IADR Abstract Archives
Comparison of Polishability in Packable Composite With Different Filler Sizes
Objectives: Effective polishing of composite restorations may reduce tissue irritation, plaque accumulation, staining, and optimize esthetics. This study compares the polishability of composite resins with a range of filler sizes.
Methods: Four commercial resin-based composites were examined: a nanocomposite, Filtek Supreme Ultra (3M ESPE), two nanohybrid composites, NovaPro Fill (NANOVA) and Dentsply Sirona TPH Spectra HV (Dentsply Sirona), and a microhybrid composite, Z250 (3M ESPE). Ten specimens of each composite of dimensions 7mm diamter×3 mm thick were fabricated. These were condensed by a ball burnisher, incrementally cured 60s with BluePhase 20i high mode (Ivoclar Vivadent), and mounted on epoxy bases. Standardized polishing was conducted using a Buehler Ecomet 250 Grinder-Polisher in the following sequence: 70µm and 45µm diamond disk (30s), 15µm diamond disk (150s), 6µm diamond suspension (120s) and 1µm alumina suspension (150s). Surface roughness, gloss index, and abrasivity (thickness reduction) were measured after each polishing grit using a SJ201 Profilometer (Mitutoyo), Novo-Curve (Rhopoint), and ABSOLUTE Digimatic Indicator (Mitutoyo), respectively. The filler size and distribution of the composite were analyzed with an electron microscope (SEM). The difference of roughness and gloss index were compared by the filler type and polishing grit with two-way ANOVA analysis by JMP.
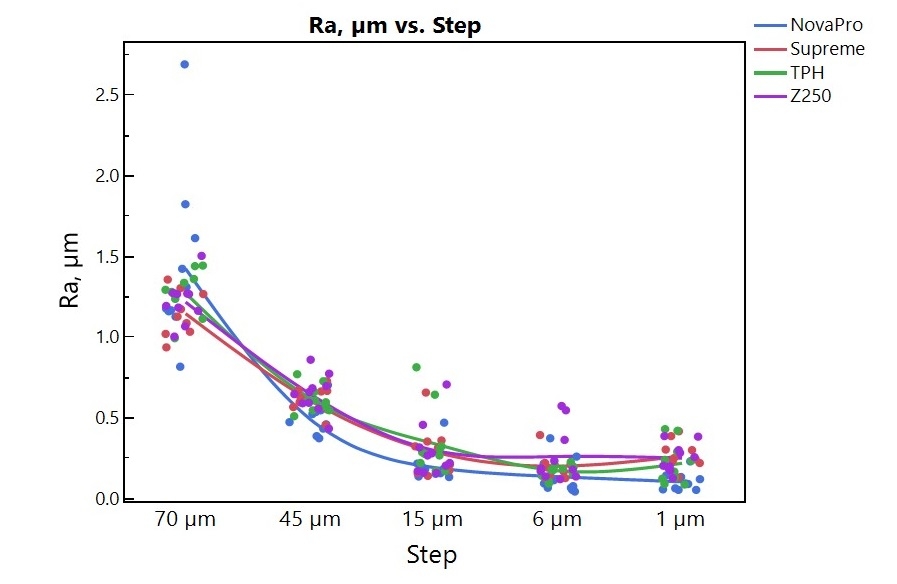
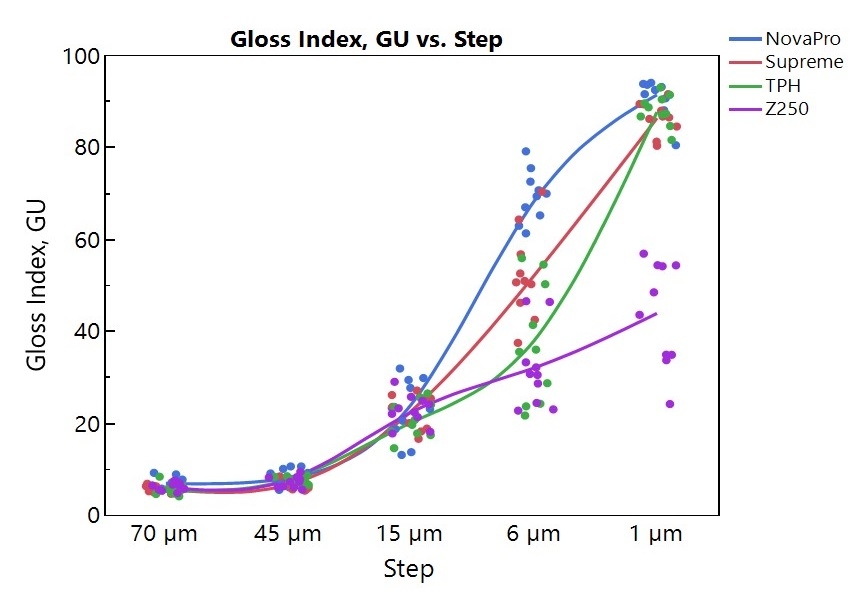
Results: The mean roughness (Ra) and gloss index (GU) are shown in Figures 1 and 2. A significant difference in Ra was found between each polishing step, but no significant difference in Ra was found between composites. The microhybrid composite presents a significantly lower GU comparing to the nanocomposites and nanohybrid composites; the GU of NovaPro is higher than the rest. TPH has the highest abrasivity; Z250 and NovaPro show significantly higher abrasivity than Supreme Ultra.
Conclusions: The mircohybrid composite shows a low gloss compared to nanofilled composite after fine polishing. The composite abrasivity is affected by filler size and the filler composition.
Methods: Four commercial resin-based composites were examined: a nanocomposite, Filtek Supreme Ultra (3M ESPE), two nanohybrid composites, NovaPro Fill (NANOVA) and Dentsply Sirona TPH Spectra HV (Dentsply Sirona), and a microhybrid composite, Z250 (3M ESPE). Ten specimens of each composite of dimensions 7mm diamter×3 mm thick were fabricated. These were condensed by a ball burnisher, incrementally cured 60s with BluePhase 20i high mode (Ivoclar Vivadent), and mounted on epoxy bases. Standardized polishing was conducted using a Buehler Ecomet 250 Grinder-Polisher in the following sequence: 70µm and 45µm diamond disk (30s), 15µm diamond disk (150s), 6µm diamond suspension (120s) and 1µm alumina suspension (150s). Surface roughness, gloss index, and abrasivity (thickness reduction) were measured after each polishing grit using a SJ201 Profilometer (Mitutoyo), Novo-Curve (Rhopoint), and ABSOLUTE Digimatic Indicator (Mitutoyo), respectively. The filler size and distribution of the composite were analyzed with an electron microscope (SEM). The difference of roughness and gloss index were compared by the filler type and polishing grit with two-way ANOVA analysis by JMP.
Results: The mean roughness (Ra) and gloss index (GU) are shown in Figures 1 and 2. A significant difference in Ra was found between each polishing step, but no significant difference in Ra was found between composites. The microhybrid composite presents a significantly lower GU comparing to the nanocomposites and nanohybrid composites; the GU of NovaPro is higher than the rest. TPH has the highest abrasivity; Z250 and NovaPro show significantly higher abrasivity than Supreme Ultra.
Conclusions: The mircohybrid composite shows a low gloss compared to nanofilled composite after fine polishing. The composite abrasivity is affected by filler size and the filler composition.