structure. The application of magnesium-containing remineralization may have an application in calculus inhibition.
Methods: Human teeth were sectioned into 0.5 mm thick slices. Samples were etched with a 5% HNO3 solution for 20 seconds, rinsed with distilled water, and placed into 20 mL scintillation vials. Biomimetic mineralization solution (BMS) was prepared using supersaturated CaCl2, and KH2PO4 with a neutral pH 7.1. After adding BMS in each vial, doped F, Mg, and Sr ions were added at various desired concentrations. Specimens were incubated for 8 hours at 37 °C to initiate crystal growth on the etched enamel surfaces. The remineralized crystal morphology on enamel surfaces and the crystal elemental composition were assayed by FE-SEM and EDS, respectively. Three sets of solutions containing different F, Sr, and Mg levels that led to promising crystal growth and density were selected for 9 days of treatment on etched tooth specimens, and assayed by FE-SEM, EDS, and microhardness test.
Results: In the presence of fluoride, the morphology of crystals was needle-like. In the presence of magnesium, the crystals were distorted plate-like and the growth rate was obviously supressed. In the coexisting of magnesium, strontium, and fluoride, morphology became needle-like with greater packing density. The Vicker's microhardness test values for the 9-day experimental specimens in the presence of Mg, Sr, and F are 180.65 kg/mm2, 125.58 kg/mm2, and 159.78 kg/mm2. In the presence of increased fluoride, strontium, and magnesium, needle-like crystals grew faster, but the crystal layer showed lower hardness than that without Mg.
Conclusions: Fluoride, magnesium, and strontium ions have a synergistic effect on enamel crystal growth by changing crystal morphology, density, composition, and potentially enamel-like crystallographic structure. The application of magnesium-containing remineralization may have an application in calculus inhibition.