IADR Abstract Archives
Strontium-modified peptide-loaded silicate nanoparticles for enhanced osteogenesis and antimicrobial activity
Objectives: Mesoporous calcium silicate nanostructures (CaMSN) have drawn great attention as bioactive materials for bone tissue regeneration and drug delivery applications. Incorporating strontium (Sr) within CaMSN is known to alter their degradation profile and enhance the therapeutic effects of silicates for bone regeneration. Here we aimed to develop Sr-modified CaMSN with antimicrobial peptide (AMP) cargo and assess their multi-bioactivity.
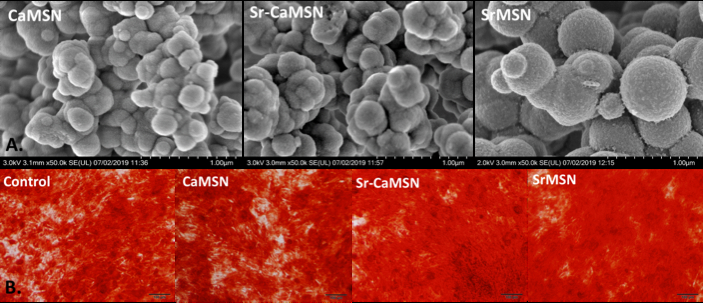
Methods: Different MSNs (CaMSN, Sr-doped CaMSN with 20:80 Sr:Ca ratio (Sr-CaMSN), and SrMSN were synthesized by sol-gel self-assembly. As-prepared MSNs were characterized using scanning electron miscroscopy with energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDS) and wide-angle x-ray diffractometry (WA-XRD). MSNs were loaded with fluorescent-labelled GL13K and release profile assessed in phosphate buffer saline. MSNs cytotoxicity (CCK8 assay) and their effects on osteogenic differentiation were assessed in a dose dependent manner with induced pluripotent stem cell derived mesenchymal stromal cells (iMSCs). Alkaline phosphatase activity, expression of osteogenesis related proteins and matrix mineralization were used to determined iMSCs early, late, and terminal osteogenic differentiation. Cells cultured in the absence of MSNs were used as control groups. Statistically significant differences were assessed by one-way ANOVA with Tukey post-hoc tests (p-value<0.05).
Results: Ca-MSNs and Sr-CaMSNs size were 200±50nm and 400± 0nm, respectively. The chemical composition was validated by EDS and WA-XRD confirmed the amorphous nature of all MSNs. Our MSNs had high AMP-loading efficiency (94±1%) and slow releasing profiles. During the first 72 h Sr-CaMSNs, Ca-MSNs and SrMSN released 17±1%, 18±2% and 40± 2%release of AMP, respectively. Statistically increased osteogenic differentiation was mediated by MSNs compared to untreated controls, from early to terminal differentiation.
Conclusions: We successfully synthesized bioactive Sr-modified CaMSNs with prolonged release of AMP release with potential for supporting bone regeneration and combating infection.
Methods: Different MSNs (CaMSN, Sr-doped CaMSN with 20:80 Sr:Ca ratio (Sr-CaMSN), and SrMSN were synthesized by sol-gel self-assembly. As-prepared MSNs were characterized using scanning electron miscroscopy with energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDS) and wide-angle x-ray diffractometry (WA-XRD). MSNs were loaded with fluorescent-labelled GL13K and release profile assessed in phosphate buffer saline. MSNs cytotoxicity (CCK8 assay) and their effects on osteogenic differentiation were assessed in a dose dependent manner with induced pluripotent stem cell derived mesenchymal stromal cells (iMSCs). Alkaline phosphatase activity, expression of osteogenesis related proteins and matrix mineralization were used to determined iMSCs early, late, and terminal osteogenic differentiation. Cells cultured in the absence of MSNs were used as control groups. Statistically significant differences were assessed by one-way ANOVA with Tukey post-hoc tests (p-value<0.05).
Results: Ca-MSNs and Sr-CaMSNs size were 200±50nm and 400± 0nm, respectively. The chemical composition was validated by EDS and WA-XRD confirmed the amorphous nature of all MSNs. Our MSNs had high AMP-loading efficiency (94±1%) and slow releasing profiles. During the first 72 h Sr-CaMSNs, Ca-MSNs and SrMSN released 17±1%, 18±2% and 40± 2%release of AMP, respectively. Statistically increased osteogenic differentiation was mediated by MSNs compared to untreated controls, from early to terminal differentiation.
Conclusions: We successfully synthesized bioactive Sr-modified CaMSNs with prolonged release of AMP release with potential for supporting bone regeneration and combating infection.