IADR Abstract Archives
Correlating a New Depth-of-cure Test Against Light-attenuation-coefficient and ISO-4049
Objectives: (1) To investigate the correlating strength of the ISO 4049 depth-of-cure (DoCISO) method against the depth-of-cure (DoC), determined by an attenuation-coefficient method, and the degree-of-polymerization (DegPoly), determined by the Fourier transform infrared attenuated total reflection (FTIR-ATR) spectroscopy, and (2) to evaluate whether a new depth-of-cure (DoCNew) method, utilizing various stainless steel (SS) cylindrical molds, having modified diameters and heights, can better approximate the DoC and DegPoly than the standard DoCISO method.
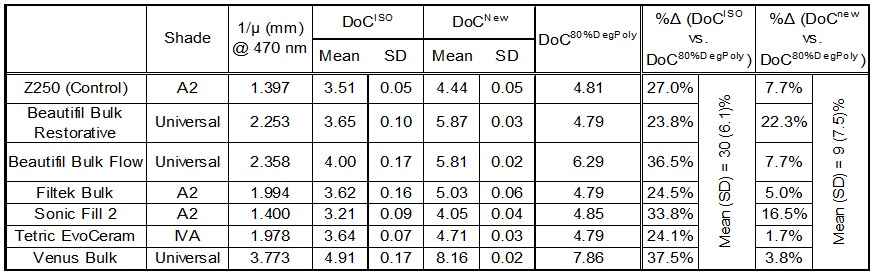
Methods: DoCISO and DoCNew values were measured according to DoCISO and DoCNew methods respectively for all specimens (n=3/group). Paradigm (3M-ESPE) curing light was used to cure all specimens. In the DoCnew method, molds (Ø=10mm with various heights) were used. Similarly, four cylindrical specimens of varying thicknesses per composite brand were made. Then, using an integrating sphere (LabSphere), the transmitted-versus-incident curing-light intensities were measured as a function of specimen thicknesses from which the total attenuation coefficients (μT) were calculated. Finally, the DegPoly per composite brand were measured as a function of specimen thicknesses, and these data were used to predict the curing depth at which a composite polymerization has dropped to 80% of its bottom-to-top-surface DegPoly ratio (DoC80%DegPoly). Data were analyzed with statistical regressions and unpaired t-test (α=0.05).
Results: Significant differences (p<0.01) were found between the DoCISO and DoCNew mean values for all composite brands. Bivariate regression analysis demonstrated that (1/μT) correlated slightly better with DoCNew values (r2=0.968) than with DoCISO values (r2=0.938). For all composite brands, the overall mean percent deviation between DoCISO and DoC80%DegPoly (30±6.1%) was significantly different (p<0.01) than between DoCNew and DoC80%DegPoly (9±7.5%).
Conclusions: The DoCNew method provided a lower overall percent deviation than DoCISO method when compared to the DoC80%DegPoly values. The DoCNew method is a suitable alternative to the attenuation coefficient measurement and DoCISO standard.
Methods: DoCISO and DoCNew values were measured according to DoCISO and DoCNew methods respectively for all specimens (n=3/group). Paradigm (3M-ESPE) curing light was used to cure all specimens. In the DoCnew method, molds (Ø=10mm with various heights) were used. Similarly, four cylindrical specimens of varying thicknesses per composite brand were made. Then, using an integrating sphere (LabSphere), the transmitted-versus-incident curing-light intensities were measured as a function of specimen thicknesses from which the total attenuation coefficients (μT) were calculated. Finally, the DegPoly per composite brand were measured as a function of specimen thicknesses, and these data were used to predict the curing depth at which a composite polymerization has dropped to 80% of its bottom-to-top-surface DegPoly ratio (DoC80%DegPoly). Data were analyzed with statistical regressions and unpaired t-test (α=0.05).
Results: Significant differences (p<0.01) were found between the DoCISO and DoCNew mean values for all composite brands. Bivariate regression analysis demonstrated that (1/μT) correlated slightly better with DoCNew values (r2=0.968) than with DoCISO values (r2=0.938). For all composite brands, the overall mean percent deviation between DoCISO and DoC80%DegPoly (30±6.1%) was significantly different (p<0.01) than between DoCNew and DoC80%DegPoly (9±7.5%).
Conclusions: The DoCNew method provided a lower overall percent deviation than DoCISO method when compared to the DoC80%DegPoly values. The DoCNew method is a suitable alternative to the attenuation coefficient measurement and DoCISO standard.