IADR Abstract Archives
Water Sorption and Solubility of 3D-printed Restoration Grade Resins
Objectives: This pilot study is to investigate how water sorption and solubility of commercially available SLA/DLP biocompatible 3D-printed (3DP) polymers compare to clinically available dental resin composites in a stimulated carious oral cavity environment.
Methods: Conventional dental restoration material, Beautifil II LS (Shofu)(Group1) and 3DP dental restoration grade polymers were tested, C&B MFH (NextDent)(Group2) and Denture Teeth Resin(FormLabs)(Group3). Groups were subdivided into two different conditions: dry (n=20) and caries-inducing acidic solution(n=20). Group1, was prepared in a mold with internal dimensions of 15mm (±0.1) in diameter and 1.0mm (±0.1) deep as specified by ISO 4049. 3DP samples were designed on MeshMaker and printed on a Moon Ray S printer(SprintRay) for Group2 and Form2(FormLabs) printer for Group3. Samples were kept in acidic solution at 37°C for 14 days, simulating caries-inducing condition. Water sorption(Wsp) for each sample was calculated using the equation: Wsp=M2-M3/V, where M2=mass of sample, after water immersion; M3=reconditioned mass of sample after dry and V=volume of the sample. Solubility(Wsl,) for each sample was be calculated using the following equation: Wsl=(M1 – M3)/V. Mean values of different groups under same condition was compared using one–way ANOVA and Post Hoc analysis via Tukey test was used to obtain p-values for mean comparison. Statistical comparison between dry versus acidic condition within the group was done by independent sample t-test.
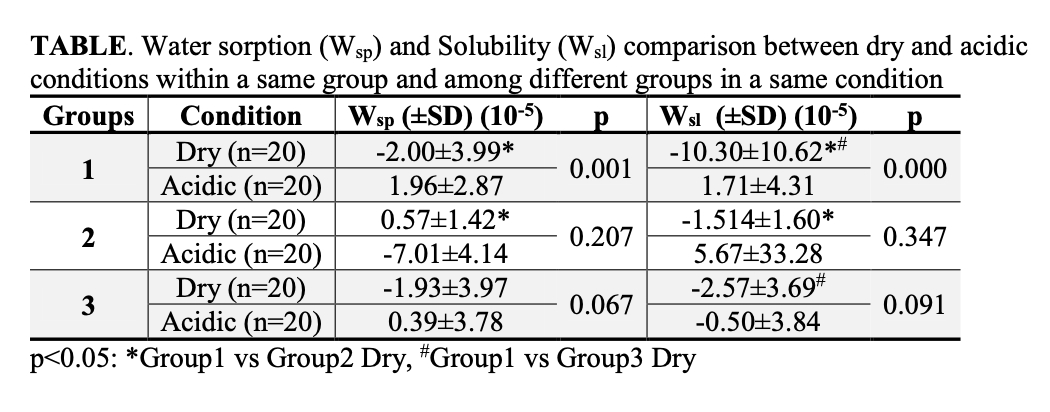
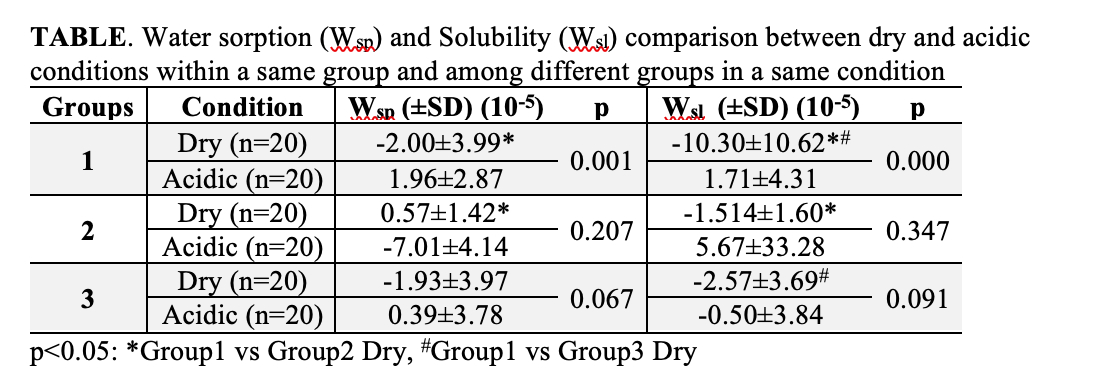
Results: TABLE presents mean values of Wsp and Wsl and results of statistical comparisons. Group1 showed higher Wsp and Wsvalues than both Group2 and 3 regardless of condition. Group2 and 3 showed low water sorption and solubility, and there were no significant differences between the two.
Conclusions: In an aqueous solution, Group1 exhibited significantly greater water sorption than Group2 and significantly greater solubility than both Groups2 and 3. In the acidic solution, Group1 exhibited significantly greater water sorption and solubility than the aqueous solution.
Methods: Conventional dental restoration material, Beautifil II LS (Shofu)(Group1) and 3DP dental restoration grade polymers were tested, C&B MFH (NextDent)(Group2) and Denture Teeth Resin(FormLabs)(Group3). Groups were subdivided into two different conditions: dry (n=20) and caries-inducing acidic solution(n=20). Group1, was prepared in a mold with internal dimensions of 15mm (±0.1) in diameter and 1.0mm (±0.1) deep as specified by ISO 4049. 3DP samples were designed on MeshMaker and printed on a Moon Ray S printer(SprintRay) for Group2 and Form2(FormLabs) printer for Group3. Samples were kept in acidic solution at 37°C for 14 days, simulating caries-inducing condition. Water sorption(Wsp) for each sample was calculated using the equation: Wsp=M2-M3/V, where M2=mass of sample, after water immersion; M3=reconditioned mass of sample after dry and V=volume of the sample. Solubility(Wsl,) for each sample was be calculated using the following equation: Wsl=(M1 – M3)/V. Mean values of different groups under same condition was compared using one–way ANOVA and Post Hoc analysis via Tukey test was used to obtain p-values for mean comparison. Statistical comparison between dry versus acidic condition within the group was done by independent sample t-test.
Results: TABLE presents mean values of Wsp and Wsl and results of statistical comparisons. Group1 showed higher Wsp and Wsvalues than both Group2 and 3 regardless of condition. Group2 and 3 showed low water sorption and solubility, and there were no significant differences between the two.
Conclusions: In an aqueous solution, Group1 exhibited significantly greater water sorption than Group2 and significantly greater solubility than both Groups2 and 3. In the acidic solution, Group1 exhibited significantly greater water sorption and solubility than the aqueous solution.