IADR Abstract Archives
Effectiveness of Potassium Iodide in Preventing Silver Diamine Fluoride Staining
Objectives: Silver Diamine fluoride (SDF) has been used to reduce the incidence of primary dentitions caries and the results have been well documented.
The major drawback with SDF application is the dark staining of both teeth and restorative materials. Therefore SDF use on adult dentition is limited. Improving the esthetic outcome by stain reduction would greatly enhance the opportunity for its universal use.
The aim of this study is to rinvestigate the effectiveness of various reducing and oxidizing agents on reduction of SDF staining.
Methods: 36 bovine teeth had the labial enamel removed to expose dentin. All exposed dentin surface were treated with 0.6N HCL acid for two hours to simulate demineralization. Teeth were divided equally and randomly into SDF and SN groups. SDF under investigation was (38% w/v Ag(NH3)2F, 30% w/w), a colorless topical agent comprised of 24.4-28.8% (w/v) silver and 5.0-5.9% fluoride, at pH 10 (Advantage Arrest™ by Elevate Oral Care, LLC). SN 50% w/v is a well-studied microleakage indicator.
18 teeth in each group was subdivided into control (n=3), 40% hydrogen peroxide (Boost, Ultradent Inc.; n=5), NaCl saturated solution (Morton Iodized Salt; n=5), and potassium iodide SSKI (Upsher-Smith Oral solution, USP 1g/ml saturated; n=5). The agents were applied to each tooth for 30 seconds using a microbrush. Immediately following applications, photographic records were made. Teeth were stored in distilled water and exposed to continuous 60 watt LED light. Teeth were photographed on days 3, 7, 14, 21, 28 and 70 and color comparisons were made using Photoshop and associated software. For each specimen at every evaluation period, the color change was compared to the control group and calculated using CIE Delta E 2000.
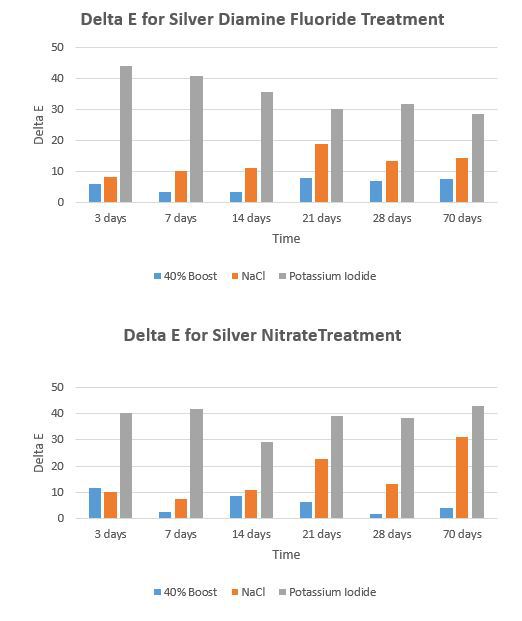
Results: DeltaE was compared using a Two-Factor Repeated Measures ANOVA and Holm-Sidak Post-hoc testing. Results is shown in Table 1 and Figures 1 and 2. A white precipitate forms on the KI treated surfaces. The KI treatment prevents staining but it fades with time. All other treatments were not as effective. 40% hydrogen peroxide has no effect at all on reducing staining.
Conclusions: The use of KI after SDF and SN application reduces staining. All other protocols was not effective. A more detailed protocol e.g concentration and time, will need to be evaluated for clinical use.
The major drawback with SDF application is the dark staining of both teeth and restorative materials. Therefore SDF use on adult dentition is limited. Improving the esthetic outcome by stain reduction would greatly enhance the opportunity for its universal use.
The aim of this study is to rinvestigate the effectiveness of various reducing and oxidizing agents on reduction of SDF staining.
Methods: 36 bovine teeth had the labial enamel removed to expose dentin. All exposed dentin surface were treated with 0.6N HCL acid for two hours to simulate demineralization. Teeth were divided equally and randomly into SDF and SN groups. SDF under investigation was (38% w/v Ag(NH3)2F, 30% w/w), a colorless topical agent comprised of 24.4-28.8% (w/v) silver and 5.0-5.9% fluoride, at pH 10 (Advantage Arrest™ by Elevate Oral Care, LLC). SN 50% w/v is a well-studied microleakage indicator.
18 teeth in each group was subdivided into control (n=3), 40% hydrogen peroxide (Boost, Ultradent Inc.; n=5), NaCl saturated solution (Morton Iodized Salt; n=5), and potassium iodide SSKI (Upsher-Smith Oral solution, USP 1g/ml saturated; n=5). The agents were applied to each tooth for 30 seconds using a microbrush. Immediately following applications, photographic records were made. Teeth were stored in distilled water and exposed to continuous 60 watt LED light. Teeth were photographed on days 3, 7, 14, 21, 28 and 70 and color comparisons were made using Photoshop and associated software. For each specimen at every evaluation period, the color change was compared to the control group and calculated using CIE Delta E 2000.
Results: DeltaE was compared using a Two-Factor Repeated Measures ANOVA and Holm-Sidak Post-hoc testing. Results is shown in Table 1 and Figures 1 and 2. A white precipitate forms on the KI treated surfaces. The KI treatment prevents staining but it fades with time. All other treatments were not as effective. 40% hydrogen peroxide has no effect at all on reducing staining.
Conclusions: The use of KI after SDF and SN application reduces staining. All other protocols was not effective. A more detailed protocol e.g concentration and time, will need to be evaluated for clinical use.