IADR Abstract Archives
Surface Roughness Analysis of CAD/CAM Milled Materials
Objectives: To analyze the surface roughness of different computer-aided design/ computer-aided manufacturing (CAD/CAM) materials using three axis milling machine.
Methods: Five dental ceramics were used in this study: 1. Lithium disilicate glass ceramic, IPS e.max CAD, Ivoclar Vivadent. 2. Leucite-reinforced glass ceramic, IPS Empress CAD, Ivoclar Vivadent. 3. Hybrid ceramic, Enamic, VITA. 4. Feldspathic porcelain, Vitablocks MarkII, VITA. 5. Nanoceramic filled composite, Lava ultimate, 3M.
Ten rectangular bar specimens with dimension of 4×4×16mm designed by Sirona inLab software system (SW4 4.2.5) were milled with a CEREC inLab MC XL using a new set of burs (cylinder and step) for each material. After milling each surface of the milled bars was labelled as cylinder bur milled, step bur milled and side (mixed bur milled) surfaces. The surface roughness (Ra) was measured using profilometer (Surftest SJ-201, Mitutoyo) on each designated surface. Average value of three readings were taken in the cylinder bur surface and the step bur surface and one reading in each side of the bar. The comparison of Ra on different surface locations and different materials were analyzed by two-way ANOVA using JMP12.0 with α=0.05.
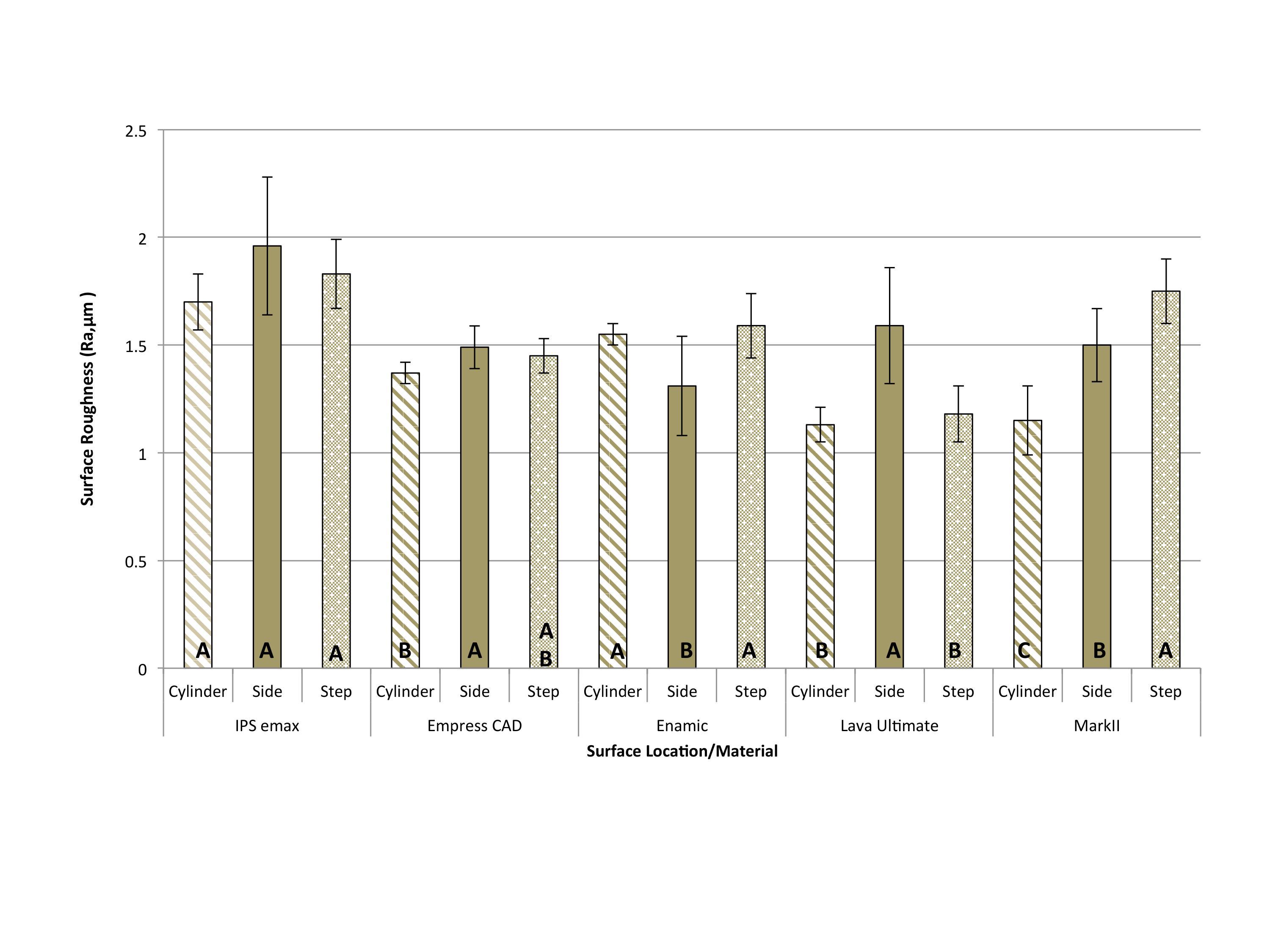
Results: Surface roughness on different materials and surface locations is shown in Figure 1. The surface roughness was significantly associated with the material type and milling surface locations.
Conclusions: The surface roughness was affected by the material type, as the ceramic materials had a higher roughness values than composite materials.
In general, step and side surfaces had higher roughness values than cylinder bur surface.
Methods: Five dental ceramics were used in this study: 1. Lithium disilicate glass ceramic, IPS e.max CAD, Ivoclar Vivadent. 2. Leucite-reinforced glass ceramic, IPS Empress CAD, Ivoclar Vivadent. 3. Hybrid ceramic, Enamic, VITA. 4. Feldspathic porcelain, Vitablocks MarkII, VITA. 5. Nanoceramic filled composite, Lava ultimate, 3M.
Ten rectangular bar specimens with dimension of 4×4×16mm designed by Sirona inLab software system (SW4 4.2.5) were milled with a CEREC inLab MC XL using a new set of burs (cylinder and step) for each material. After milling each surface of the milled bars was labelled as cylinder bur milled, step bur milled and side (mixed bur milled) surfaces. The surface roughness (Ra) was measured using profilometer (Surftest SJ-201, Mitutoyo) on each designated surface. Average value of three readings were taken in the cylinder bur surface and the step bur surface and one reading in each side of the bar. The comparison of Ra on different surface locations and different materials were analyzed by two-way ANOVA using JMP12.0 with α=0.05.
Results: Surface roughness on different materials and surface locations is shown in Figure 1. The surface roughness was significantly associated with the material type and milling surface locations.
Conclusions: The surface roughness was affected by the material type, as the ceramic materials had a higher roughness values than composite materials.
In general, step and side surfaces had higher roughness values than cylinder bur surface.