IADR Abstract Archives
Dimensional Stability of Novel Resin-Composite
Objectives: The aim was to assess the effect of Polylysine and Monocalcium Phosphate Monohydrate (MCPM) on the dimensional stability and H+ release of novel resin-composite with water aging.
Methods: Four resin-composite pastes were prepared by combining urethane dimethacrylate (UDMA) and poly(propylene glycol) dimethacrylate (PPGDMA) monomers with filler. The dental glass filler had high or low levels of Polylysine and MCPM included to promote novel dentine sealing (Table1). Composite discs (2mm thickness×10mm diameter) were prepared and light cured for 40s on top and bottom surfaces using light-emitting-diode light curing unit (Demi Plus, Kerr) (n=3). All specimens were stored in 10 mL of deionized water and incubated at 37°C. The water acidity and the weight measurements were recorded over time at 0, 2, 4, 6, 24, 48, 72 hours of storage and then every week. Mass and volume change and H+ release were calculated for 11 weeks. The polymerization shrinkage was calculated as a percentage using Archimedes principal and ISO 17304:2013. Factorial analysis for two variables (MCPM and Polylysine) was used to assess the effect of variables on properties of composites (α=0.05).
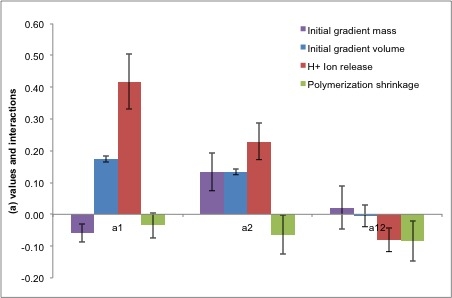
Results: After 4 weeks, mass changes were -0.85(±0.2), 0.13(±0.1), 1.1(±0.1) and 1.2(0.1) and volume changes were 3.7(±0.1), 3.7(±0.1), 3.9(±0.3) and 2.6(±0.1) for F16-8, F16-4, F8-8 and F8-4, respectively. The highest average H+ release by 11 weeks was 20mmol/L (±1.5%) and the lowest was 5.5mmol/L (±1.1%). The polymerization shrinkage ranged between 2.96% to 3.98%. Polylysine significantly influenced mass change (p<0.005). Both components had a significant impact on volume change, H+ release and polymerization shrinkage (p<0.005) (Figure1).
Conclusions: Based on the findings of this study the following can be concluded:
The increase of Polylysine led to higher mass change.
The increase of MCPM and Polylysine led to higher H+ release, volume change and lower polymerization shrinkage.
Methods: Four resin-composite pastes were prepared by combining urethane dimethacrylate (UDMA) and poly(propylene glycol) dimethacrylate (PPGDMA) monomers with filler. The dental glass filler had high or low levels of Polylysine and MCPM included to promote novel dentine sealing (Table1). Composite discs (2mm thickness×10mm diameter) were prepared and light cured for 40s on top and bottom surfaces using light-emitting-diode light curing unit (Demi Plus, Kerr) (n=3). All specimens were stored in 10 mL of deionized water and incubated at 37°C. The water acidity and the weight measurements were recorded over time at 0, 2, 4, 6, 24, 48, 72 hours of storage and then every week. Mass and volume change and H+ release were calculated for 11 weeks. The polymerization shrinkage was calculated as a percentage using Archimedes principal and ISO 17304:2013. Factorial analysis for two variables (MCPM and Polylysine) was used to assess the effect of variables on properties of composites (α=0.05).
Results: After 4 weeks, mass changes were -0.85(±0.2), 0.13(±0.1), 1.1(±0.1) and 1.2(0.1) and volume changes were 3.7(±0.1), 3.7(±0.1), 3.9(±0.3) and 2.6(±0.1) for F16-8, F16-4, F8-8 and F8-4, respectively. The highest average H+ release by 11 weeks was 20mmol/L (±1.5%) and the lowest was 5.5mmol/L (±1.1%). The polymerization shrinkage ranged between 2.96% to 3.98%. Polylysine significantly influenced mass change (p<0.005). Both components had a significant impact on volume change, H+ release and polymerization shrinkage (p<0.005) (Figure1).
Conclusions: Based on the findings of this study the following can be concluded:
The increase of Polylysine led to higher mass change.
The increase of MCPM and Polylysine led to higher H+ release, volume change and lower polymerization shrinkage.