IADR Abstract Archives
Low-Concentration NaOCL Oral Rinse: Efficacy in Reducing Plaque
Objectives: Reducing dental plaque is important because of its association with bacterial density, downstream periodontal disease, and bacteremia. Sodium hypochlorite (NaOCL) is a common ingredient in therapeutic oral rinses because it is inexpensive and has antimicrobial, fungicidal, and antiviral properties. However, it is unclear whether reported oral health improvements are due specifically to NaOCL use or to increased patient hygiene. This study tested whether a low concentration NaOCL-containing mouth rinse (0.0125%) significantly reduced plaque area coverage (PAC) in predisposed populations, relative to a placebo rinse.
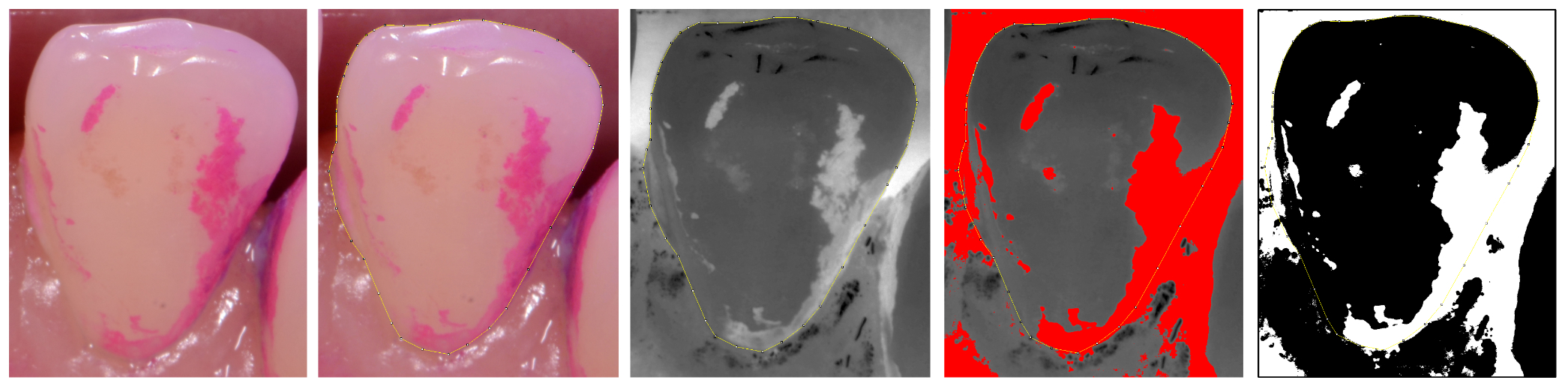
Methods: Forty-five patients were identified by hygienists as struggling with plaque accumulation and were subsequently enrolled in this IRB-approved study. Each participant was randomly assigned to receive a NaOCL-containing treatment rinse or a similar placebo rinse that did not contain the NaOCL (both from Century Pharmaceuticals Inc., Indianapolis, IN). Participants were instructed to swish with 5mL once daily after brushing and flossing. Baseline photographs were taken of disclosed tooth surfaces at the beginning of the study and again after 90 ± 7 days of use. PAC was quantified for 528 tooth surfaces representing all lower anterior teeth (see Fig. 1). PAC values were statistically compared using a linear mixed model test for differences within and between groups (α=0.05).
Results: There was significant PAC reduction at 90 days for both groups (F = 11.08, p-value < 0.0001) (see Table 1). However, there were no significant differences in the magnitude of this change between groups for either facial or lingual tooth surfaces.
Conclusions: The group using the NaOCL-containing rinse had a similar reduction in PAC to the placebo group. This implies that increased patient hygiene awareness and/or the mechanics of rinsing were more important in managing PAC than the presence of low concentration NaOCL.
Methods: Forty-five patients were identified by hygienists as struggling with plaque accumulation and were subsequently enrolled in this IRB-approved study. Each participant was randomly assigned to receive a NaOCL-containing treatment rinse or a similar placebo rinse that did not contain the NaOCL (both from Century Pharmaceuticals Inc., Indianapolis, IN). Participants were instructed to swish with 5mL once daily after brushing and flossing. Baseline photographs were taken of disclosed tooth surfaces at the beginning of the study and again after 90 ± 7 days of use. PAC was quantified for 528 tooth surfaces representing all lower anterior teeth (see Fig. 1). PAC values were statistically compared using a linear mixed model test for differences within and between groups (α=0.05).
Results: There was significant PAC reduction at 90 days for both groups (F = 11.08, p-value < 0.0001) (see Table 1). However, there were no significant differences in the magnitude of this change between groups for either facial or lingual tooth surfaces.
Conclusions: The group using the NaOCL-containing rinse had a similar reduction in PAC to the placebo group. This implies that increased patient hygiene awareness and/or the mechanics of rinsing were more important in managing PAC than the presence of low concentration NaOCL.