IADR Abstract Archives
Alternative Low Stress Diurethane Dimethacrylate For BisGMA-Free Resin Composites
Objectives: In recent years, concerns over BPA contamination and potential deleterious effects on patients has motivated the development of materials for dentistry free of BisGMA. The aim of this study was to create and evaluate BisGMA-free systems based on a newly synthesized diurethane dimethacrylate (2EMATE-BDI) as co-monomer for resin composites.
Methods: 2EMATE-BDI or TEGDMA were copolymerized with UDMA in 40/60 and 60/40 mass ratios. BisGMA-TEGDMA at 60/40 mass ratio served as control (BT). 0.2wt% DMPA and 0.4wt% DPI-PF6 were used as photoinitiators. Inorganic filler particles were incorporated at 70wt%. Photocuring procedures were accomplished with a mercury arc lamp (320-500nm, 800mW/cm2, Acticure). Composites were tested for kinetics of polymerization (RPMAX), polymerization stress, flexure strength (3-point bending), water stability and S. mutans biofilm formation. Data were analyzed with one-way ANOVA/Tukey’s and Student’s t-tests (α=0.05).
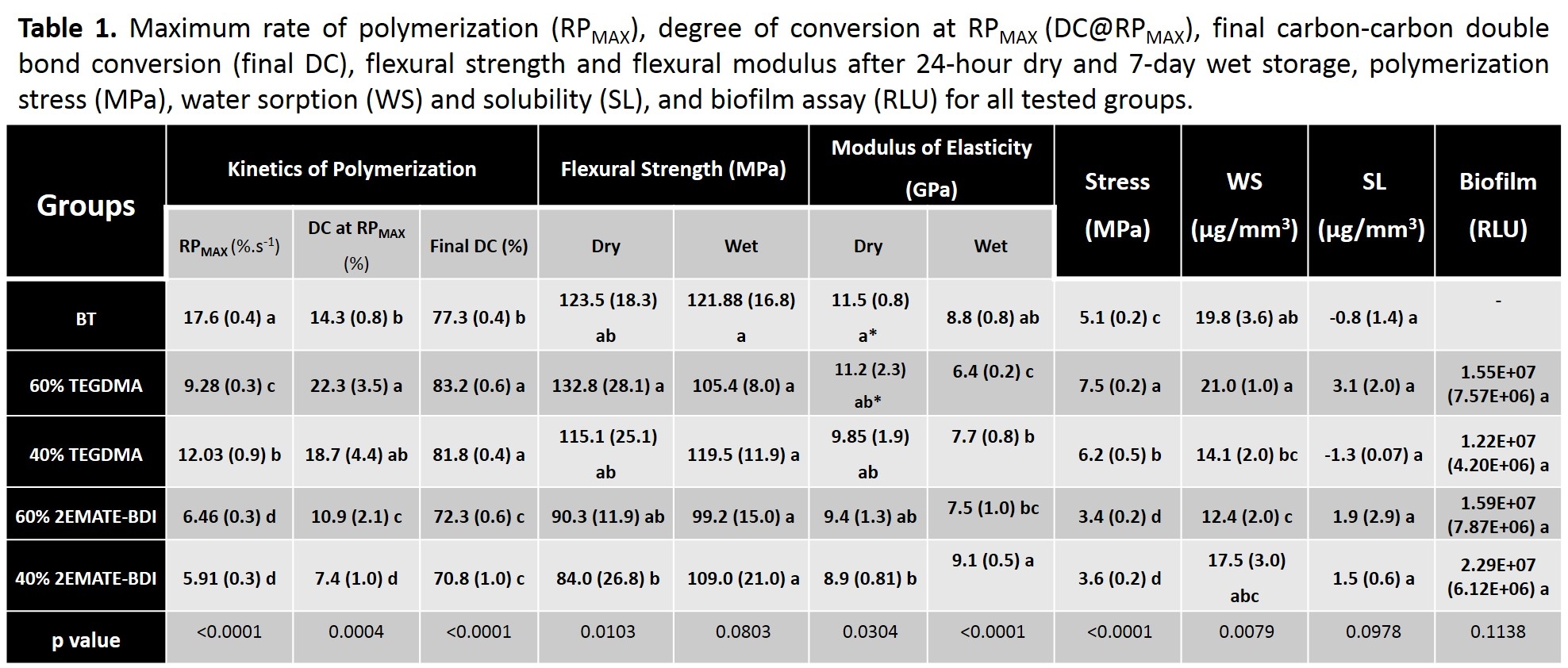
Results: Results are shown in Table 1. In general, in comparison to BT, formulations containing 2EMATE-BDI showed significant reduction in RPMAX, and slight reduction in final DC (Table). The polymerization stress for the 2EMATE-BDI-containing materials was 30% and 50% lower than BT and analog TEGDMA-containing formulations, respectively. This likely can be only partially explained by the lower conversion (less than 10% reduction). Flexural strengths were similar for all groups after 7 days in water. The elastic moduli of the 2EMATE-BDI-containing materials were equal or higher than the TEGDMA-containing materials. The incorporation of 60wt% 2EMATE-BDI decreased water sorption by 38% in comparison to BT. Biofilm formation was similar among the tested groups, which may also indicate equivalent biocompatibility.
Conclusions: The stark reduction in polymerization stress associated with the markedly enhanced hydrophobicity, and without significantly compromising mechanical properties and handling characteristics, supports the use of the newly synthesized 2EMATE-BDI monomer as a co-monomer for BisGMA-free dental resin composites.
Methods: 2EMATE-BDI or TEGDMA were copolymerized with UDMA in 40/60 and 60/40 mass ratios. BisGMA-TEGDMA at 60/40 mass ratio served as control (BT). 0.2wt% DMPA and 0.4wt% DPI-PF6 were used as photoinitiators. Inorganic filler particles were incorporated at 70wt%. Photocuring procedures were accomplished with a mercury arc lamp (320-500nm, 800mW/cm2, Acticure). Composites were tested for kinetics of polymerization (RPMAX), polymerization stress, flexure strength (3-point bending), water stability and S. mutans biofilm formation. Data were analyzed with one-way ANOVA/Tukey’s and Student’s t-tests (α=0.05).
Results: Results are shown in Table 1. In general, in comparison to BT, formulations containing 2EMATE-BDI showed significant reduction in RPMAX, and slight reduction in final DC (Table). The polymerization stress for the 2EMATE-BDI-containing materials was 30% and 50% lower than BT and analog TEGDMA-containing formulations, respectively. This likely can be only partially explained by the lower conversion (less than 10% reduction). Flexural strengths were similar for all groups after 7 days in water. The elastic moduli of the 2EMATE-BDI-containing materials were equal or higher than the TEGDMA-containing materials. The incorporation of 60wt% 2EMATE-BDI decreased water sorption by 38% in comparison to BT. Biofilm formation was similar among the tested groups, which may also indicate equivalent biocompatibility.
Conclusions: The stark reduction in polymerization stress associated with the markedly enhanced hydrophobicity, and without significantly compromising mechanical properties and handling characteristics, supports the use of the newly synthesized 2EMATE-BDI monomer as a co-monomer for BisGMA-free dental resin composites.