IADR Abstract Archives
Electronic Cigarettes Exacerbate Virulence Potential in the Disease-naive Subgingival Microbiome
Objectives: 20.4 million individuals use electronic cigarettes(e-cigs), partly due to a perception that they are safer than cigarettes. Although the initial point of contact of e-cigs, and the first-affected system, is the oral cavity, its effects on the oral microbiome are little studied. Therefore, the present investigation aimed to investigate the effects of e-cigs on the subgingival microbiome.
Methods: Subgingival plaque samples were collected from 100 periodontally and systemically healthy individuals from 5 groups: e-cig users (E), cigarette smokers (S), dual users (SE), former smokers currently using e-cigs (FSE), and controls (NSNE). Whole genome shotgun-sequencing was used for functional and taxonomic characterization. The findings were validated using an in vitro biofilm model.
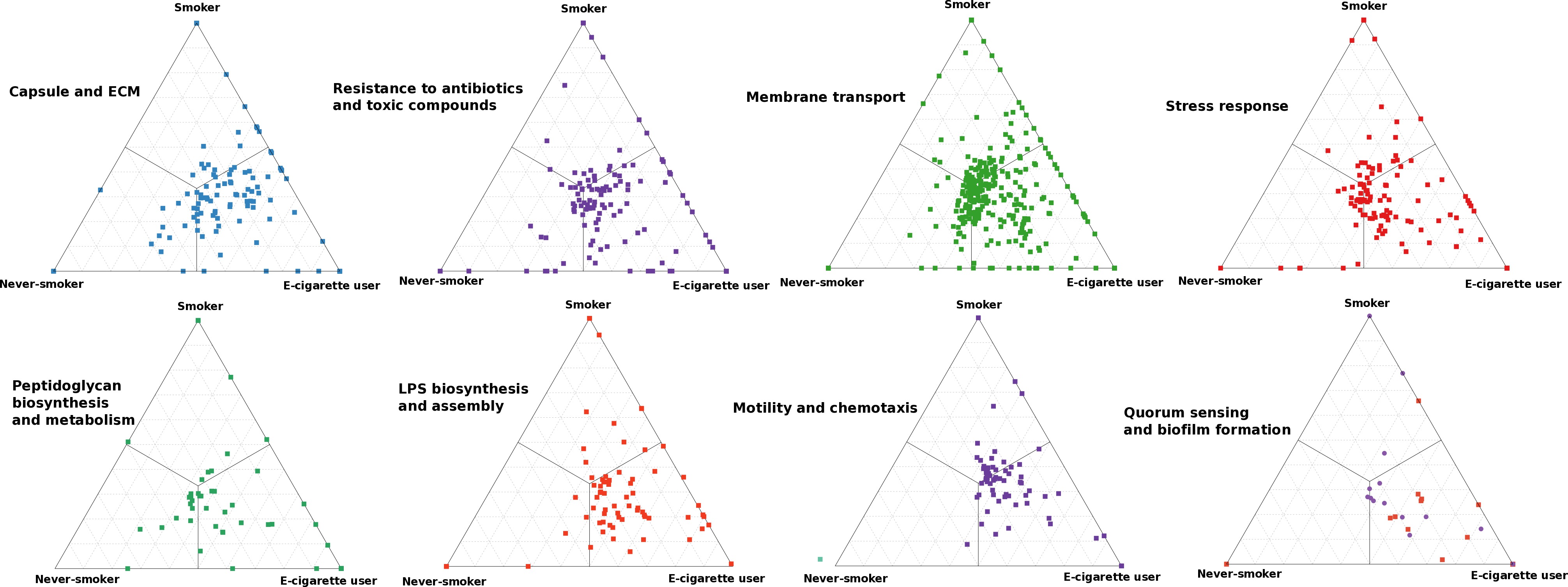
Results: 8879 functionally-annotated genes were identified in the e-cig microbiome, over one-third of which were found in all individuals in the E, SE and FSE groups. By contrast, individuals in S and NSNE groups shared a maximum of 15% of their genes. E-cig users were functionally and taxonomically distinct from both smokers and nonsmokers. 1353 genes were unique to E, SE and FSE groups, encoding for antibiotic-resistance, motility-chemotaxis, stress-response, horizontal gene- transfer, cell-wall, iron-acquisition, and membrane-transport. These functionalities were encoded by several known pathogens, belonging to the genera Fusobacteria, Treponema, Prevotella and Bacteroides, as well as to several as-yet-uncultivated-species. E, SE, and FSE groups were compositionally and functionally similar. These differences in functional-potential were also evident at the transcriptional level. 51 biomarkers of e-cig exposure were identified.
Conclusions: The risk-for-harm associated with e-cigs may be similar to or greater than smoking. The similarity in the microbiomes of former, current or never smokers who use e-cigs does not support the hypothesis that e-cigs promote harm-reduction in cigarette-smokers. The pathogen and virulence enrichment observed in clinically healthy individuals might augur the emergence of a new risk factor for periodontal diseases.
Methods: Subgingival plaque samples were collected from 100 periodontally and systemically healthy individuals from 5 groups: e-cig users (E), cigarette smokers (S), dual users (SE), former smokers currently using e-cigs (FSE), and controls (NSNE). Whole genome shotgun-sequencing was used for functional and taxonomic characterization. The findings were validated using an in vitro biofilm model.
Results: 8879 functionally-annotated genes were identified in the e-cig microbiome, over one-third of which were found in all individuals in the E, SE and FSE groups. By contrast, individuals in S and NSNE groups shared a maximum of 15% of their genes. E-cig users were functionally and taxonomically distinct from both smokers and nonsmokers. 1353 genes were unique to E, SE and FSE groups, encoding for antibiotic-resistance, motility-chemotaxis, stress-response, horizontal gene- transfer, cell-wall, iron-acquisition, and membrane-transport. These functionalities were encoded by several known pathogens, belonging to the genera Fusobacteria, Treponema, Prevotella and Bacteroides, as well as to several as-yet-uncultivated-species. E, SE, and FSE groups were compositionally and functionally similar. These differences in functional-potential were also evident at the transcriptional level. 51 biomarkers of e-cig exposure were identified.
Conclusions: The risk-for-harm associated with e-cigs may be similar to or greater than smoking. The similarity in the microbiomes of former, current or never smokers who use e-cigs does not support the hypothesis that e-cigs promote harm-reduction in cigarette-smokers. The pathogen and virulence enrichment observed in clinically healthy individuals might augur the emergence of a new risk factor for periodontal diseases.