IADR Abstract Archives
Iloprost Reduces IL-6 and IL-12 Expression by “Inflamed” Pulp Cell
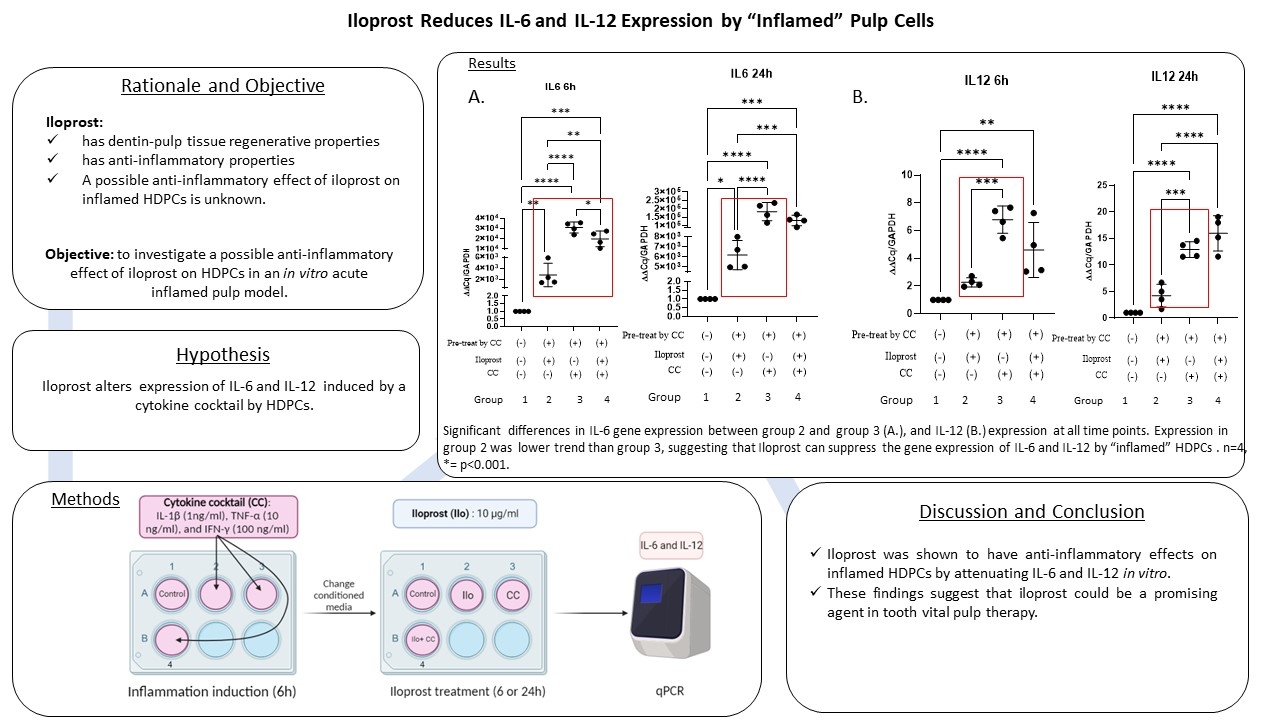
Objectives: Dental pulp capping materials should have anti-inflammatory effects and promote hard tissue regeneration. Iloprost has been reported to increase angiogenesis and to induce dentin formation. The aim of this study was to investigate possible anti-inflammatory effects of iloprost on human dental pulp cells (HDPCs) in an in vitro acute inflamed pulp model.
Methods: To create an in vitro inflammation model, HDPCs were treated with a cytokine cocktail (CC) consisting of 1ng/ml IL-1β, 10 ng/ml TNF-α, and 100 ng/ml IFN-γ for 6 hours. The efficacy of the CC was compared with 10µg/ml LPS treatment. After inducing inflammation, the cells were divided into 3 groups and incubated as follows: (1) with 10-6 M/ml iloprost (ilo), (2) with CC, and (3) with CC+ilo. After 6 or 24 hours, IL-6 and IL-12 mRNA expression were assessed by RT-qPCR and ELISA. The results were analyzed with one-way ANOVA or the Kruskal-Wallis test.
Results: CC induced robust IL-6 and IL-12 expression compared with the LPS-treated HDPCs. After incubating the HDPCs with CC, Iloprost significantly downregulated the expression of IL-6 and IL-12 mRNA and protein expression at 6 and 24 hours. Pretreatment of the HDPCs with iloprost before challenging with CC did not attenuate IL-6 and IL-12 mRNA expression.
Conclusions: The data presented in this study, for the first time, suggests that a cytokine cocktail consisting of IL-1β, TNF-α, and IFN-γ creates a more reliable acute inflammation model compared with LPS. This was shown by a marked increase in inflammatory cytokine expression compared with LPS. Iloprost demonstrated anti-inflammatory effects on “inflamed” HDPCs by attenuating IL-6 and IL-12 expression. These findings suggest that iloprost could be a promising agent in tooth vital pulp therapy.
Methods: To create an in vitro inflammation model, HDPCs were treated with a cytokine cocktail (CC) consisting of 1ng/ml IL-1β, 10 ng/ml TNF-α, and 100 ng/ml IFN-γ for 6 hours. The efficacy of the CC was compared with 10µg/ml LPS treatment. After inducing inflammation, the cells were divided into 3 groups and incubated as follows: (1) with 10-6 M/ml iloprost (ilo), (2) with CC, and (3) with CC+ilo. After 6 or 24 hours, IL-6 and IL-12 mRNA expression were assessed by RT-qPCR and ELISA. The results were analyzed with one-way ANOVA or the Kruskal-Wallis test.
Results: CC induced robust IL-6 and IL-12 expression compared with the LPS-treated HDPCs. After incubating the HDPCs with CC, Iloprost significantly downregulated the expression of IL-6 and IL-12 mRNA and protein expression at 6 and 24 hours. Pretreatment of the HDPCs with iloprost before challenging with CC did not attenuate IL-6 and IL-12 mRNA expression.
Conclusions: The data presented in this study, for the first time, suggests that a cytokine cocktail consisting of IL-1β, TNF-α, and IFN-γ creates a more reliable acute inflammation model compared with LPS. This was shown by a marked increase in inflammatory cytokine expression compared with LPS. Iloprost demonstrated anti-inflammatory effects on “inflamed” HDPCs by attenuating IL-6 and IL-12 expression. These findings suggest that iloprost could be a promising agent in tooth vital pulp therapy.