IADR Abstract Archives
Physicochemical and Nano-mechanical Analysis of Fluoroapatite Coatings
Objectives: Bacterial antibiotic resistance has increased the interest in antimicrobial dental implants. Fluorapatite (FA) is known to induce bone growth and according to our previous studies presents significant antibacterial properties against pathogens implicated in peri-implantitis. The aim of this study was to perform detailed physicochemical and mechanical surface analysis in order to further explore the role of surface properties in the antibacterial and osteoinductive performance of FA coatings.
Methods: Either ordered or disordered FA coatings were achieved on etched stainless steel surfaces using a mild hydrothermal method. The materials were sintered at 800°C for either 30min or 180min and examined before and after sintering. The produced surfaces were characterized in terms of roughness and thickness using an optical profiler. Surface chemistry was examined using energy dispersive spectroscopy. Fluoride and other ion release was evaluated using ion chromatography and inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectroscopy. The mechanical stability of the coatings was assessed using a nano-scratch technique and elastic and visco-elastic properties were assessed using advanced dynamic AFM techniques.
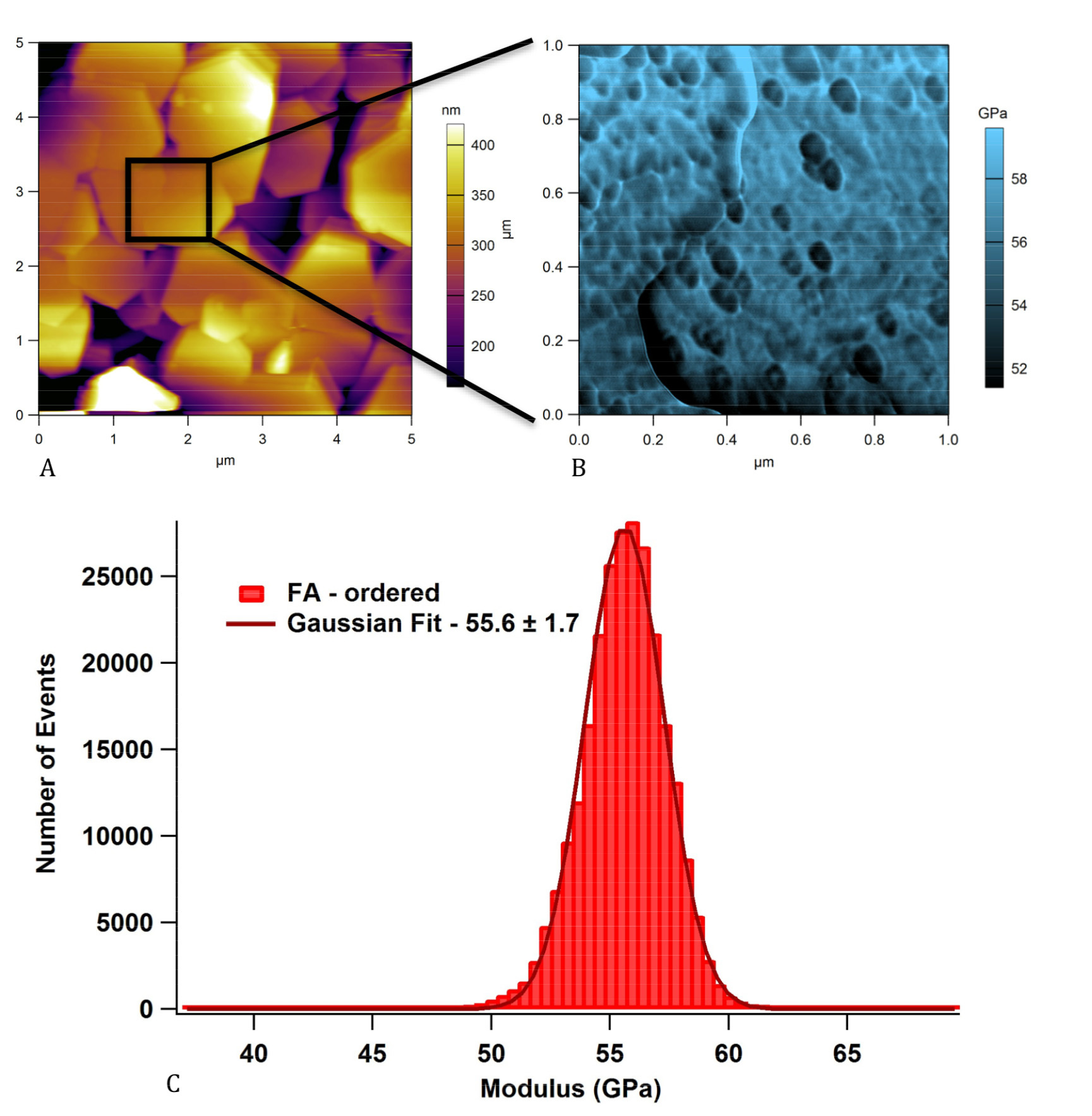
Results: The crystals in the ordered coatings were well aligned, in contrast to the disordered coating, which gave higher roughness and thickness values, and fluoride content. AFM images confirmed the formation of rod-like hexagonal crystals (Fig. 1a). Sintering significantly affected both the chemical but also the mechanical stability of the coatings and their ion release. Figure 1b shows the modulus map on a 1μm scan area on a non-sintered sample, the Gaussian distribution gives a modulus of 55.6±1.6GPa (Fig. 1c). Nano-scratch hardness testing showed enhanced properties of the coatings, following the heat treatments.
Conclusions: Detailed characterization of the coatings allows for better interpretation of the combined antimicrobial and osteoinductive performance of the ordered FA coatings, compared to the disordered. Sintering is effective in bringing about an enhancement in the mechanical and chemical stability of the coating.
Methods: Either ordered or disordered FA coatings were achieved on etched stainless steel surfaces using a mild hydrothermal method. The materials were sintered at 800°C for either 30min or 180min and examined before and after sintering. The produced surfaces were characterized in terms of roughness and thickness using an optical profiler. Surface chemistry was examined using energy dispersive spectroscopy. Fluoride and other ion release was evaluated using ion chromatography and inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectroscopy. The mechanical stability of the coatings was assessed using a nano-scratch technique and elastic and visco-elastic properties were assessed using advanced dynamic AFM techniques.
Results: The crystals in the ordered coatings were well aligned, in contrast to the disordered coating, which gave higher roughness and thickness values, and fluoride content. AFM images confirmed the formation of rod-like hexagonal crystals (Fig. 1a). Sintering significantly affected both the chemical but also the mechanical stability of the coatings and their ion release. Figure 1b shows the modulus map on a 1μm scan area on a non-sintered sample, the Gaussian distribution gives a modulus of 55.6±1.6GPa (Fig. 1c). Nano-scratch hardness testing showed enhanced properties of the coatings, following the heat treatments.
Conclusions: Detailed characterization of the coatings allows for better interpretation of the combined antimicrobial and osteoinductive performance of the ordered FA coatings, compared to the disordered. Sintering is effective in bringing about an enhancement in the mechanical and chemical stability of the coating.