IADR Abstract Archives
Comparison of 3 Occlusal Splint Designs on the EMG Muscle Activity of Masticatory Muscles During Clenching and Excursive Movements
Objectives: This study compared the effect of anterior (MCI), soft (Proform [PF]) and full arch stabilization (SS) splints on the EMG activity of masticatory muscles during clenching. It was hypothesized that anterior splints will reduce both temporalis and masseteric muscle activity in contrast to other splints evaluated. The null hypothesis was that there would be no difference between the splints in the EMG activity measured.
Methods: Twelve patients with bruxism and no debilitating TMD/psychological distress and 3 aged-matched controls were recruited. Mean age of the subjects was 23.5 years. A cross-over design was used where the EMG activity of subjects were measured after insertion of each splint type. Subjects were randomised into 3 groups (with a control in each group) and tested in the following sequence: Group 1 – SS, MCI, PF; Group 2 – MCI, PF, SS; Group 3 – PF, SS, MCI. EMG measurements were repeated 3 times for each splint, with a 5 mins interval between each splint type. Results were analyzed using Kruskal Wallis and Mann-Whitney Test (p<0.05).
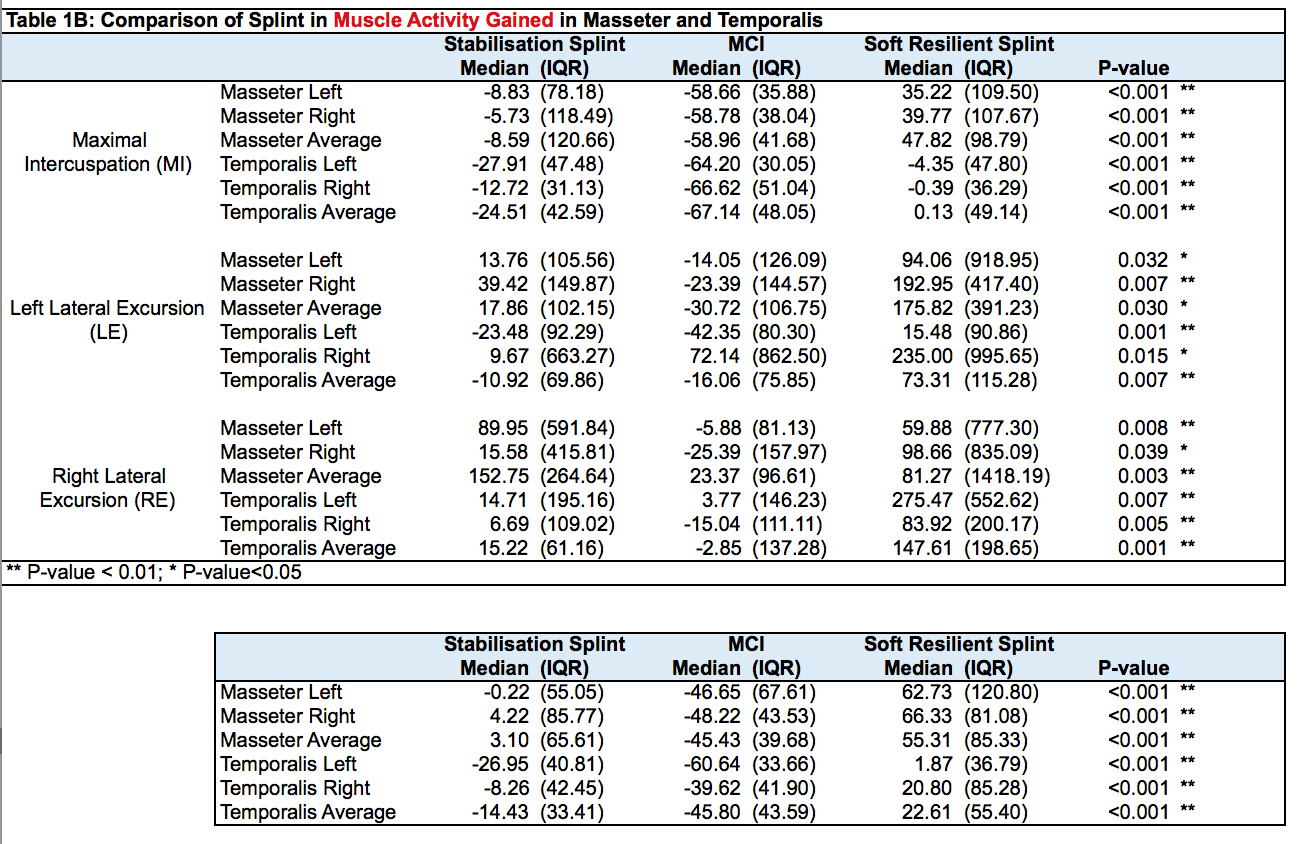
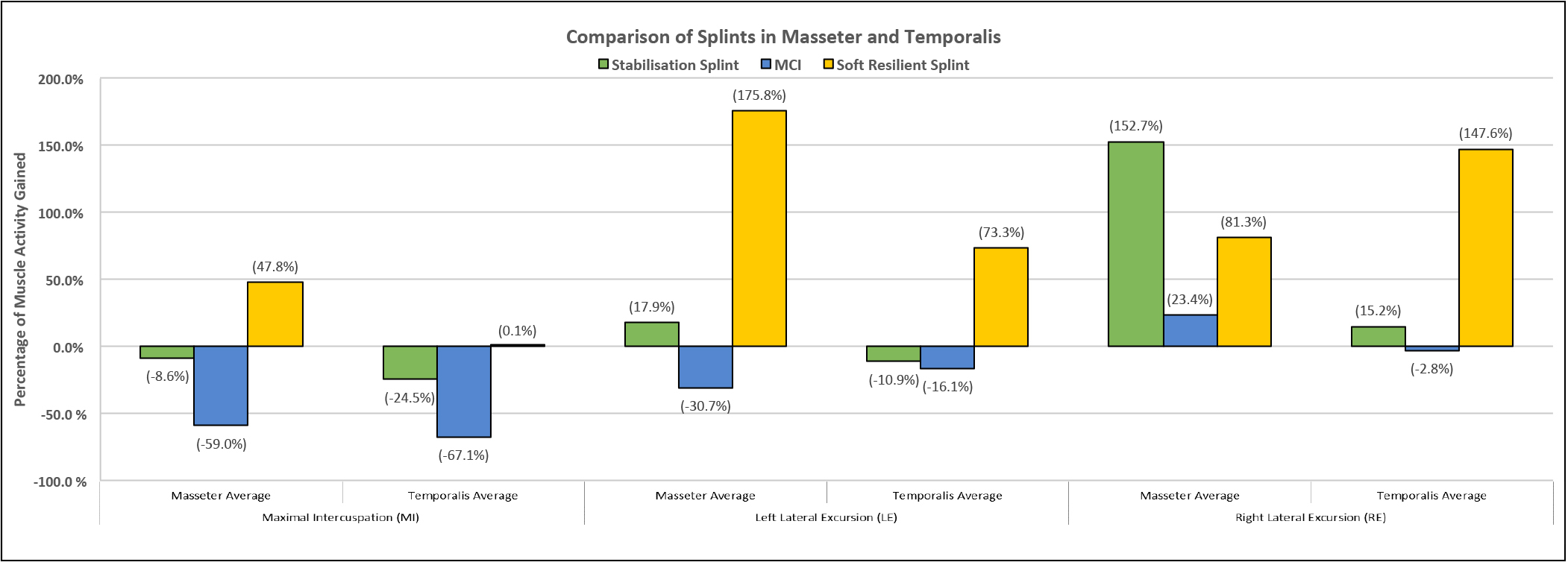
Results: During MI, average percentage gain in masseter EMG ranged from 47.8% (PF) to -59.0% (MCI) while gain in temporalis EMG ranged from 0.1% (PF) to -67.1% (MCI).
During Left Lateral Excursion, average percentage gain in masseter EMG ranged from 47.8% (PF) to -59.0% (MCI) while gain in temporalis EMG ranged from 73.3% (PF) to -16.1% (MCI).
During Right Lateral Excursion, average percentage gain in masseter EMG ranged from 152.7% (SS) to 23.4% (MCI) while gain in temporalis EMG ranged from 147.6% (PF) to -2.8% (MCI) .
