IADR Abstract Archives
Comparative Analysis of Diabetic and Non-Diabetic Patients With Periodontal Disease
Objectives: The relationships between periodontal disease (PD) and diabetes, PD with infectious disease, neurologic conditions, gastric/hepatic/intestinal disorders, skin, retinal problems, and obesity have been documented. However, there has not been much done to establish the relationships and effect in diabetes. This study assesses diabetics (DM) and non-diabetics (N-DM) with PD, utilizing the health history and dental examination information in a dental school clinic.
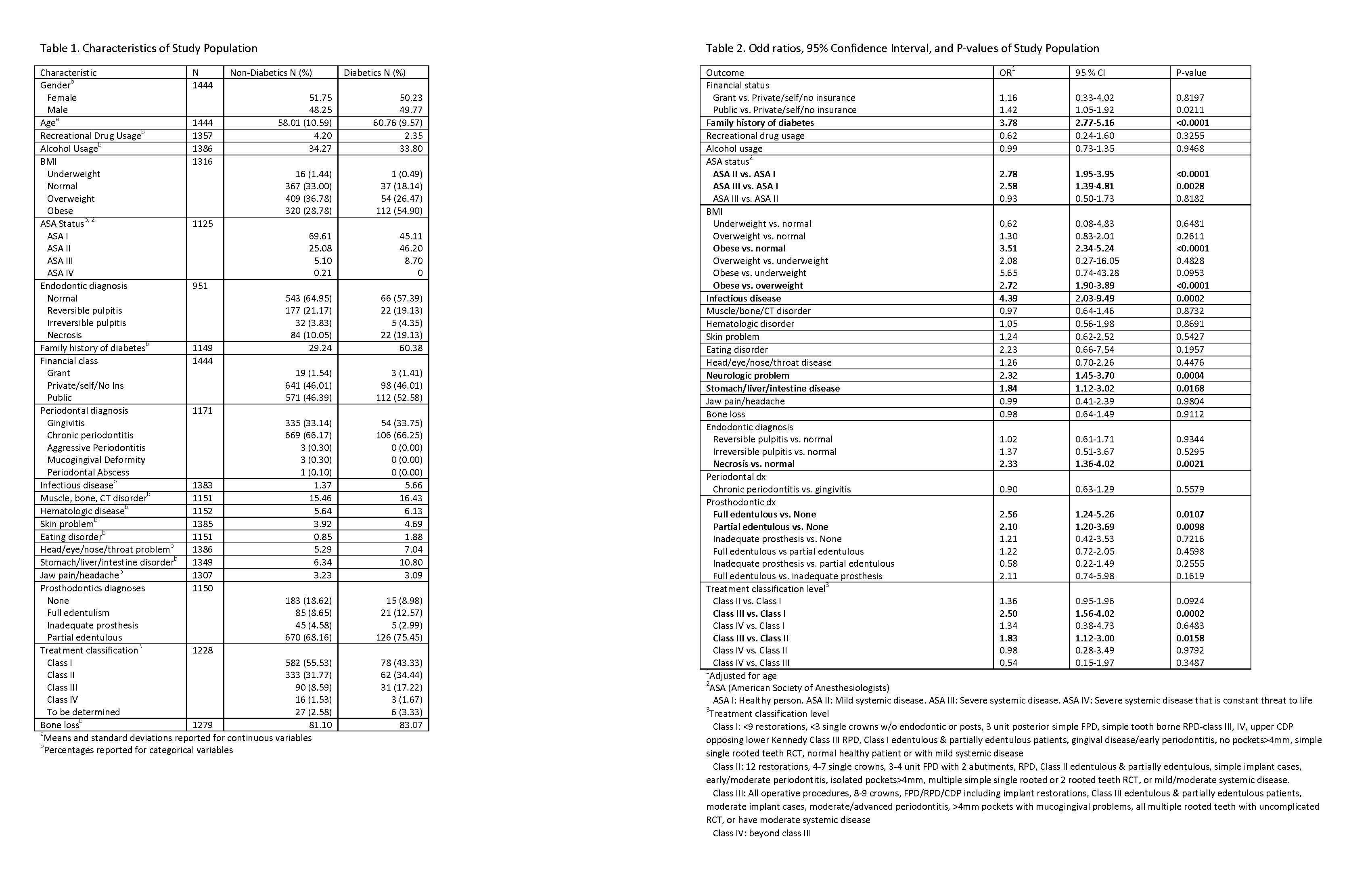
Methods: In a five-year retrospective chart review, 302 records of 40+ year-old DM with PD and 1231 records of 40+ year-old N with PD were collected. The demographic profiles and the self-reported health history (alcohol/ drug usage, infectious disease (ID), neurologic conditions (NC), muscle/bone/connective tissue disease (MBCT), hematologic disease, eating disorder, skin, head/eye/nose/throat problem, gastric/hepatic/intestinal (SLI), jaw pain/headache), and ASA classifications were collected. The intra-oral findings (Endodontics /Prosthodontics diagnosis, treatment classification) were collected. BMI was calculated. Data were compared between DM and N-DM by logistic regression and multinomial logistic regression, adjusting for age.
