IADR Abstract Archives
Effects of Doxycycline on Bone Regeneration. Tomographic and Histomorphometric Analysis
Objectives: The great demand for reconstructive bone surgery promote development of new biomaterials. Doxycycline, a structural isomer of tetracycline, have been studied, and its applicability directed to topical treatment of periodontitis and periimplantites. Recent studies showed that in addition to the antibacterial, anti-inflammatory, immunosuppressive and anti-collagenase properties, doxycycline inhibits osteoclastogenesis. The aim of this study was to evaluate the local effect of doxycycline in the form of gel on bone regeneration of critical defects in rat calvaria by means of a histomorphometric and tomographic (TCCB) study.
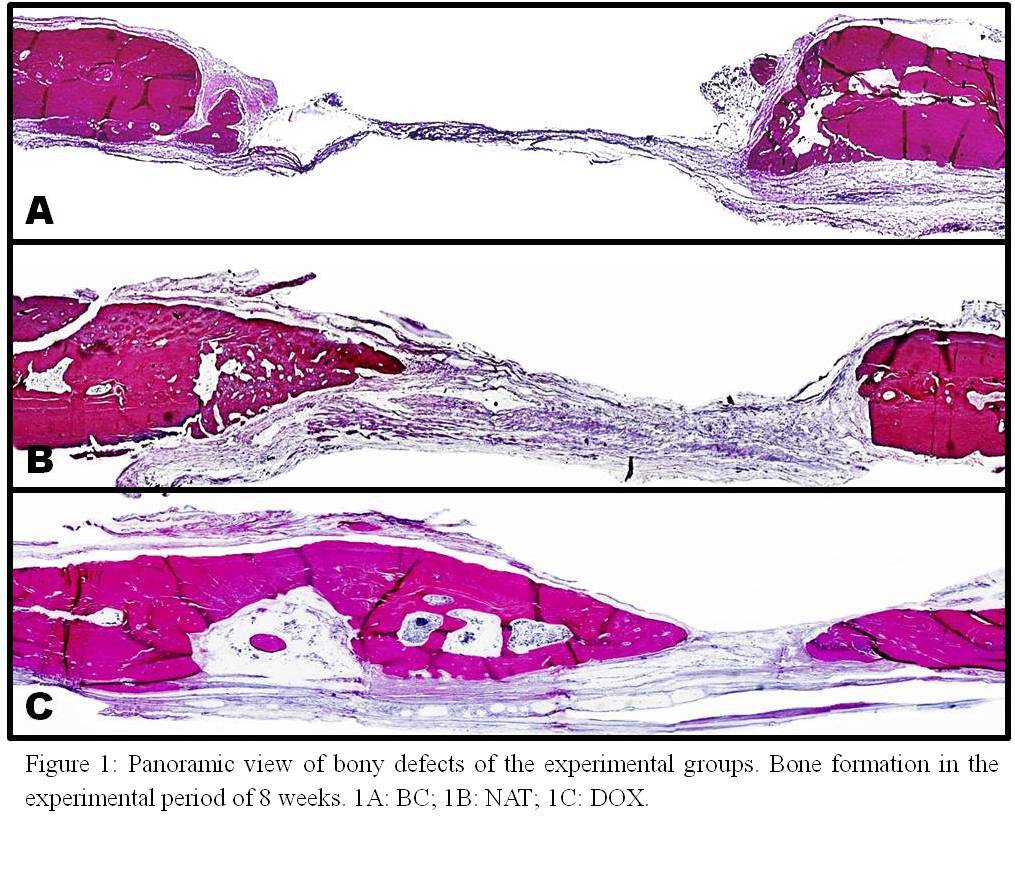
Methods: 24 rats were randomly divided into three groups: BC (blood clot); NAT (Natrosol gel); DOX (doxycycline 10% gel). The animals were euthanized after 4 and 8 weeks. The new bone area (NBA) was calculated as a percentage of the total area (TA) for histomorphometric analysis. To tomographic analysis (TCCB), the average density of the defect area was calculated as a percentage relative to the native bone density. The data obtained were subjected to analysis of variance (ANOVA) and Tukey test.
Results: Histomorphometry in the DOX group presented NBA value statistically higher (38.7876%) that the BC group (14.1250%) and, when considered experimental periods (Tab.1), the DOX group of eight weeks (61.1090%) showed values statistically higher than all other (23.1149% and 34.3146% for BC and NAT respectively). The tomographic analysis showed statistically higher density values for DOX compared to the other (p<0.05).
Conclusions: The data allows concluding that the doxycycline gel 10% showed positive effect on bone regeneration in rat calvaria defects.
Methods: 24 rats were randomly divided into three groups: BC (blood clot); NAT (Natrosol gel); DOX (doxycycline 10% gel). The animals were euthanized after 4 and 8 weeks. The new bone area (NBA) was calculated as a percentage of the total area (TA) for histomorphometric analysis. To tomographic analysis (TCCB), the average density of the defect area was calculated as a percentage relative to the native bone density. The data obtained were subjected to analysis of variance (ANOVA) and Tukey test.
Results: Histomorphometry in the DOX group presented NBA value statistically higher (38.7876%) that the BC group (14.1250%) and, when considered experimental periods (Tab.1), the DOX group of eight weeks (61.1090%) showed values statistically higher than all other (23.1149% and 34.3146% for BC and NAT respectively). The tomographic analysis showed statistically higher density values for DOX compared to the other (p<0.05).
Conclusions: The data allows concluding that the doxycycline gel 10% showed positive effect on bone regeneration in rat calvaria defects.