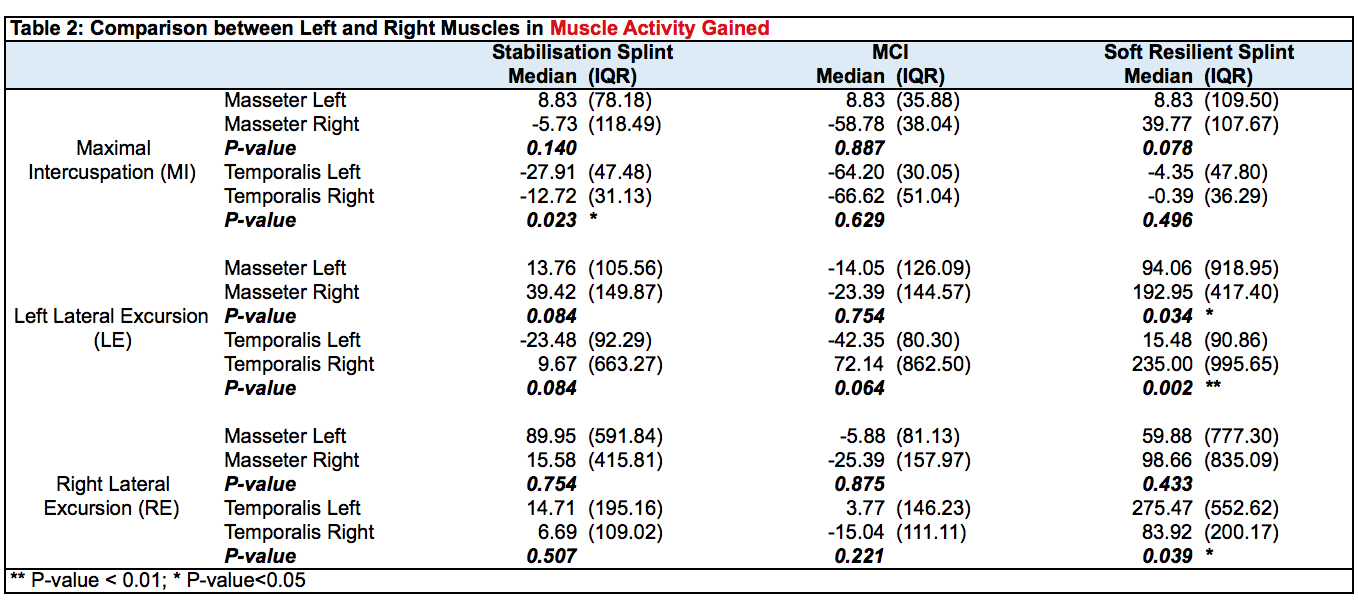
Statistically significant differences in percentage EMG reduction were observed for both temporalis and masseteric muscles between the splints during MI, left lateral excursion and right lateral excursion (p<0.05).
The general trend (most reduction to least reduction) for all scenarios were as follows: Masseter – MCI > SS > PF; Temporalis – MCI > SS, PF, except for Masseter EMG muscle activity during right lateral excursion (MCI > PF > SS).
Conclusions: The use of soft or full arch stabilization splints may increase masticatory muscle activity during clenching and excursive movements. Anterior splints were effective in reducing both temporalis and masseteric muscle activity during clenching.
Methods: Twelve patients with bruxism and no debilitating TMD/psychological distress and 3 aged-matched controls were recruited. Mean age of the subjects was 23.5 years. A cross-over design was used where the EMG activity of subjects were measured after insertion of each splint type. Subjects were randomised into 3 groups (with a control in each group) and tested in the following sequence: Group 1 – SS, MCI, PF; Group 2 – MCI, PF, SS; Group 3 – PF, SS, MCI. EMG measurements were repeated 3 times for each splint, with a 5 mins interval between each splint type. Results were analyzed using Kruskal Wallis and Mann-Whitney Test (p<0.05).
Results: During MI, average percentage gain in masseter EMG ranged from 47.8% (PF) to -59.0% (MCI) while gain in temporalis EMG ranged from 0.1% (PF) to -67.1% (MCI).
During Left Lateral Excursion, average percentage gain in masseter EMG ranged from 47.8% (PF) to -59.0% (MCI) while gain in temporalis EMG ranged from 73.3% (PF) to -16.1% (MCI).
During Right Lateral Excursion, average percentage gain in masseter EMG ranged from 152.7% (SS) to 23.4% (MCI) while gain in temporalis EMG ranged from 147.6% (PF) to -2.8% (MCI) .
Statistically significant differences in percentage EMG reduction were observed for both temporalis and masseteric muscles between the splints during MI, left lateral excursion and right lateral excursion (p<0.05).
The general trend (most reduction to least reduction) for all scenarios were as follows: Masseter – MCI > SS > PF; Temporalis – MCI > SS, PF, except for Masseter EMG muscle activity during right lateral excursion (MCI > PF > SS).
Conclusions: The use of soft or full arch stabilization splints may increase masticatory muscle activity during clenching and excursive movements. Anterior splints were effective in reducing both temporalis and masseteric muscle activity during clenching.