Results: DM with PD had significant associations with ID (OR: 4.39, 95% CI: 2.03-9.49), NC (OR: 2.32, 95%CI: 1.45-3.70), and SLI (OR: 1.84, 95%CI: 1.12-3.02). Significant associations were found comparing DM to N-DM and class III vs. I treatment (OR: 2.5, CI 1.56-4.02), class III vs. II treatment (OR: 1.834, 95% CI: 1.12-3.00), obese vs. normal-weight (OR: 3.51, 95%CI: 2.34-5.24), overweight vs. obese (OR: 2.72, 95%CI: 1.90-3.89), ASAII vs. I (OR: 2.78, 95%CI: 1.95-3.95), necrosis vs. normal endodontics (OR: 2.34, 95%CI: 1.36-4.02), Prosthodontics full edentulous vs. none (OR: 2.56, 95%CI: 1.24-5.26).
Conclusions: These findings support the association of PD with diabetes requiring advanced dental care, and having ID, NC, and SLI. No significant association was found with eating disorder, jaw pain/headache, MBCT, hematologic diseases. Further investigation to understand diabetes and periodontal disease with different comorbidities is needed.
Methods: In a five-year retrospective chart review, 302 records of 40+ year-old DM with PD and 1231 records of 40+ year-old N with PD were collected. The demographic profiles and the self-reported health history (alcohol/ drug usage, infectious disease (ID), neurologic conditions (NC), muscle/bone/connective tissue disease (MBCT), hematologic disease, eating disorder, skin, head/eye/nose/throat problem, gastric/hepatic/intestinal (SLI), jaw pain/headache), and ASA classifications were collected. The intra-oral findings (Endodontics /Prosthodontics diagnosis, treatment classification) were collected. BMI was calculated. Data were compared between DM and N-DM by logistic regression and multinomial logistic regression, adjusting for age.
Results: DM with PD had significant associations with ID (OR: 4.39, 95% CI: 2.03-9.49), NC (OR: 2.32, 95%CI: 1.45-3.70), and SLI (OR: 1.84, 95%CI: 1.12-3.02). Significant associations were found comparing DM to N-DM and class III vs. I treatment (OR: 2.5, CI 1.56-4.02), class III vs. II treatment (OR: 1.834, 95% CI: 1.12-3.00), obese vs. normal-weight (OR: 3.51, 95%CI: 2.34-5.24), overweight vs. obese (OR: 2.72, 95%CI: 1.90-3.89), ASAII vs. I (OR: 2.78, 95%CI: 1.95-3.95), necrosis vs. normal endodontics (OR: 2.34, 95%CI: 1.36-4.02), Prosthodontics full edentulous vs. none (OR: 2.56, 95%CI: 1.24-5.26).
Conclusions: These findings support the association of PD with diabetes requiring advanced dental care, and having ID, NC, and SLI. No significant association was found with eating disorder, jaw pain/headache, MBCT, hematologic diseases. Further investigation to understand diabetes and periodontal disease with different comorbidities is needed.