IADR Abstract Archives
Novel Dual-Functional pH-Responsive Nanocomposite to Prevent Secondary Caries
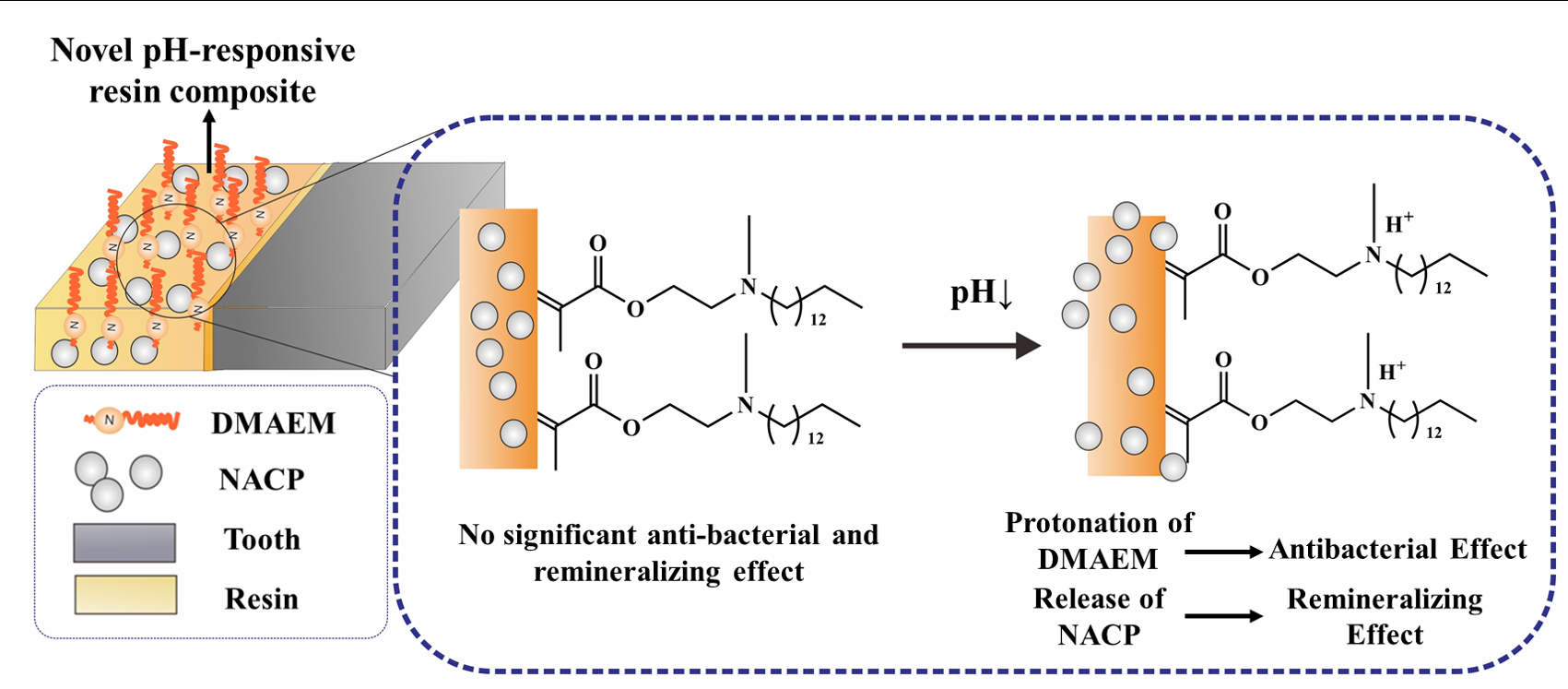
Objectives: Secondary caries remains a great problem for resin restoration. Recently, we reported tertiary amine monomers dodecylmethylaminoethyl methacrylate (DMAEM) modified resin adhesives showed pH-responsive anti-bacterial effect. Yet, when DMAEM showed acid-induced effect at around pH5.5, the demineralization could already start. The combination of remineralizing property for improved anti-caries effect of resin composites is also necessary. Here, our objectives were (1) to develop a novel nanocomposite co-incorporated with DMAEM and nanoparticles of amorphous calcium phosphate (NACP) for the first time, to combine the pH-responsive antibacterial and rematerializing effect; (2) to investigate the anti-bacterial and remineralizing effect of the nanocomposite.
Methods: The tested groups are: (1) Commercial control, (2) Experimental control (0% NACP, 0% DMAHDM), (3) 20%NACP, (4) 3%DMAEM, (5) 3%DMAEM+20%NACP, (6) 4%DMAEM, (7) 4%DMAEM+20%NACP. The flexural strength(n=6), cytotoxicity(n=6), release of Ca-P ions in different pH(n=4) were tested. Then, saliva-derived biofilms were incubated on the nanocomposites. The MTT test(n=6), lactic acid production measurement(n=6) and live/dead staining(n=3) were conducted. The in-vitro biofilm-induced secondary caries model was used and the microhardness of the bovine enamel was tested(n=6).
Results: The 3%DMAEM+20% NACP and 4%DMAEM+20% NACP groups showed good mechanical properties(MPa) (99.3±14.8,97.9±14.1) and biosafety, which were comparable to the control groups(P>0.05). They also showed long-term release of Ca-P ions. In the biofilm tests, the novel nanocomposites effectively inhibited the metabolism and lactic acid production of saliva-derived biofilms (P<0.01). The portion of live cells also decreased obviously(P<0.01). In the secondary caries model, DMAEM+NACP groups showed increased enamel microhardness(Gpa), about 2-fold those of control groups (3%DMAEM+20%NACP 1.5±0.2, 4%DMAEM+20% NACP 1.6±0.4 , P<0.01).
Conclusions: Conclusion: The novel nanocomposite co-incorporated with DMAEM and NACP demonstrated antibacterial and remineralizing effect. The dual-functional intelligent nanocomposite had great application potential for the prevention and treatment for secondary caries.
Methods: The tested groups are: (1) Commercial control, (2) Experimental control (0% NACP, 0% DMAHDM), (3) 20%NACP, (4) 3%DMAEM, (5) 3%DMAEM+20%NACP, (6) 4%DMAEM, (7) 4%DMAEM+20%NACP. The flexural strength(n=6), cytotoxicity(n=6), release of Ca-P ions in different pH(n=4) were tested. Then, saliva-derived biofilms were incubated on the nanocomposites. The MTT test(n=6), lactic acid production measurement(n=6) and live/dead staining(n=3) were conducted. The in-vitro biofilm-induced secondary caries model was used and the microhardness of the bovine enamel was tested(n=6).
Results: The 3%DMAEM+20% NACP and 4%DMAEM+20% NACP groups showed good mechanical properties(MPa) (99.3±14.8,97.9±14.1) and biosafety, which were comparable to the control groups(P>0.05). They also showed long-term release of Ca-P ions. In the biofilm tests, the novel nanocomposites effectively inhibited the metabolism and lactic acid production of saliva-derived biofilms (P<0.01). The portion of live cells also decreased obviously(P<0.01). In the secondary caries model, DMAEM+NACP groups showed increased enamel microhardness(Gpa), about 2-fold those of control groups (3%DMAEM+20%NACP 1.5±0.2, 4%DMAEM+20% NACP 1.6±0.4 , P<0.01).
Conclusions: Conclusion: The novel nanocomposite co-incorporated with DMAEM and NACP demonstrated antibacterial and remineralizing effect. The dual-functional intelligent nanocomposite had great application potential for the prevention and treatment for secondary caries.