IADR Abstract Archives
Edge Chipping Resistance of Glass Ceramic Block for CAD/CAM
Objectives: In accordance with the dramatic progress of digital technology, lithium disilicate glass ceramic for CAD/CAM has become popular thanks to aesthetic and high strength. The chipping resistance of materials for CAD/CAM during grinding is one of the important factors for single-visit dentistry. The purpose of this study was to evaluate the edge chipping resistance of the novel lithium disilicate glass ceramic block for CAD/CAM.
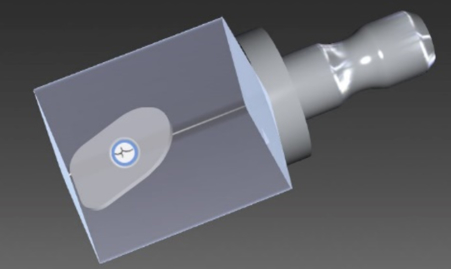
Methods: A thin flat plate(0.4mm thickness) like anterior tooth veneer was designed(Figure 1) and two different CAD/CAM blocks, Initial LiSi Block(LS, GC Corp.) and IPS e.max CAD(EM, Ivoclar Vivadent), were fabricated with CEREC MC XL(Dentsply Sirona) (n=10). The chipping area of the specimen was calculated by Photoshop CS6(Adobe Systems) after grinding test. The result was analyzed by t-test. To analyze crystal structure of each material, SEM(SU-70, HITACHI) observation was also carried out, and related crystalline surface area was calculated by image analysis software Image-J(NIH).
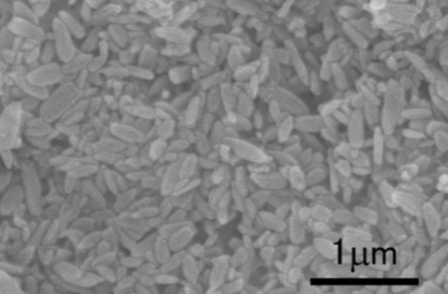
Results: All specimens of LS were not observed unacceptable edge chipping, whereas half of specimens of EM were observed it after grinding test. LS showed significantly lower chipping area compared to EM(Table 1, *: p<0.05, t-test). SEM observation confirmed high density and fine crystal precipitation in LS glass matrix(relative crystalline surface area is 71.3%) and demonstrated that LS had much smaller lithium disilicate crystals compared to EM(Figure 2).
Conclusions: Initial LiSi Block as a new lithium disilicate glass ceramic block has high chipping resistance and is a useful restorative dental material for single-visit treatment. The investigation of this study suggests that the fine and high density crystals of LS can stop crack growth and increase the edge chipping resistance.
Methods: A thin flat plate(0.4mm thickness) like anterior tooth veneer was designed(Figure 1) and two different CAD/CAM blocks, Initial LiSi Block(LS, GC Corp.) and IPS e.max CAD(EM, Ivoclar Vivadent), were fabricated with CEREC MC XL(Dentsply Sirona) (n=10). The chipping area of the specimen was calculated by Photoshop CS6(Adobe Systems) after grinding test. The result was analyzed by t-test. To analyze crystal structure of each material, SEM(SU-70, HITACHI) observation was also carried out, and related crystalline surface area was calculated by image analysis software Image-J(NIH).
Results: All specimens of LS were not observed unacceptable edge chipping, whereas half of specimens of EM were observed it after grinding test. LS showed significantly lower chipping area compared to EM(Table 1, *: p<0.05, t-test). SEM observation confirmed high density and fine crystal precipitation in LS glass matrix(relative crystalline surface area is 71.3%) and demonstrated that LS had much smaller lithium disilicate crystals compared to EM(Figure 2).
Conclusions: Initial LiSi Block as a new lithium disilicate glass ceramic block has high chipping resistance and is a useful restorative dental material for single-visit treatment. The investigation of this study suggests that the fine and high density crystals of LS can stop crack growth and increase the edge chipping resistance.