IADR Abstract Archives
Can CAD/CAM Resin Blocks be Considered as a Substitute to Conventional Resins?
Objectives: Studies on commercial CAD/CAM resin blocks are done with the aim of comparing these to ceramic materials for CAD/CAM application. Few studies comparing both composition and mechanical properties to the conventional composite materials. Many of the new materials have scarce scientific evidence, except from the producer’s description and in-house laboratory testing of the material. The aim of the study was to evaluate if they outperform conventional composites, and as such, represent a cost-benefit for dental patients and practitioners?
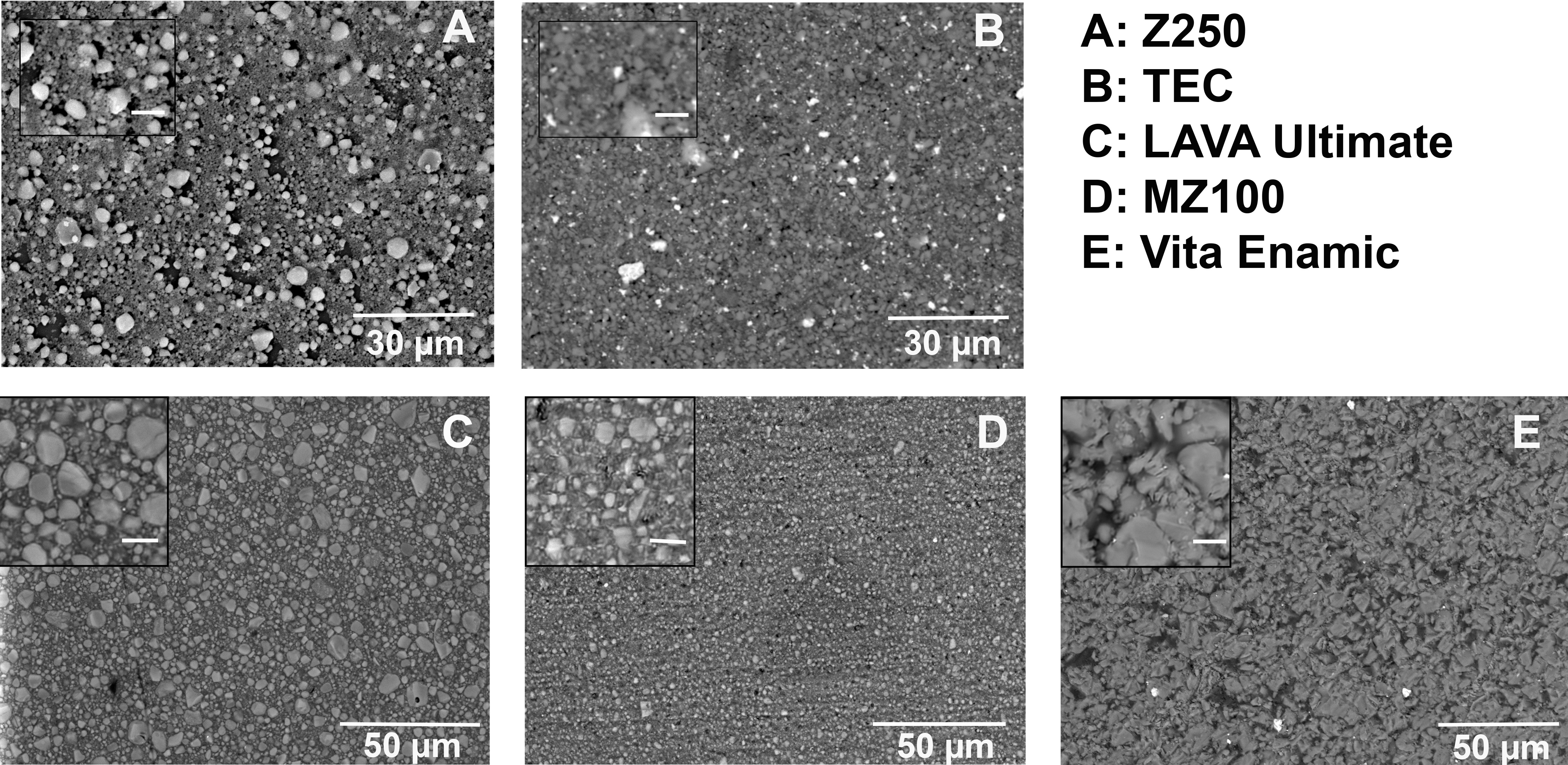
Methods: We evaluated and compared the monomer elution, cytotoxicity, morphology of filler particles, filler volume, filler content and hardness of three prepolymerized into ready-to-mill blocks RBC ((Lava Ultimate (LAVA), Vita Enamic (VITA), Paradigm MZ100 (MZ100) for CAD/CAM with two of the most used conventional composites in Norway (Filtek Z250 (Z250) and Tetric EvoCeram (TEC) ).
Results: None of the CAD/CAM materials showed leakage of monomers tested. Z 250 showed low values of bis-GMA (<0.1ppm). TEC showed higher elution of bis-GMA than all the other materials. Vita showed the statistic significant highest content of filler wt% and Lava had the lowest.
