IADR Abstract Archives
Displacement of Resin Composite Restorations Due to Polymerization Shrinkage
Objectives: Polymerization shrinkage causes displacement of composite restorations at its unbound surface/s. Debonding at the floor of a Class-I cavity causes the displacement to be distributed between the surface and base of the restoration. This study compared the amount and distribution of displacement of a fully and partially bonded composite restoration.
Methods: Class-I cavities of approximately 4x4x3mm3 were prepared in 10 extracted molars and randomly divided into two groups: Group 1 (G1) - bonded at all surfaces; Group 2 (G2) – bonded at the walls only. Cavities were then filled with a bulk-fill material (3M ESPE). Micro-computed tomography (micro-CT) images were taken pre- and post-curing of the restorations. For both groups, total linear displacement was measured (DmT) while for G2, the measurements were further divided into surface (DmS) and base (DmB) displacements. The linear displacement was also predicted (Dp) by multiplying the volumetric shrinkage strain (1.84%) by the height of the restoration. One-way ANOVA was used to compare mean of DmT between groups and Intraclass Correlation Coefficient (ICC), to assess the agreement between DmT and Dp. The pre- and post-cured 3D images were also subjected to image subtraction to illustrate the distribution of linear displacement.
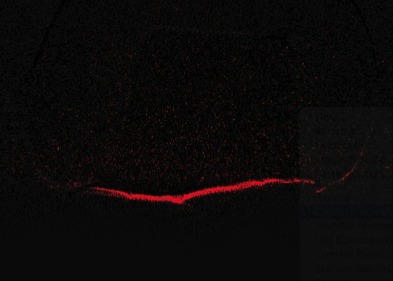
Results: The measurements normalized to a 3-mm deep restoration. One-way ANOVA showed no significant difference of DmT between the groups (p>0.05). Paired T-test showed that there was no significant difference between DmT and Dp in both groups (p>0.05). The ICC between DmT and Dp was 0.60. The subtracted images clearly identify the displacement areas with the highest displacement occurring at the middle of the unbounded surfaces (Figure 1).
Conclusions: Measurement of displacements due to polymerization shrinkage concurred with those derived theoretically. About 60% of the displacement of floor-debonded composite restoration occurred at the base, indicating that debonding extended to the walls.
Methods: Class-I cavities of approximately 4x4x3mm3 were prepared in 10 extracted molars and randomly divided into two groups: Group 1 (G1) - bonded at all surfaces; Group 2 (G2) – bonded at the walls only. Cavities were then filled with a bulk-fill material (3M ESPE). Micro-computed tomography (micro-CT) images were taken pre- and post-curing of the restorations. For both groups, total linear displacement was measured (DmT) while for G2, the measurements were further divided into surface (DmS) and base (DmB) displacements. The linear displacement was also predicted (Dp) by multiplying the volumetric shrinkage strain (1.84%) by the height of the restoration. One-way ANOVA was used to compare mean of DmT between groups and Intraclass Correlation Coefficient (ICC), to assess the agreement between DmT and Dp. The pre- and post-cured 3D images were also subjected to image subtraction to illustrate the distribution of linear displacement.
Results: The measurements normalized to a 3-mm deep restoration. One-way ANOVA showed no significant difference of DmT between the groups (p>0.05). Paired T-test showed that there was no significant difference between DmT and Dp in both groups (p>0.05). The ICC between DmT and Dp was 0.60. The subtracted images clearly identify the displacement areas with the highest displacement occurring at the middle of the unbounded surfaces (Figure 1).
Conclusions: Measurement of displacements due to polymerization shrinkage concurred with those derived theoretically. About 60% of the displacement of floor-debonded composite restoration occurred at the base, indicating that debonding extended to the walls.