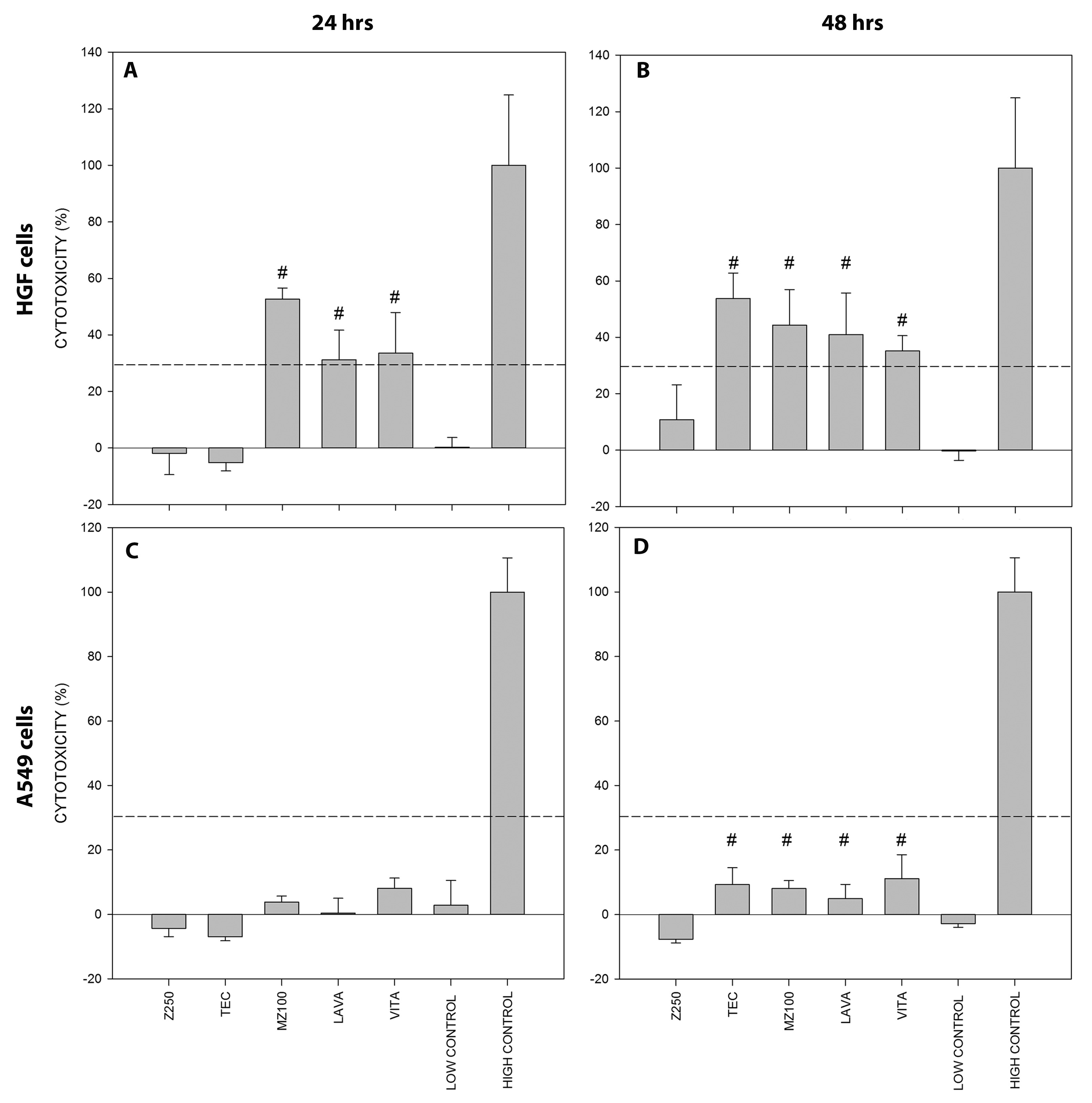
LAVA, VITA and MZ100 showed significantly higher LDH activity compared to the low control group, showing all of these groups cytotoxicity values above 30% (Fig. 1). We did not detect any elution of monomers, so we cannot contribute the high cytotoxicity to elution of monomers. There might be some monomers that our tests did not detect and therefore this should be investigated thoroughly. Cytotoxicity can also be contributed to filler fractions of the material; there might be some particles on the surface that can contribute to cell death. However this should be further investigated.
Conclusions: Our null hypothesis that there is no difference between resin blocks for CAD/CAM and conventional composite was falsified and rejected. The RBC outperformed conventional composite regarding mechanical characteristics (hardness), but showed some worrisome results regarding material safety (cytotoxicity). By today the cost-benefit is not superior for RBCs. There were also differences between the CAD/CAM materials internally. More studies regarding material safety and mechanical characteristics should be performed.
Methods: We evaluated and compared the monomer elution, cytotoxicity, morphology of filler particles, filler volume, filler content and hardness of three prepolymerized into ready-to-mill blocks RBC ((Lava Ultimate (LAVA), Vita Enamic (VITA), Paradigm MZ100 (MZ100) for CAD/CAM with two of the most used conventional composites in Norway (Filtek Z250 (Z250) and Tetric EvoCeram (TEC) ).
Results: None of the CAD/CAM materials showed leakage of monomers tested. Z 250 showed low values of bis-GMA (<0.1ppm). TEC showed higher elution of bis-GMA than all the other materials. Vita showed the statistic significant highest content of filler wt% and Lava had the lowest.
LAVA, VITA and MZ100 showed significantly higher LDH activity compared to the low control group, showing all of these groups cytotoxicity values above 30% (Fig. 1). We did not detect any elution of monomers, so we cannot contribute the high cytotoxicity to elution of monomers. There might be some monomers that our tests did not detect and therefore this should be investigated thoroughly. Cytotoxicity can also be contributed to filler fractions of the material; there might be some particles on the surface that can contribute to cell death. However this should be further investigated.
Conclusions: Our null hypothesis that there is no difference between resin blocks for CAD/CAM and conventional composite was falsified and rejected. The RBC outperformed conventional composite regarding mechanical characteristics (hardness), but showed some worrisome results regarding material safety (cytotoxicity). By today the cost-benefit is not superior for RBCs. There were also differences between the CAD/CAM materials internally. More studies regarding material safety and mechanical characteristics should be performed.